今天的题目是:
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
Example 1:
nums1 = [1, 3]
nums2 = [2]
The median is 2.0
Example 2:
nums1 = [1, 2]
nums2 = [3, 4]
The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
翻译一下:有两个分别排好序的数组num1和num2,大小分别为m和n。找到这两个数组合并后的中位数。时间复杂度应该为O(log(m+n))。
第一种解法:方法是首先排好序(排序只需要排到一半),然后找到中位数。
package com.test;
public class Median {
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
int[] a = {1,4,6};
int[] b = {2,6,8};
System.out.println( "中位数为" + getMedian(a,b));
}
public double getMedian(int[] arrayA,int[] arrayB){
int lengthA = arrayA.length;
int lengthB = arrayB.length;
int halfLength = (lengthA + lengthB) / 2 + 1;
int[] newArray = new int[halfLength];
int i = 0,j = 0,k = 0;
while( i < lengthA && j < lengthB && k < halfLength){
if(arrayA[i] <= arrayB[j]){
newArray[k++] = arrayA[i++];
}else{
newArray[k++] = arrayB[j++];
}
}
while(i < lengthA && k < halfLength){
newArray[k++] = arrayA[i++];
}
while(j < lengthB && k < halfLength){
newArray[k++] = arrayB[j++];
}
if((lengthA + lengthB) % 2 == 0){
return ((double)newArray[k-1] + (double)newArray[k-2])/2;
}else{
return (double)(newArray[k-1]);
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O((m+n)/2) = O(m+n)。
空间复杂度:O((m+n)/2) = O(m+n)。
第二种解法:
首先我们用一个随机数 i 将数组A分成两部分:
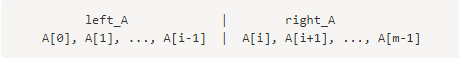
既然A有m个元素,那么就有m+1中分法(i = 0 ~ m)。那么就有 len(left_A)= i ,len(right_A) = m - i,注意当 i = 0时,left_A是空的,并且当i = m时,right_A是空的。
对于数组B我们用同样的方式处理:
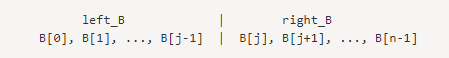
现在把left_A和left_B放在左边,然后把right_A和right_B放到另一边,我们起名叫left_part和right_part。

只要我们把{A,B}分成相等的两部分,并且其中一部分比另一部分大。那么就有

为了确保这两个条件,我们只需要确保
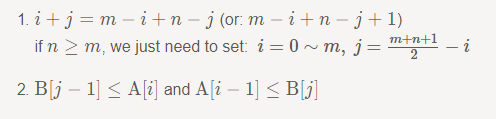
注意1:为简单起见,我们假定即使当i = 0,i = m,j = 0,j = n时A[i-1],B[J-1],A[i],B[j]都是合法的。我们在最后在讨论如何处理这些边界值。
注意2:为什么n >= m ?因为我们必须确保 j 是非负的。如果n < m,j也许是负数,这将导致错误的结果。
接下来需要做的是:




package com.test;
public class Median {
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
int[] a = {1,4,6};
int[] b = {2,6,8};
System.out.println( "中位数为" + findMedianSortedArrays(a,b));
}
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] A, int[] B) {
int m = A.length;
int n = B.length;
if (m > n) { // to ensure m<=n
int[] temp = A; A = B; B = temp;
int tmp = m; m = n; n = tmp;
}
int iMin = 0, iMax = m, halfLen = (m + n + 1) / 2;
while (iMin <= iMax) {
int i = (iMin + iMax) / 2;
int j = halfLen - i;
if (i < iMax && B[j-1] > A[i]){
iMin = iMin + 1; // i is too small
}
else if (i > iMin && A[i-1] > B[j]) {
iMax = iMax - 1; // i is too big
}
else { // i is perfect
int maxLeft = 0;
if (i == 0) { maxLeft = B[j-1]; }
else if (j == 0) { maxLeft = A[i-1]; }
else { maxLeft = Math.max(A[i-1], B[j-1]); }
if ( (m + n) % 2 == 1 ) { return maxLeft; }
int minRight = 0;
if (i == m) { minRight = B[j]; }
else if (j == n) { minRight = A[i]; }
else { minRight = Math.min(B[j], A[i]); }
return (maxLeft + minRight) / 2.0;
}
}
return 0.0;
}
}
结果:
时间复杂度:O(log(min(m,n)))。最开始,查找的范围是[0,m]。并且每次循环查找的范围都会少一半,因此,我们仅仅需要log(m)次循环。每次循环都是常量级操作,因此时间复杂度为O(log(m))。又因为m <= n,因此时间复杂度为O(log(min(m,n)))。
空间复杂度:O(1)。