spring-cloud-openFeign源码深度解析
如何使用spring cloud feign
1 @SpringBootApplication 2 @EnableFeignClients 3 public class WebApplication { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 SpringApplication.run(WebApplication.class, args); 7 } 8 9 @FeignClient("name") 10 static interface NameService { 11 @RequestMapping("/") 12 public String getName(); 13 } 14 }
从官网的例子中,可以看出是通过注解驱动的,所以从注解开始看起。
spring cloud feign是如何工作的
Feign涉及了两个注解,一个是@EnableFeignClients,用来开启 Feign,另一个是@FeignClient,用来标记要用 Feign 来拦截的请求接口。
1 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 2 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 3 @Documented 4 @Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class) 5 public @interface EnableFeignClients { 6 7 String[] value() default {}; 8 9 String[] basePackages() default {}; 10 11 Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; 12 13 Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {}; 14 15 Class<?>[] clients() default {}; 16 }
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 public @interface FeignClient { 5 6 @AliasFor("name") 7 String value() default ""; 8 9 @Deprecated 10 String serviceId() default ""; 11 12 @AliasFor("value") 13 String name() default ""; 14 15 String qualifier() default ""; 16 17 String url() default ""; 18 19 boolean decode404() default false; 20 21 Class<?>[] configuration() default {}; 22 23 Class<?> fallback() default void.class; 24 25 Class<?> fallbackFactory() default void.class; 26 27 String path() default ""; 28 29 boolean primary() default true; 30 31 }
@EnableFeignClients 是关于注解扫描的配置,比如扫描路径,配置等。@FeignClient 则是关于对该接口进行代理的时候,一些实现细节的配置,比如访问url是什么, fallback 方法,关于404的请求是抛错误还是正常返回。
注册client
先关注对EnableFeignClients 的处理,可以看出它使用了@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class),看名字可知是一个注册器,通过扫描某个特性的类,将bean注册到IOC中。Spring 通过调用其 registerBeanDefinitions 方法来获取其提供的 bean definition。
1 public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { 2 //注册configuration 3 registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry); 4 //注册注解 5 registerFeignClients(metadata, registry); 6 }
1 private void registerDefaultConfiguration(AnnotationMetadata metadata,BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { 2 //获取注解@EnableFeignClients 下设置的属性值 3 Map<String, Object> defaultAttrs = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName(), true); 4 5 if (defaultAttrs != null && defaultAttrs.containsKey("defaultConfiguration")) { 6 String name; 7 //判断传入的defaultConfiguration的是不是topClass,所谓topClass就是说此类不是别的类的内部类 8 if (metadata.hasEnclosingClass()) { 9 name = "default." + metadata.getEnclosingClassName(); 10 } 11 else { 12 name = "default." + metadata.getClassName(); 13 } 14 registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,defaultAttrs.get("defaultConfiguration")); 15 } 16 }
1 private void registerClientConfiguration(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object name,Object configuration) { 2 //加载FeignClientSpecification bean 3 BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientSpecification.class); 4 builder.addConstructorArgValue(name); 5 builder.addConstructorArgValue(configuration); 6 //注册 7 registry.registerBeanDefinition(name + "." + FeignClientSpecification.class.getSimpleName(),builder.getBeanDefinition()); 8 }
这里会往 Registry 里面添加一个BeanDefinition,即 FeignClientSpecification,configuration是通过 EnableFeignClients 注解的 defaultConfiguration 参数传入。
1 public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { 2 ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner(); 3 scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader); 4 5 Set<String> basePackages; 6 7 Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata 8 .getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName()); 9 // 扫描带有FeignClient注解的类 10 AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter( 11 FeignClient.class); 12 //获取@EnableFeignClients 中clients的值 13 final Class<?>[] clients = attrs == null ? null 14 : (Class<?