1 网络概念
1.1 网络通信三要素
- IP地址:唯一标识网络上的每一台计算机。两台计算机之间通信的必备有素
- 端口号:计算机中应用的标号(代表一个应用程序)
- 0-1024 为系统使用或保留端口;
- 常见端口:http:80,stmp:25,ftp:21;
- 有效端口0-65536,开发者可以的端口是1025-65536之间。一些第三方引用如 mysql:3306,Oracle:1251。
- 通信协议:通信的规则 TCP,UDP
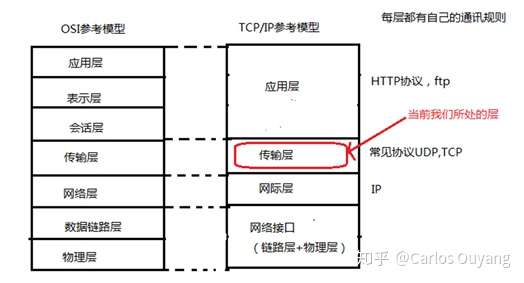
1.2 网络通信模型
2 InetAddress
1 public class Test01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 // 获取本机IP地址 4 InetAddress ip1; 5 try { 6 ip1 = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); 7 // 将打印计算机名以及IP地址 8 System.out.println(ip1.toString()); 9 10 // 获取主机名称 11 System.out.println(ip1.getHostName()); 12 System.out.println(ip1.getHostAddress()); 13 14 } catch (UnknownHostException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
3 TCP 编程
TCP编程中,如果要完成通信,通信双方必须要创建 socket,通过 socket 完成通信。
TCP通信步骤:
- 服务器启动 ServerSocket 作为通信的 Server 端,等待客户端链入。
- 客户端创建 Socket 作为通信的 Client 端
- Client 端链入 Server 端后建立可靠的、双向的、持续性的、点对点的通讯连接,即可通信。
案例一:完成一次单向通信
服务器端:
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.io.OutputStream; 3 import java.net.ServerSocket; 4 import java.net.Socket; 5 6 public class Server01 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 System.out.println("服务器启动..."); 10 11 // 【1】创建server socket 12 ServerSocket serverSocket = null; 13 Socket clientSocket = null; 14 try { 15 16 serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8000); 17 // 【2】等待客户端的链入->阻塞式函数->监听8000端口,看是否有client链入 18 clientSocket = serverSocket.accept(); 19 20 System.out.println(clientSocket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()+"链入!"); 21 22 // 【3】给客户端主动发信息 23 OutputStream out = clientSocket.getOutputStream(); 24 25 String msg = "hello 兄弟"; 26 byte[] buf = msg.getBytes("UTF-8"); 27 out.write(buf); 28 //输出结束后,要记得socket.shudownOutput() 29 clientSocket.shutdownOutput(); 30 31 out.close(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 } 36 }
客户端:
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.io.InputStream; 3 import java.net.Socket; 4 5 public class Client01 { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 System.out.println("客户端运行..."); 8 9 // 【1】创建客户端socket 10 Socket socket = null; 11 try { 12 socket = new Socket("192.168.2.56", 8000); 13 14 // 【2】接收来自服务器的消息 15 InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); 16 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 17 int len = in.read(buf); 18 19 String msg = new String(buf, 0, len, "UTF-8"); 20 System.out.println(msg); 21 // 读取结束后,socket.shutdownInput() 22 socket.shutdownInput(); 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 }
案例二:双向通信,模拟登录验证,采用传输对象的方式
服务器:
1 package objectTCP.server; 2 3 import java.io.DataOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStream; 6 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 7 import java.io.OutputStream; 8 import java.net.ServerSocket; 9 import java.net.Socket; 10 11 import objectTCP.User; 12 13 public class Server { 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 15 System.out.println("Server started"); 16 try { 17 //创建服务器端 18 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8000); 19 Socket client = server.accept(); 20 System.out.println(client.getInetAddress().getHostName() + " connected"); 21 //接收 22 InputStream in = client.getInputStream(); 23 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in); 24 User user = (User)ois.readObject(); 25 client.shutdownInput(); 26 27 System.out.println(user.toString()); 28 //发送 29 if(user.getUsr().equals("admin") && user.getPsw().equals("12345")) { 30 OutputStream out = client.getOutputStream(); 31 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out); 32 dos.writeUTF("验证成功!"); 33 client.shutdownOutput(); 34 }else { 35 OutputStream out = client.getOutputStream(); 36 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out); 37 dos.writeUTF("密码、或用户名错误,验证失败!"); 38 client.shutdownOutput(); 39 } 40 client.close(); 41 server.close(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 }
客户端:
