code spliting 把代码分离到不同的 bundle 中,然后可以按需加载或并行加载这些文件。
代码分离可以用于获取更小的 bundle,以及控制资源加载优先级,如果使用合理,会极大缩减加载时间。
首先,看一组概念。参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a1ccd6d1b4ba
bundle:形式上是块的集合,意义是代表一个可以运行的整体
chunk和bundle:what-are-module-chunk-and-bundle-in-webpack
比较难说明,搜的基本都是个人总结,官方描述也比较抽象。
一个js文件就是一个模块,若干个js模块会打包成一个总的js文件,这个js文件称作bundle。但如果是多页面应用,往往会安排为一个html对应一个bundle,那么两个html的bundle之间重复的模块就是重复代码。此时我们会把这两个bundle重复的模块抽出来,称为common chunk,余下的两部分直接称作两个chunk。即此时一共有3个chunk,但依然只有两个bundle。
单页面应用中异步加载,或者单纯想分离出不变的第三方库,均可采用该手段进行优化。
有三种常用的代码分离方法:
- 入口起点:使用
entry配置手动地分离代码(多页面应用;存在重复引用)。entry: { index: './src/index.js', another: './src/another-module.js' },
another-module.js与index.js中,都存在lodash引用。
- 防止重复:使用 SplitChunksPlugin 去重和分离 chunk。(使用SplitChunksPlugin不需要安装任何依赖,只需在配置中添加 optimization 属性)
当满足以下条件时,来自相同块chunk和缓存组的模块将形成一个新块。
minSize(默认值:30000)块的最小大小minChunks(默认值:1)在拆分之前共享模块的最小块数(a. 可以是来自node_modules b. 在两个或两个以上的引入调用共享)maxInitialRequests(默认值为3)入口点的最大并行请求数maxAsyncRequests(默认为5)按需加载时并行请求的最大数量
官网对splitChunks给出的默认配置如下:
optimization:{
splitChunks: { chunks: "async", minSize: 30000, minChunks: 1, maxAsyncRequests: 5, maxInitialRequests: 3, automaticNameDelimiter: '~', name: true, cacheGroups: { vendors: { test: /[\/]node_modules[\/]/, priority: -10 }, default: { minChunks: 2, priority: -20, reuseExistingChunk: true } } }
}
cacheGroups(缓存组) 在默认设置中,会将 node_mudules 文件夹中的模块打包进一个叫 vendors的bundle中,所有引用超过两次的模块分配到 default bundle 中。更可以通过 priority 来设置优先级。
3. 动态导入:通过模块的内联函数调用来分离代码。
在webpack.prod.js中添加:
output:{ chunkFilename: '[name].bundle.js' // 非入口chunk的文件名 }
在index.js中使用动态加载的方式加载lodash
function component() { return import(/* webpackChunkName: "lodash" */ 'lodash').then(_ => { let element = document.createElement('div'); element.innerHTML = _.join(['hello','webpack,', cube(5)],' '); element.classList.add('hello'); let button = document.createElement('button'); button.innerHTML = 'click me and check the console!'; button.onclick = myPrint; element.appendChild(button); return element; }).catch(err => 'an error occured while loading the component'); } // 动态加载 component().then(element => { document.body.appendChild(element); if (module.hot) { //告诉 webpack 接受热替换的模块 module.hot.accept('./print.js', () => { console.log('Accepting the updated printMe module!'); document.body.removeChild(element); //删掉旧的element element = component(); //重新渲染页面后,component 更新 click 事件处理 document.body.appendChild(element); //重新插入到网页中 }) } })
由此,lodash会单独形成一个chunk
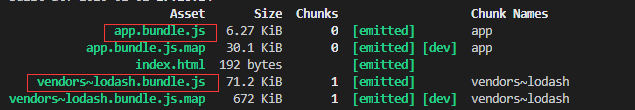
在注释中使用了 webpackChunkName。这样做会导致我们的 bundle 被命名为 lodash.bundle.js ,而不是 [id].bundle.js.
由于 import() 会返回一个 promise,因此它可以和 async 函数一起使用。但是,需要使用像 Babel 这样的预处理器和Syntax Dynamic Import Babel Plugin。
async function component() { let element = document.createElement('div'); const _ = await import(/* webpackChunkName: "lodash" */ 'lodash') element.innerHTML = _.join(['hello','webpack,', cube(5)],' '); element.classList.add('hello'); let button = document.createElement('button'); button.innerHTML = 'click me and check the console!'; button.onclick = myPrint; element.appendChild(button); return element; }
懒加载 当发生用户交互时,再加载被分离的块。
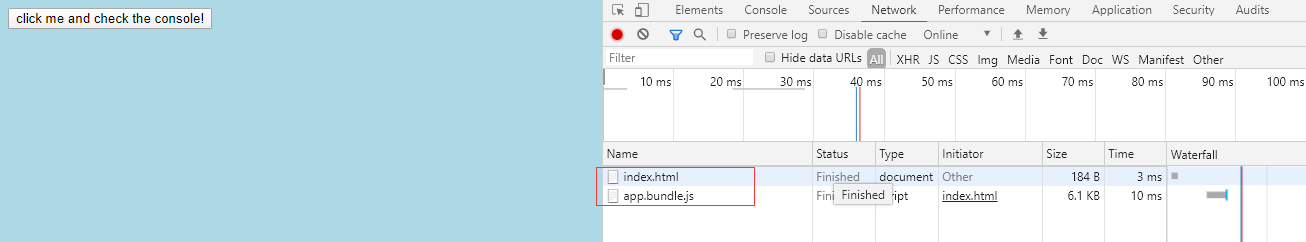
在上述code spliting代码中,虽然lodash被单独分离成一个chunk。但分离后lodash加载与用户交互没有任何联系,换句话说,每次加载页面时都会去请求它。
async function component() { let element = document.createElement('div'); let button = document.createElement('button'); button.innerHTML = 'click me and check the console!'; // 懒加载 button.onclick = e => import(/* webpackChunkName: "print" */ './print.js').then(module => { const print = module.default; print(); }) element.appendChild(button); return element; }
点击后,
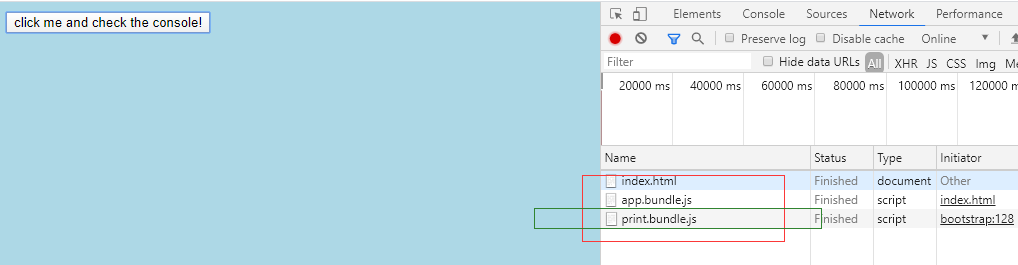
注意:当调用 ES6 模块的 import() 方法引入模块时,必须指向module.default ,因为它才是 promise 被处理后返回的实际的 module 对象。
Vue懒加载: https://alexjover.com/blog/lazy-load-in-vue-using-webpack-s-code-splitting/
React懒加载: https://reacttraining.com/react-router/web/guides/code-splitting