>[]) attrs.get("clients"); 15 if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) { 16 //如果没有设置,那么加入要扫描的注解和扫描的包 17 scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter); 18 // 确定扫描的包路径列表 19 basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata); 20 } 21 else { 22 //如果设置了,最终扫出来的Bean必须是注解中设置的那些 23 final Set<String> clientClasses = new HashSet<>(); 24 basePackages = new HashSet<>(); 25 for (Class<?> clazz : clients) { 26 basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz)); 27 clientClasses.add(clazz.getCanonicalName()); 28 } 29 AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter filter = new AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter() { 30 @Override 31 protected boolean match(ClassMetadata metadata) { 32 String cleaned = metadata.getClassName().replaceAll("\$", "."); 33 return clientClasses.contains(cleaned); 34 } 35 }; 36 scanner.addIncludeFilter( 37 new AllTypeFilter(Arrays.asList(filter, annotationTypeFilter))); 38 } 39 //循环扫描,并把根据注解信息,进行相关注册 40 for (String basePackage : basePackages) { 41 Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner 42 .findCandidateComponents(basePackage); 43 for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) { 44 if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { 45 // verify annotated class is an interface 46 AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent; 47 AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata(); 48 //必须注解在interface上 49 Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(), 50 "@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface"); 51 52 Map<String, Object> attributes = annotationMetadata 53 .getAnnotationAttributes( 54 FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName()); 55 56 String name = getClientName(attributes); 57 registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,attributes.get("configuration")); 58 59 registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<String, Object> attributes) { 66 String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName(); 67 BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder 68 .genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class); 69 validate(attributes); 70 //将属性设置到FeignClientFactoryBean 中 71 definition.addPropertyValue("url", getUrl(attributes)); 72 definition.addPropertyValue("path", getPath(attributes)); 73 String name = getName(attributes); 74 definition.addPropertyValue("name", name); 75 definition.addPropertyValue("type", className); 76 definition.addPropertyValue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404")); 77 definition.addPropertyValue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback")); 78 definition.addPropertyValue("fallbackFactory", attributes.get("fallbackFactory")); 79 //设置Autowire 类型 80 definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE); 81 82 String alias = name + "FeignClient"; 83 AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition(); 84 85 boolean primary = (Boolean)attributes.get("primary"); // has a default, won't be null 86 87 beanDefinition.setPrimary(primary); 88 89 String qualifier = getQualifier(attributes); 90 if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) { 91 alias = qualifier; 92 } 93 //注册bean 94 BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className, 95 new String[] { alias }); 96 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry); 97 }
另一个往 Registry 里面添加的 BeanDefinition则是FeignClientFactoryBean,负责注册FeignClient。
也就是说,Feign的注册一共分为一下几步:
- 扫描@EnableFeignClients注解,如果有defaultConfiguration属性配置,则将configuration注册到BeanDefinition中,如果不指定的话,spring 提供的默认配置是FeignClientsConfiguration。
- 扫描 basePackage 下面所有包含了 @FeignClient 注解的类
- 如果@EnableFeignClients中配置了clients属性,则扫描出来的bean只有在clients中配置的那些
- 循环扫描@FeignClient注解,如果配置了configuration,则将configuration按照 1 注册打BeanDefinition中,也就是说Feign既支持用作统一的默认的Config作为全局配置,也可以分别在@FeignClient中单独配置configuration 作为局部配置。
- 将@FeignClient中的其他配置设置到FeignClientFactoryBean中。
- 最后调用FeignClientFactoryBean#getObject来创建client实例。
加载配置项
接下来来看下 FeignClientFactoryBean,Spring Context 创建 Bean 实例时会调用它的 getObject 方法。
