1.数据查看和转置
import numpy as np import pandas as pd # 导入numpy、pandas模块 # 数据查看、转置 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(8,2)*100, columns = ['a','b']) print(df.head(2)) #查看前两条数据 print(df.tail()) # .head()查看头部数据 # .tail()查看尾部数据 # 默认查看5条 print(df.T) # .T 转置
输出结果:
a b 0 64.231620 24.222954 1 3.004779 92.549576 a b 3 54.787062 17.264577 4 13.106864 5.500618 5 8.631310 79.109355 6 22.107241 94.901685 7 29.034599 54.156278 0 1 2 3 4 5 a 64.231620 3.004779 25.002825 54.787062 13.106864 8.631310 b 24.222954 92.549576 87.818090 17.264577 5.500618 79.109355 6 7 a 22.107241 29.034599 b 94.901685 54.156278
2.(1)添加与修改_1
# 添加与修改 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, columns = ['a','b','c','d']) print(df) df['e'] = 10 df.loc[4] = 20 print(df) # 新增列/行并赋值 df['e'] = 20 df[['a','c']] = 100 print(df) # 索引后直接修改值 #注意:不能同时添加两列,否则会报错,如:df[['f','g']] = 200 ,必须一列一列的添加
输出结果:
a b c d 0 14.342082 52.604100 26.561995 60.441731 1 20.331108 43.537490 1.020098 7.171418 2 35.226542 9.573718 99.273254 0.867227 3 47.511549 56.783730 47.580639 67.007725 a b c d e 0 14.342082 52.604100 26.561995 60.441731 10 1 20.331108 43.537490 1.020098 7.171418 10 2 35.226542 9.573718 99.273254 0.867227 10 3 47.511549 56.783730 47.580639 67.007725 10 4 20.000000 20.000000 20.000000 20.000000 20 a b c d e 0 100 52.604100 100 60.441731 20 1 100 43.537490 100 7.171418 20 2 100 9.573718 100 0.867227 20 3 100 56.783730 100 67.007725 20 4 100 20.000000 100 20.000000 20
(2)添加与修改_2
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, columns = ['a','b','c','d']) df.iloc[0] = 100 print(df) df.iloc[0] = [1,2,3,4] print(df) #增加一行尽量曲用loc去增加,iloc是不能增加的,会报错 df.loc[5] = 100 print(df)
输出结果:
a b c d 0 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 1 93.941010 7.951216 77.744847 66.842114 2 72.795874 40.031626 22.842638 92.876458 3 40.474858 53.663771 48.452597 66.444382 a b c d 0 1.000000 2.000000 3.000000 4.000000 1 93.941010 7.951216 77.744847 66.842114 2 72.795874 40.031626 22.842638 92.876458 3 40.474858 53.663771 48.452597 66.444382 a b c d 0 1.000000 2.000000 3.000000 4.000000 1 93.941010 7.951216 77.744847 66.842114 2 72.795874 40.031626 22.842638 92.876458 3 40.474858 53.663771 48.452597 66.444382 5 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000
3.删除
(1)
# 删除 del / drop() df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, columns = ['a','b','c','d']) print(df) del df['a'] print(df) print('-----') # del语句 - 删除列 #注意:删除行的时候不能用del df.loc[index]或者df.iloc[index] 否则会报错 可以变相的删除 如删除第一行 可令df = df.iloc[1:] print(df.drop(0)) print(df.drop([1,2])) print(df) print('-----') # drop()删除行,inplace=False → 删除后生成新的数据,不改变原数据 print(df.drop(['d'], axis = 1)) #axis =0 的时候删除行 print(df) # drop()删除列,需要加上axis = 1,inplace=False → 删除后生成新的数据,不改变原数据
输出结果:
a b c d 0 71.238538 6.121303 77.988034 44.047009 1 34.018365 78.192855 50.467246 81.162337 2 86.311980 44.341469 49.789445 35.657665 3 78.073272 31.457479 74.385014 24.655976 b c d 0 6.121303 77.988034 44.047009 1 78.192855 50.467246 81.162337 2 44.341469 49.789445 35.657665 3 31.457479 74.385014 24.655976 ----- b c d 1 78.192855 50.467246 81.162337 2 44.341469 49.789445 35.657665 3 31.457479 74.385014 24.655976 b c d 0 6.121303 77.988034 44.047009 3 31.457479 74.385014 24.655976 b c d 0 6.121303 77.988034 44.047009 1 78.192855 50.467246 81.162337 2 44.341469 49.789445 35.657665 3 31.457479 74.385014 24.655976 ----- b c 0 6.121303 77.988034 1 78.192855 50.467246 2 44.341469 49.789445 3 31.457479 74.385014 b c d 0 6.121303 77.988034 44.047009 1 78.192855 50.467246 81.162337 2 44.341469 49.789445 35.657665 3 31.457479 74.385014 24.655976
(2)
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, columns = ['a','b','c','d']) print(df.drop(0)) print(df) #源数据不会改变 print(df.drop(0,inplace = True)) #这个方法改变了源数据,并不生成新的值了,所以输出为空 print(df) #有inplace 参数的时候就替换了源数据
输出结果:
a b c d 1 78.187118 19.237655 94.443127 67.466532 2 37.921956 84.157197 23.311418 24.128222 3 12.330334 6.034799 62.023747 28.034041 a b c d 0 60.558857 94.367826 88.690379 33.957380 1 78.187118 19.237655 94.443127 67.466532 2 37.921956 84.157197 23.311418 24.128222 3 12.330334 6.034799 62.023747 28.034041 None a b c d 1 78.187118 19.237655 94.443127 67.466532 2 37.921956 84.157197 23.311418 24.128222 3 12.330334 6.034799 62.023747 28.034041
4.对齐
# 对齐 df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 4), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(7, 3), columns=['A', 'B', 'C']) print(df1) print(df2) print(df1 + df2) #有共同的列名和共同的标签的话 就会相加 。没有共同的部分就会变为空值。任何值和空值进行运算都会变为空值 # DataFrame对象之间的数据自动按照列和索引(行标签)对齐 ,
输出结果:
A B C D 0 -1.528903 0.519125 -0.214881 -0.591775 1 -0.334501 -0.837666 0.568927 -0.599237 2 0.753145 0.569262 -1.181976 1.225363 3 -0.177136 -0.367530 0.382826 1.447591 4 0.215967 -0.612947 0.844906 0.130414 5 0.414375 -0.207225 0.140776 1.086686 6 0.008855 2.873956 -0.650806 -2.631485 7 -0.634085 0.625107 0.046198 -0.352343 8 0.646812 0.928476 0.519168 -0.644997 9 -0.697006 -0.178875 0.856392 -0.512101 A B C 0 -0.373297 0.607873 0.120016 1 0.343563 -2.901778 -0.370051 2 0.428568 0.319359 -3.263585 3 1.042845 -0.314763 -0.198816 4 0.071258 -0.484855 0.563127 5 -2.270312 -0.145558 0.931203 6 2.493652 -0.232491 -0.216451 A B C D 0 -1.902200 1.126998 -0.094865 NaN 1 0.009061 -3.739444 0.198876 NaN 2 1.181713 0.888620 -4.445561 NaN 3 0.865710 -0.682293 0.184010 NaN 4 0.287224 -1.097802 1.408034 NaN 5 -1.855938 -0.352783 1.071979 NaN 6 2.502507 2.641465 -0.867257 NaN 7 NaN NaN NaN NaN 8 NaN NaN NaN NaN 9 NaN NaN NaN NaN
6.排序
(1)按值排序
# 排序1 - 按值排序 .sort_values # 同样适用于Series df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, columns = ['a','b','c','d']) print(df1) print(df1.sort_values(['a'], ascending = True)) # 升序 #也可以这样写:print(df1.sort_values(by = 'a',ascending = True)) print(df1.sort_values(['a'], ascending = False)) # 降序 print('------') # ascending参数:设置升序降序,默认升序 # 单列排序 df2 = pd.DataFrame({'a':[1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2], 'b':list(range(8)), 'c':list(range(8,0,-1))}) print(df2) print(df2.sort_values(['a','c'])) # 多列排序,按列顺序排序 # 注意inplace参数
输出结果:
a b c d 0 28.598118 8.037050 51.856085 45.859414 1 91.412263 59.797819 27.912198 6.996883 2 92.001255 76.467245 76.524894 33.463836 3 47.054750 37.376781 94.286800 53.429360 a b c d 0 28.598118 8.037050 51.856085 45.859414 3 47.054750 37.376781 94.286800 53.429360 1 91.412263 59.797819 27.912198 6.996883 2 92.001255 76.467245 76.524894 33.463836 a b c d 2 92.001255 76.467245 76.524894 33.463836 1 91.412263 59.797819 27.912198 6.996883 3 47.054750 37.376781 94.286800 53.429360 0 28.598118 8.037050 51.856085 45.859414 ------ a b c 0 1 0 8 1 1 1 7 2 1 2 6 3 1 3 5 4 2 4 4 5 2 5 3 6 2 6 2 7 2 7 1 a b c 3 1 3 5 2 1 2 6 1 1 1 7 0 1 0 8 7 2 7 1 6 2 6 2 5 2 5 3 4 2 4 4
(2)索引排序
# 排序2 - 索引排序 .sort_index df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, index = [5,4,3,2], columns = ['a','b','c','d']) df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, index = ['h','s','x','g'], columns = ['a','b','c','d']) print(df1) print(df1.sort_index()) print(df2) print(df2.sort_index()) # 按照index排序 # 默认 ascending=True, inplace=False
输出结果:
a b c d 5 80.932585 71.991854 64.582943 23.443231 4 82.054030 87.459058 12.108433 83.047490 3 56.329863 14.926822 47.884418 59.880352 2 0.347007 69.794103 74.375345 12.736429 a b c d 2 0.347007 69.794103 74.375345 12.736429 3 56.329863 14.926822 47.884418 59.880352 4 82.054030 87.459058 12.108433 83.047490 5 80.932585 71.991854 64.582943 23.443231 a b c d h 53.041921 93.834097 13.423132 82.702020 s 0.003814 75.721426 73.086606 20.597472 x 32.678307 58.369155 70.487505 24.833117 g 46.232889 19.365147 9.872537 98.246438 a b c d g 46.232889 19.365147 9.872537 98.246438 h 53.041921 93.834097 13.423132 82.702020 s 0.003814 75.721426 73.086606 20.597472 x 32.678307 58.369155 70.487505 24.833117
(3)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100, index = [5,4,3,2], columns = ['a','b','c','d']) print(df1) print(df1.sort_index()) print(df1) # df1并没有变 print(df1.sort_index(inplace = True)) print(df1) # df1发生改变
输出结果:
a b c d 5 45.004735 23.449962 52.756124 60.237141 4 74.945903 63.813663 29.937821 66.420415 3 45.737208 82.376775 80.615108 40.479094 2 41.743173 82.013411 83.372130 76.195150 a b c d 2 41.743173 82.013411 83.372130 76.195150 3 45.737208 82.376775 80.615108 40.479094 4 74.945903 63.813663 29.937821 66.420415 5 45.004735 23.449962 52.756124 60.237141 a b c d 5 45.004735 23.449962 52.756124 60.237141 4 74.945903 63.813663 29.937821 66.420415 3 45.737208 82.376775 80.615108 40.479094 2 41.743173 82.013411 83.372130 76.195150 None a b c d 2 41.743173 82.013411 83.372130 76.195150 3 45.737208 82.376775 80.615108 40.479094 4 74.945903 63.813663 29.937821 66.420415 5 45.004735 23.449962 52.756124 60.237141
练习:
作业1:创建一个3*3,值在0-100区间随机值的Dataframe(如图),分别按照index和第二列值大小,降序排序

import numpy as np import pandas as pd #练习1 # df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(9).reshape(3,3)*100, # index=['a','b','c'], # columns=['v1','v2','v3']) # print(df) # # print(df.sort_index()) # df.sort_values(by = 'v2',ascending= False,inplace = True) # print(df)
作业2:创建一个5*2,值在0-100区间随机值的Dataframe(如图)df1,通过修改得到df2
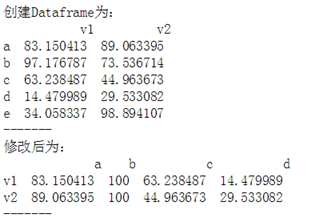
#练习2 # df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10).reshape(5,2)*100, # index=['a','b','c','d','e'], # columns=['v1','v2']) # print(df1) # print(df1.drop(['e'],axis = 0).T)
作业3:如图创建Series,并按照要求修改得到结果

#练习3 df2 = pd.Series(np.arange(10),index= ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j']) print(df2) df2.loc[['a','e','f']] = 100 print(df2) #或者 # df2.iloc[0] = 100 # df2.iloc[3] = 100 # df2.iloc[4] = 100