前期mysql准备
数据库
CREATE DATABASE mybatis; use mybatis; CREATE TABLE user( id int PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL, pwd VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL )ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHAR SET utf8
实体类
public class User { private int id; private String name; private String password; ... }
上面的数据库与实体类的字段不一致,运行程序会出错,需要用到一个关键字ResultMap
resultMap 标签可以建立查询的列名和实体类的属性名称不一致时建立对应关系。从而实现封装。
这样写了的话,返回结果用的是resultMap,而不是resultType,它有的属性
- id 属性:给定一个唯一标识,是给查询 select 标签引用用的
- type 属性:指定实体类的全限定类名
- id 标签:(resultMap标签里面的id)用于指定主键字段
- result 标签:用于指定非主键字段
- column 属性:用于指定数据库列名
- property 属性:用于指定实体类属性名称
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.cong.pojo.User"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> <result column="name" property="name"></result> <result column="pwd" property="password"></result> </resultMap>
1.查找
select是用的最多的标签
模糊查询执行的时候要为String两边加上%,
List<User> userList = userMapper.getUserByName("%李%");
List<Account> findAll();//查询所有 Account findById(int id);//根据id查询 List<Account> findByName(String name);//根据名字模糊查询 int findTotal();//查询数量 <select id="findAll" resultType="userMap"> select * from user </select> <select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="userMap"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> <select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="userMap"> select * from user where name like #{name}; </select> <select id="findTotal" resultType="int"> select count(*) from user; </select>
模糊查询还有一种方式,也就是在sql语句中拼接通配符,会引起sql注入
执行 List<User> userList = userMapper.getUserByName("李"); 查询方法 <select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="user"> select * from account where name like '%${value}%'; </select>
如果需要根据用户名和密码,查询用户,要怎么做,因为有两个参数了
思路一:直接在方法中传递参数
1. 在接口方法的参数前加 @Param属性
2. Sql语句编写的时候,直接取@Param中设置的值即可,不需要单独设置参数类型
User getUserByNP(@Param("name") String name, @Param("pwd") String password);//根据用户名和密码查询 <select id="getUserByNP" resultType="user"> select * from user where name = #{name} and pwd = #{pwd} </select>
思路二:万能的Map
1. 在接口方法中,参数直接传递Map;
User getUserByNP2(Map<String,String> map);//根据用户名和密码查询
2. 编写sql语句的时候,需要传递参数类型,参数类型为map
<select id="getUserByNP2" resultType="user" parameterType="map"> select * from user where name = #{username} and pwd = #{password}; </select>
3. 在使用方法的时候,Map的 key 为 sql中取的值即可,没有顺序要求!
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("username", "彩虹"); map.put("password", "1889869"); User user = userMapper.getUserByNP2(map);
总结:
如果参数过多,我们可以考虑直接使用Map实现,如果参数比较少,直接传递参数即可
2.插入
int addUser(User user); <insert id="addUser" parameterType="user"> insert into user (name,pwd) values(#{name},#{pwd}) </insert>
3.更新
int updateUser(User user); <update id="updateUser" parameterType="user"> update user set name = #{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id } </update>
4.删除
int deleteUser(int id); <delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int"> delete from user where id = #{id} </delete>
小结:
- 所有的增删改操作都需要提交事务!
- 接口所有的普通参数,尽量都写上@Param参数,尤其是多个参数时,必须写上!
- 有时候根据业务的需求,可以考虑使用map传递参数!
- 为了规范操作,在SQL的配置文件中,我们尽量将Parameter参数和resultType都写上!
另外关于查询中的两种方式
一种是like #{name}
我们在配置文件中没有加入%来作为模糊查询的条件,所以在传入字符串实参时,就需要给定模糊查询的标
识%。 配置文件中的#{username}也只是一个占位符,所以 SQL 语句显示为“?”
查询语句 <select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="account"> select * from account where name like #{name}; </select> 对应的test测试方法 List<Account> accounts = mapper.findByName("%on%")
在控制台,它的查询语句是
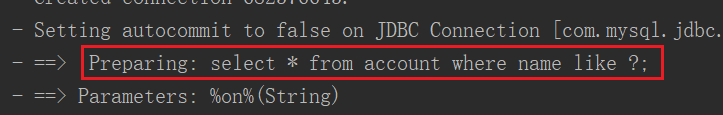
两外一种是like '%${value}%'
我们在上面将原来的#{}占位符,改成了${value}。注意如果用模糊查询的这种写法,那么${value}的写
法就是固定的,不能写成其它名字。
可以发现,我们在程序代码中就不需要加入模糊查询的匹配符%了,这两种方式的实现效果是一样的,但执行
的语句是不一样的
查询语句 <select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="account"> select * from account where name like '%${value}%'; </select> 对应的test测试语句 List<Account> accounts = mapper.findByName("on");
在控制台,它的查询语句是
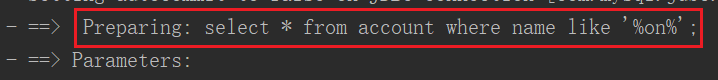
#{}与${}的区别
#{}表示一个占位符号
通过#{}可以实现 preparedStatement 向占位符中设置值,自动进行 java 类型和 jdbc 类型转换,
#{}可以有效防止 sql 注入。 #{}可以接收简单类型值或 pojo 属性值。 如果 parameterType 传输单个简单类
型值, #{}括号中可以是 value 或其它名称。
${}表示拼接 sql 串
通过${}可以将 parameterType 传入的内容拼接在 sql 中且不进行 jdbc 类型转换, ${}可以接收简
单类型值或 pojo 属性值,如果 parameterType 传输单个简单类型值, ${}括号中只能是 value。
查看以下模糊查询${value}的源码
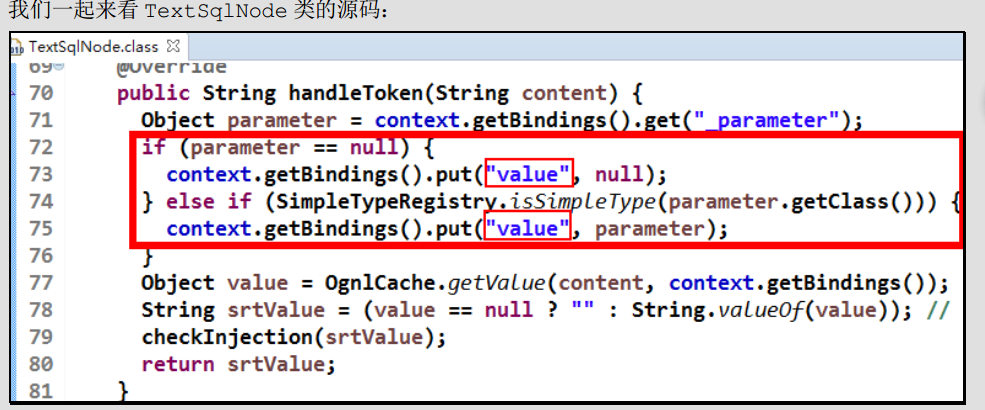
这就说明了源码中指定了读取的 key 的名字就是”value”,所以我们在绑定参数时就只能叫 value 的名字
了