1 public Object getObject() throws Exception { 2 return getTarget(); 3 } 4 5 /** 6 * @param <T> the target type of the Feign client 7 * @return a {@link Feign} client created with the specified data and the context information 8 */ 9 <T> T getTarget() { 10 FeignContext context = applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class); 11 Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);//1 12 13 if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) { 14 //如果没有指定url,获取name值拼接默认url 15 String url; 16 if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) { 17 url = "http://" + this.name; 18 } 19 else { 20 url = this.name; 21 } 22 url += cleanPath(); 23 return (T) loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, 24 this.name, url)); 25 } 26 if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) { 27 this.url = "http://" + this.url; 28 } 29 String url = this.url + cleanPath(); 30 Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class); 31 if (client != null) { 32 if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) { 33 //使用ribbon提供的负载均衡 34 // not load balancing because we have a url, 35 // but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap 36 client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient)client).getDelegate(); 37 } 38 builder.client(client); 39 } 40 Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class); 41 return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>( 42 this.type, this.name, url)); 43 }
- 如果未指定url,则根据client的name来拼接url,并开启负载均衡
- 如果指定了URL,没有指定client,那么就根据url来调用,相当于直连,没有负载均衡。如果没有指定client的话,可以使用负载均衡。现在的版本是默认开启负载均衡。
首先在1处可以看出通过feign(context)方法初始化了Feign.Builder,所以着重看一下这个方法:
1 protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) { 2 //获取FeignClientsConfiguration 中注册的bean ,设置到feign中 3 FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class); 4 Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(this.type); 5 6 // @formatter:off 7 Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class) 8 // required values 9 .logger(logger) 10 .encoder(get(context, Encoder.class)) 11 .decoder(get(context, Decoder.class)) 12 .contract(get(context, Contract.class)); 13 // @formatter:on 14 15 configureFeign(context, builder); 16 17 return builder; 18 }
这里被设置到builder的bean来自于FeignClientsConfiguration在启动时加载到了context中,这是spring的默认配置,即使在@EnableFeignClients和@FeignClient没有配置configuration也能保证可以使用。
1 @Configuration 2 public class FeignClientsConfiguration { 3 ... 4 @Bean 5 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 6 public Decoder feignDecoder() { 7 return new OptionalDecoder(new ResponseEntityDecoder(new SpringDecoder(this.messageConverters))); 8 } 9 10 @Bean 11 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 12 public Encoder feignEncoder() { 13 return new SpringEncoder(this.messageConverters); 14 } 15 16 @Bean 17 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 18 public Contract feignContract(ConversionService feignConversionService) { 19 return new SpringMvcContract(this.parameterProcessors, feignConversionService); 20 } 21 22 @Bean 23 @Scope("prototype") 24 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 25 public Feign.Builder feignBuilder(Retryer retryer) { 26 return Feign.builder().retryer(retryer); 27 } 28 ... 29 }
那么自定义的configuration在哪里加载呢,可以看到方法feign(context)中最后一行调用了configureFeign(context, builder),来看一下这个方法。
1 protected void configureFeign(FeignContext context, Feign.Builder builder) { 2 //获取.properties的属性 3 FeignClientProperties properties = applicationContext.getBean(FeignClientProperties.class); 4 if (properties != null) { 5 if (properties.isDefaultToProperties()) { 6 //默认为true 7 configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); 8 configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder); 9 configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(this.name), builder); 10 } else { 11 configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder); 12 configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(this.name), builder); 13 configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); 14 } 15 } else { 16 configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); 17 } 18 } 19 //获取用户通过configuration @Bean的自定义配置 20 protected void configureUsingConfiguration(FeignContext context, Feign.Builder builder) { 21 Logger.Level level = getOptional(context, Logger.Level.class); 22 if (level != null) { 23 builder.logLevel(level); 24 } 25 Retryer retryer = getOptional(context, Retryer.class); 26 if (retryer != null) { 27 builder.retryer(retryer); 28 } 29 ErrorDecoder errorDecoder = getOptional(context, ErrorDecoder.class); 30 if (errorDecoder != null) { 31 builder.errorDecoder(errorDecoder); 32 } 33 //connectTimeoutMillis和readTimeoutMillis的默认值 34 Request.Options options = getOptional(context, Request.Options.class); 35 if (options != null) { 36 builder.options(options); 37 } 38 Map<String, RequestInterceptor> requestInterceptors = context.getInstances( 39 this.name, RequestInterceptor.class); 40 if (requestInterceptors != null) { 41 builder.requestInterceptors(requestInterceptors.values()); 42 } 43 44 if (decode404) { 45 builder.decode404(); 46 } 47 } 48 49 50 /*** 51 * 52 * @param config 获取.properties中配置的bean 53 * @param builder feign 54 */ 55 protected void configureUsingProperties(FeignClientProperties.FeignClientConfiguration config, Feign.Builder builder) { 56 if (config == null) { 57 return; 58 } 59 60 if (config.getLoggerLevel() != null) { 61 builder.logLevel(config.getLoggerLevel()); 62 } 63 //设置connectTimeoutMillis和readTimeoutMillis的值,这里的属性值来自于.properties配置的 64 if (config.getConnectTimeout() != null && config.getReadTimeout() != null) { 65 builder.options(new Request.Options(config.getConnectTimeout(), config.getReadTimeout())); 66 } 67 68 if (config.getRetryer() != null) { 69 Retryer retryer = getOrInstantiate(config.getRetryer()); 70 builder.retryer(retryer); 71 } 72 73 if (config.getErrorDecoder() != null) { 74 ErrorDecoder errorDecoder = getOrInstantiate(config.getErrorDecoder()); 75 builder.errorDecoder(errorDecoder); 76 } 77 78 if (config.getRequestInterceptors() != null && !config.getRequestInterceptors().isEmpty()) { 79 // this will add request interceptor to builder, not replace existing 80 //这里只会往原有的interceptor中添加新的,而不会删掉原有的。 81 for (Class<RequestInterceptor> bean : config.getRequestInterceptors()) { 82 RequestInterceptor interceptor = getOrInstantiate(bean); 83 builder.requestInterceptor(interceptor); 84 } 85 } 86 87 if (config.getDecode404() != null) { 88 if (config.getDecode404()) { 89 builder.decode404(); 90 } 91 } 92 93 if (Objects.nonNull(config.getEncoder())) { 94 builder.encoder(getOrInstantiate(config.getEncoder())); 95 } 96 97 if (Objects.nonNull(config.getDecoder())) { 98 builder.decoder(getOrInstantiate(config.getDecoder())); 99 } 100 101 if (Objects.nonNull(config.getContract())) { 102 builder.contract(getOrInstantiate(config.getContract())); 103 } 104 }
把配置文件中的配置项在启动时初始化到FeignClientProperties中。
- 如果配置文件中没有配置,则将FeignClientsConfiguration中的bean作为默认值设置到builder。
- 如果配置文件中有配置,并且用默认加载顺序时,首先加载FeignClientsConfiguration中的bean,然后加载在注解中配置的configuration,最后加载配置文件中的。
- 如果不是默认加载顺序,则首先加载注解中配置的configuration,然后加载配置文件中的配置,最后加载FeignClientsConfiguration中的bean。注意,顺序在后面的配置会覆盖掉前面的
创建client实例
配置文件加载完之后,就是最关键的一步,创建实例.因为两种方式都是通过获取 Targeter 来生成动态代理类。这里拿出了负载均衡做例子。
1 protected <T> T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignContext context, 2 HardCodedTarget<T> target) { 3 Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class); 4 if (client != null) { 5 builder.client(client); 6 Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class); 7 return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target); 8 } 9 10 throw new IllegalStateException( 11 "No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon?"); 12 }
在 FeignAutoConfiguration 里面,配置了Target,可以看出这里配置了两种相斥的bean。
1 @Configuration 2 @ConditionalOnClass(name = "feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign") 3 protected static class HystrixFeignTargeterConfiguration { 4 @Bean 5 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 6 public Targeter feignTargeter() { 7 return new HystrixTargeter(); 8 } 9 } 10 11 @Configuration 12 @ConditionalOnMissingClass("feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign") 13 protected static class DefaultFeignTargeterConfiguration { 14 @Bean 15 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 16 public Targeter feignTargeter() { 17 return new DefaultTargeter(); 18 } 19 }