1 package objectTCP.client; 2 3 import java.io.DataInputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStream; 6 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 7 import java.io.OutputStream; 8 import java.net.Socket; 9 import java.util.Scanner; 10 11 import objectTCP.User; 12 13 public class Client { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 User user = new User(); 16 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 17 System.out.print("usrName: "); 18 user.setUsr(input.nextLine()); 19 System.out.print("psw: "); 20 user.setPsw(input.nextLine()); 21 try { 22 Socket server = new Socket("192.168.3.2", 8000); 23 OutputStream out = server.getOutputStream(); 24 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); 25 oos.writeObject(user); 26 server.shutdownOutput(); 27 28 InputStream in = server.getInputStream(); 29 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in); 30 System.out.println(dis.readUTF()); 31 server.shutdownInput(); 32 server.close(); 33 input.close(); 34 }catch (IOException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 }
这里要注意,服务器端的 User 类和客户端的 User 类要处于一样的包路径下,且拥有一样的序列化 ID,不然会出现类型转换异常。
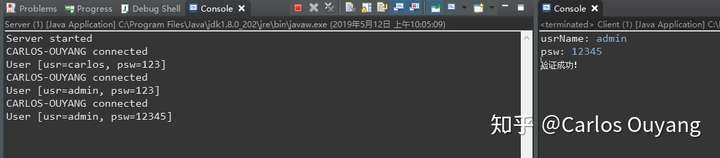
配合线程,可以实现多用户验证,效果如图:
4 UDP 编程
UDP 编程中,如果要完成通信,通信双方必须要创建 DatagramSocket,通过 DatagramSo-cket 完成通信。
DatagramPacket 数据报包用来实现无连接包投递服务。每条报文仅根据该包中包含的信息(字节数组,长度,目标ip,端口)从一台机器自动路由到另一台机器。TCP 类似于打电话,需要双方确认,而 UDP 类似于发短信,只要知道目的地即可发送。
UDP步骤:
- 创建一个DatagramSocket用于表示发送端,通过send方法发送数据报
- 创建一个DatagramSocket用于表示接收端,通过receive方法接收数据报
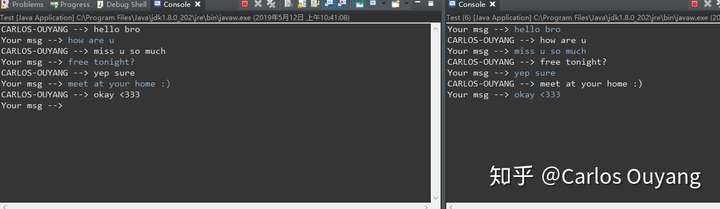
需求:两个客户端相互聊天
用户1:先接收消息再发送消息
1 package UDPClient2; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 5 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 6 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 7 import java.net.InetAddress; 8 import java.net.SocketException; 9 import java.net.UnknownHostException; 10 import java.util.Scanner; 11 12 public class Test { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 15 try { 16 // 指定此程序的端口 17 DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(4000); 18 // 指定接受端的ip 19 InetAddress desIp = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.2.138"); 20 while(true) { 21 //接收消息 22 byte[] rcvBuf = new byte[1024]; 23 DatagramPacket rcvPack = new DatagramPacket(rcvBuf, rcvBuf.length); 24 socket.receive(rcvPack); 25 System.out.println(rcvPack.getAddress().getHostName() + " --> " + new String(rcvBuf, 0, rcvPack.getLength(), "utf8")); 26 27 28 //发送消息 29 System.out.print("Your msg --> "); 30 String msg = input.nextLine(); 31 byte[] sndBuf = msg.getBytes("utf8"); 32 // 创建发送出的包,指定了内容、目的地ip、目的地端口 33 DatagramPacket sndPack = new DatagramPacket(sndBuf, sndBuf.length, desIp, 3000); 34 //发送 35 socket.send(sndPack); 36 } 37 } catch (SocketException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } catch (UnknownHostException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 } 47 }
用户2:先发送消息,再接收消息
1 package UDPClient1; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 5 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 6 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 7 import java.net.InetAddress; 8 import java.net.SocketException; 9 import java.net.UnknownHostException; 10 import java.util.Scanner; 11 12 public class Test { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 15 try { 16 // 指定此程序的端口 17 DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(3000); 18 // 指定接受端的ip 19 InetAddress desIp = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.2.138"); 20 while(true) { 21 //发送消息 22 System.out.print("Your msg --> "); 23 String msg = input.nextLine(); 24 byte[] sndBuf = msg.getBytes("utf8"); 25 // 创建发送出的包,指定了内容、目的地ip、目的地端口 26 DatagramPacket sndPack = new DatagramPacket(sndBuf, sndBuf.length, desIp, 4000); 27 //发送 28 socket.send(sndPack); 29 30 31 //接收消息 32 byte[] rcvBuf = new byte[1024]; 33 DatagramPacket rcvPack = new DatagramPacket(rcvBuf, rcvBuf.length); 34 socket.receive(rcvPack); 35 System.out.println(rcvPack.getAddress().getHostName() + " --> " + new String(rcvBuf, 0, rcvPack.getLength(), "utf8")); 36 } 37 } catch (SocketException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } catch (UnknownHostException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 } 47 }
实现效果: