# Visualize some examples from the dataset. # We show a few examples of training images from each class. classes = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'] #类别列表 num_classes = len(classes) #类别数目 samples_per_class = 7 # 每个类别采样个数 for y, cls in enumerate(classes): # 对列表的元素位置和元素进行循环,y表示元素位置(0,num_class),cls元素本身'plane'等 idxs = np.flatnonzero(y_train == y) #找出标签中y类的位置 idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, samples_per_class, replace=False) #从中选出我们所需的7个样本 for i, idx in enumerate(idxs): #对所选的样本的位置和样本所对应的图片在训练集中的位置进行循环 plt_idx = i * num_classes + y + 1 # 在子图中所占位置的计算 plt.subplot(samples_per_class, num_classes, plt_idx) # 说明要画的子图的编号 plt.imshow(X_train[idx].astype('uint8')) # 画图 plt.axis('off') if i == 0: plt.title(cls) # 写上标题,也就是类别名 plt.show() # 显示

用矩阵运算取代两次循环运算,大大减少运算时间。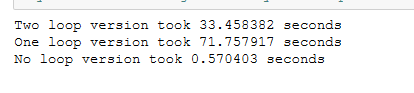
核心的公式:https://blog.csdn.net/zhyh1435589631/article/details/54236643
https://blog.csdn.net/geekmanong/article/details/51524402
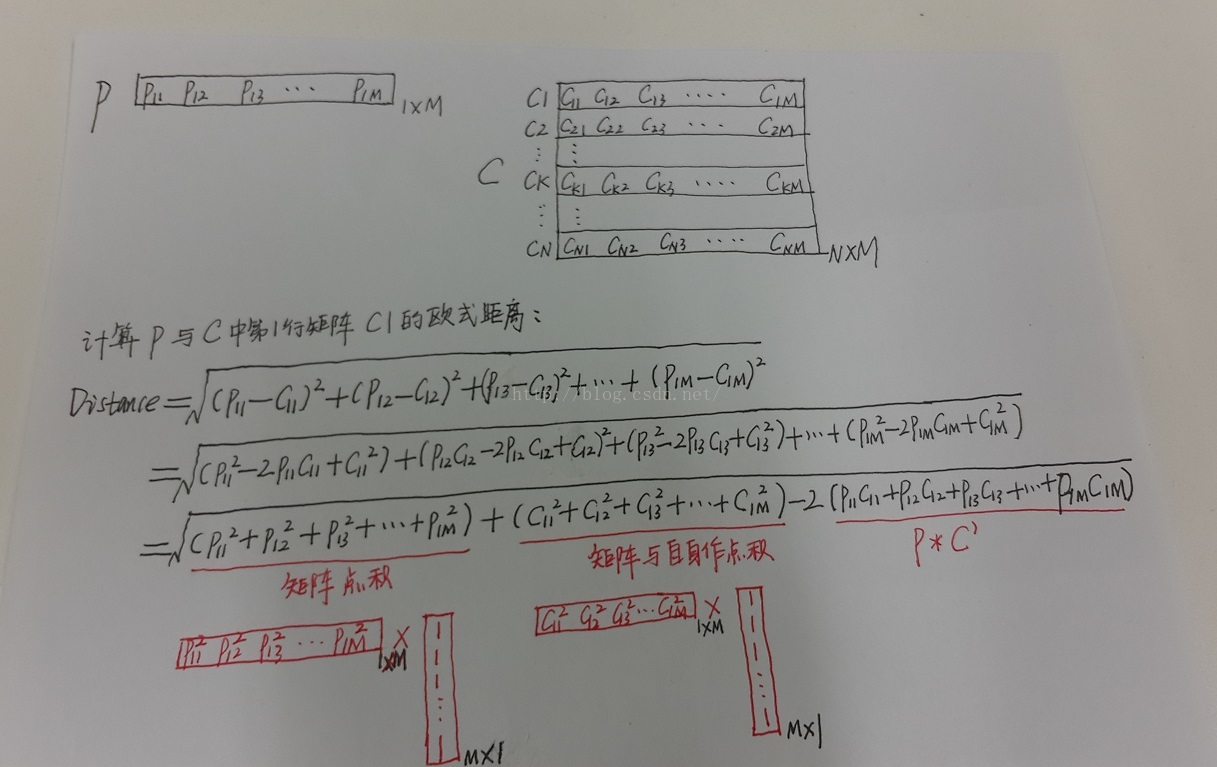
我自己的经验总结:先看最终目标矩阵的大小,可以确定前面位置。