如果 feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign`路径不存在,则直接用 FeignBuidler 中DefaultTargeter的 target 方法生成代理。
1 class HystrixTargeter implements Targeter { 2 3 @Override 4 public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign, FeignContext context,Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) { 5 if (!(feign instanceof feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder)) { 6 return feign.target(target); 7 } 8 feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder builder = (feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder) feign; 9 SetterFactory setterFactory = getOptional(factory.getName(), context, 10 SetterFactory.class); 11 if (setterFactory != null) { 12 builder.setterFactory(setterFactory); 13 } 14 Class<?> fallback = factory.getFallback(); 15 if (fallback != void.class) { 16 return targetWithFallback(factory.getName(), context, target, builder, fallback); 17 } 18 Class<?> fallbackFactory = factory.getFallbackFactory(); 19 if (fallbackFactory != void.class) { 20 return targetWithFallbackFactory(factory.getName(), context, target, builder, fallbackFactory); 21 } 22 23 return feign.target(target); 24 } 25 }
1 class DefaultTargeter implements Targeter { 2 3 @Override 4 public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign, FeignContext context,Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) { 5 return feign.target(target); 6 } 7 }
到这里spring对于创建client实例工作基本完成。接下来主要步骤在feign中。
Feign是怎么工作的
构建接口动态代理
这里会直接调用Feign的target方法:
1 public <T> T target(Target<T> target) { 2 return build().newInstance(target); 3 } 4 5 private InvocationHandlerFactory invocationHandlerFactory =new InvocationHandlerFactory.Default(); 6 7 private QueryMapEncoder queryMapEncoder = new QueryMapEncoder.Default(); 8 9 public Feign build() { 10 SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory = 11 new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger, 12 logLevel, decode404, closeAfterDecode); 13 //handlersByName将所有参数进行封装,并提供解析接口方法的逻辑 14 ParseHandlersByName handlersByName = 15 new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder, queryMapEncoder, 16 errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory); 17 return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory, queryMapEncoder); 18 }
ReflectiveFeign构造函数有三个参数:
- ParseHandlersByName 将builder所有参数进行封装,并提供解析接口方法的逻辑
- InvocationHandlerFactory 默认值是InvocationHandlerFactory.Default,通过java动态代理的InvocationHandler实现
- QueryMapEncoder 接口参数注解@QueryMap时,参数的编码器,默认值QueryMapEncoder.Default
ReflectiveFeign 生成动态代理对象。
ReflectiveFeign#newInstance
1 public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) { 2 //为每个方法创建一个SynchronousMethodHandler对象,并放在 Map 里面。 3 //targetToHandlersByName是构造器传入的ParseHandlersByName对象,根据target对象生成MethodHandler映射 4 Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target); 5 Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>(); 6 List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>(); 7 //遍历接口所有方法,构建Method->MethodHandler的映射 8 for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) { 9 if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { 10 continue; 11 } else if(Util.isDefault(method)) { 12 //如果是 default 方法,说明已经有实现了,用 DefaultHandler接口default方法的Handler 13 DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method); 14 defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler); 15 methodToHandler.put(method, handler); 16 } else { 17 //否则就用上面的 SynchronousMethodHandler 18 methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method))); 19 } 20 } 21 // 创建动态代理,factory 是 InvocationHandlerFactory.Default,创建出来的是 ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHanlder,也就是说后续对方法的调用都会进入到该对象的 inovke 方法。 22 InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler); 23 // 创建动态代理对象 24 T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler); 25 //将default方法直接绑定到动态代理上 26 for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) { 27 defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy); 28 } 29 return proxy; 30 }
这段代码主要的逻辑是:
- 创建MethodHandler的映射,这里创建的是实现类SynchronousMethodHandler
- 通过InvocationHandlerFatory创建InvocationHandler
- 绑定接口的default方法,通过DefaultMethodHandler绑定
SynchronousMethodHandler和DefaultMethodHandler实现了InvocationHandlerFactory.MethodHandler接口,动态代理对象调用方法时,如果是default方法,会直接调用接口方法,因为这里将接口的default方法绑定到动态代理对象上了,其他方法根据方法签名找到SynchronousMethodHandler对象,调用其invoke方法。
创建MethodHandler方法处理器
ReflectiveFeign#apply
1 public Map<String, MethodHandler> apply(Target key) { 2 //通过contract解析接口方法,生成MethodMetadata列表,默认的contract解析Feign自定义的http注解 3 List<MethodMetadata> metadata =contract.parseAndValidatateMetadata(key.type()); 4 Map<String, MethodHandler> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, MethodHandler>(); 5 for (MethodMetadata md : metadata) { 6 //根据目标接口类和方法上的注解信息判断该用哪种 buildTemplate 7 //BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs实现RequestTemplate.Factory,RequestTemplate的工厂 8 BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs buildTemplate; 9 if (!md.formParams().isEmpty() && md.template().bodyTemplate() == null) { 10 //如果有formParam,并且bodyTemplate不为空,请求体为x-www-form-urlencoded格式 11 //将会解析form参数,填充到bodyTemplate中 12 buildTemplate = new BuildFormEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder); 13 } else if (md.bodyIndex() != null) { 14 //如果包含请求体,将会用encoder编码请求体对象 15 buildTemplate = new BuildEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder); 16 } else { 17 //默认的RequestTemplate的工厂,没有请求体,不需要编码器 18 buildTemplate = new BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs(md); 19 } 20 //使用工厂SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory创建SynchronousMethodHandler 21 result.put(md.configKey(), 22 factory.create(key, md, buildTemplate, options, decoder, errorDecoder)); 23 } 24 return result; 25 }
这段代码的逻辑是:
- 通过Contract解析接口方法,生成MethodMetadata,默认的Contract解析Feign自定义的http注解
- 根据MethodMetadata方法元数据生成特定的RequestTemplate的工厂
- 使用SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory工厂创建SynchronousMethodHandler,这里有两个工厂不要搞混淆了,SynchronousMethodHandler工厂和RequestTemplate工厂,SynchronousMethodHandler的属性包含RequestTemplate工厂
SynchronousMethodHandlerFactory#create
1 public MethodHandler create(Target<?> target, MethodMetadata md, 2 RequestTemplate.Factory buildTemplateFromArgs, 3 Options options, Decoder decoder, ErrorDecoder errorDecoder) { 4 //buildTemplateFromArgs--RequestTemplate Facoory 5 return new SynchronousMethodHandler(target, client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger, 6 logLevel, md, buildTemplateFromArgs, options, decoder, 7 errorDecoder, decode404); 8 }
Contract解析接口方法生成MethodMetadata
这里有两个Contract,一个是feign默认的Contract,另一个是Spring实现的Contract。
Feign.Contract-Contract.Default
feign默认的解析器是Contract.Default继承了Contract.BaseContract,解析生成MethodMetadata方法入口:
1 @Override 2 public List<MethodMetadata> parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class<?> targetType) { 3 4 Map<String, MethodMetadata> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, MethodMetadata>(); 5 for (Method method : targetType.getMethods()) { 6 //... 7 MethodMetadata metadata = parseAndValidateMetadata(targetType, method); 8 //... 9 result.put(metadata.configKey(), metadata); 10 } 11 return new ArrayList<MethodMetadata>(result.values()); 12 } 13 14 protected MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method) { 15 MethodMetadata data = new MethodMetadata(); 16 data.returnType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, method.getGenericReturnType())); 17 data.configKey(Feign.configKey(targetType, method)); 18 19 if(targetType.getInterfaces().length == 1) { 20 processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType.getInterfaces()[0]); 21 } 22 //处理Class上的注解 23 processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType); 24 25 for (Annotation methodAnnotation : method.getAnnotations()) { 26 //处理方法注解 27 processAnnotationOnMethod(data, methodAnnotation, method); 28 } 29 //... 30 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); 31 Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes(); 32 33 Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations(); 34 int count = parameterAnnotations.length; 35 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 36 boolean isHttpAnnotation = false; 37 if (parameterAnnotations[i] != null) { 38 //方法参数注解 39 isHttpAnnotation = processAnnotationsOnParameter(data, parameterAnnotations[i], i); 40 } 41 if (parameterTypes[i] == URI.class) { 42 //参数类型是URI,后面构造http请求时,使用该URI 43 data.urlIndex(i); 44 } else if (!isHttpAnnotation) { 45 //如果没有被http注解,就是body参数 46 //... 