交叉验证这里:
在进行分类前,一定要通过reshape函数,来确定数据输入的形状是不是符合要求。
num_folds = 5 k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100] X_train_folds = [] y_train_folds = [] ################################################################################ # TODO: # # Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and # # y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where # # y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. # # Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. # ################################################################################ X_train_folds=np.array_split(X_train,num_folds) y_train_folds=np.array_split(y_train,num_folds) ################################################################################ # END OF YOUR CODE # ################################################################################ # A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find # when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation, # k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different # accuracy values that we found when using that value of k. k_to_accuracies = {} ################################################################################ # TODO: # # Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each # # possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, # # where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the # # last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all # # values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. # ################################################################################ num_test = X_train_folds[0].shape[0] for j in range(len(k_choices)): k = k_choices[j] for i in range(1,num_folds+1): X_train_temp = np.concatenate((X_train_folds[num_folds-i],X_train_folds[num_folds-i-1],X_train_folds[num_folds-i-2],X_train_folds[num_folds-i-3]),axis = 0) y_train_temp = np.concatenate((y_train_folds[num_folds-i],y_train_folds[num_folds-i-1],y_train_folds[num_folds-i-2],y_train_folds[num_folds-i-3])) X_test_temp = X_train_folds[num_folds-i-4] y_test_temp = y_train_folds[num_folds-i-4] classifier.train(X_train_temp, y_train_temp) y_test_pred = classifier.predict(X_test_temp, k=k) num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test_temp) accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test k_to_accuracies.setdefault(k,[]).append(accuracy) ################################################################################ # END OF YOUR CODE # ################################################################################ # Print out the computed accuracies for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies): for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]: print('k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy))
将所有数据分为train/val/test三组,使用train训练,用val调整超参数,在最后的最后,才可以使用test,并且test只允许使用这一次,并将这一次的结果作为最终结果上报。否则得到的classifier会overfitting,或者结果不准确,有cheat的嫌疑。
Evaluate on the test set only a single time, at the very end.
所谓5-fold cross validation就是将所有的train data均匀分成5份,每次取4份做train,另外一份做val,重复五次,将五次结果平均。这样做的话每个数据都做了四次train,一次val。这样做的缺点是太expensive,NN中通常不用。注意,在这个过程中,test是不参与其中的。一定先将test set拿出来放到一边,不到最后交结果的时候不要碰它。
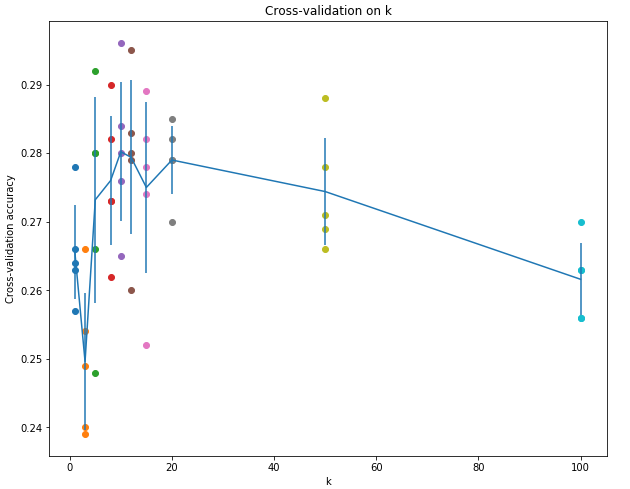
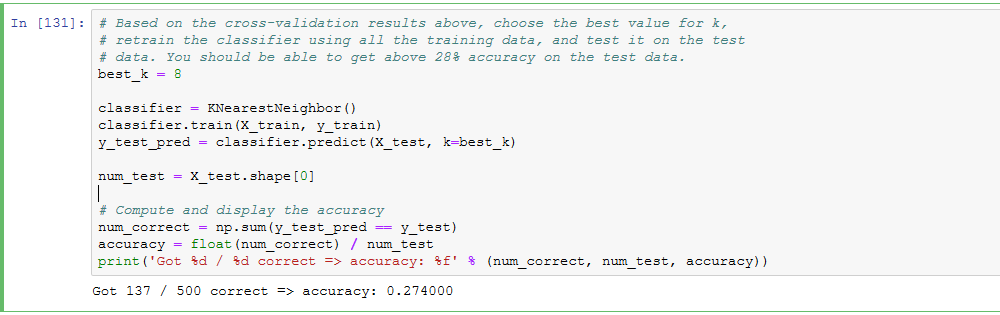

1,2显然不正确;因为kNN是非线性分类器,所以边界也是非线性的;training set越大,在predict时需要计算test example与所有training的距离,所以在相同算力条件下,taining set越大,predict一个test sample所需时间越多,时间复杂度为O(N)。