47 data.bodyIndex(i); 48 data.bodyType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, genericParameterTypes[i])); 49 } 50 } 51 52 if (data.headerMapIndex() != null) { 53 //@HeaderMap注解的参数必须是Map,key类型必须是String 54 checkMapString("HeaderMap", parameterTypes[data.headerMapIndex()], genericParameterTypes[data.headerMapIndex()]); 55 } 56 57 if (data.queryMapIndex() != null) { 58 if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[data.queryMapIndex()])) { 59 //@QueryMap注解的参数如果是Map,key类型必须是String 60 checkMapKeys("QueryMap", genericParameterTypes[data.queryMapIndex()]); 61 } 62 } 63 return data; 64 }
1.处理Class上的注解
这里主要处理@Headers
1 //处理@Headers注解 2 protected void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> targetType) { 3 if (targetType.isAnnotationPresent(Headers.class)) { 4 //被Headers注解 5 String[] headersOnType = targetType.getAnnotation(Headers.class).value(); 6 //... 7 //header解析成map,加到MethodMetadata中 8 Map<String, Collection<String>> headers = toMap(headersOnType); 9 headers.putAll(data.template().headers()); 10 data.template().headers(null); // to clear 11 data.template().headers(headers); 12 } 13 }
2.处理方法上的注解
这里主要处理@RequestLine、@Body、@Headers
1 //处理方法注解 2 protected void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data, Annotation methodAnnotation, 3 Method method) { 4 Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = methodAnnotation.annotationType(); 5 if (annotationType == RequestLine.class) { 6 //@RequestLine注解 7 String requestLine = RequestLine.class.cast(methodAnnotation).value(); 8 //... 9 if (requestLine.indexOf(' ') == -1) { 10 //... 11 data.template().method(requestLine); 12 return; 13 } 14 //http请求方法 15 data.template().method(requestLine.substring(0, requestLine.indexOf(' '))); 16 if (requestLine.indexOf(' ') == requestLine.lastIndexOf(' ')) { 17 // no HTTP version is ok 18 data.template().append(requestLine.substring(requestLine.indexOf(' ') + 1)); 19 } else { 20 // skip HTTP version 21 data.template().append( 22 requestLine.substring(requestLine.indexOf(' ') + 1, requestLine.lastIndexOf(' '))); 23 } 24 //将'%2F'反转为'/' 25 data.template().decodeSlash(RequestLine.class.cast(methodAnnotation).decodeSlash()); 26 //参数集合格式化方式,默认使用key=value0&key=value1 27 data.template().collectionFormat(RequestLine.class.cast(methodAnnotation).collectionFormat()); 28 29 } else if (annotationType == Body.class) { 30 //@Body注解 31 String body = Body.class.cast(methodAnnotation).value(); 32 //... 33 if (body.indexOf('{') == -1) { 34 //body中不存在{,直接传入body 35 data.template().body(body); 36 } else { 37 //body中存在{,就是bodyTemplate方式 38 data.template().bodyTemplate(body); 39 } 40 } else if (annotationType == Headers.class) { 41 //@Header注解 42 String[] headersOnMethod = Headers.class.cast(methodAnnotation).value(); 43 //... 44 data.template().headers(toMap(headersOnMethod)); 45 } 46 }
3.处理参数上的注解
这里主要处理@Param、@QueryMap、@HeaderMap,只要有这三个注解,则isHttpAnnotation=true。
1 //处理参数上的注解 2 protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data, Annotation[] annotations, int paramIndex) { 3 boolean isHttpAnnotation = false; 4 for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { 5 Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType(); 6 if (annotationType == Param.class) { 7 //@Param注解 8 Param paramAnnotation = (Param) annotation; 9 String name = paramAnnotation.value(); 10 //... 11 //增加到MethodMetadata中 12 nameParam(data, name, paramIndex); 13 //@Param注解的expander参数,定义参数的解释器,默认是ToStringExpander,调用参数的toString方法 14 Class<? extends Param.Expander> expander = paramAnnotation.expander(); 15 if (expander != Param.ToStringExpander.class) { 16 data.indexToExpanderClass().put(paramIndex, expander); 17 } 18 //参数是否已经urlEncoded,如果没有,会使用urlEncoded方式编码 19 data.indexToEncoded().put(paramIndex, paramAnnotation.encoded()); 20 isHttpAnnotation = true; 21 String varName = '{' + name + '}'; 22 if (!data.template().url().contains(varName) && 23 !searchMapValuesContainsSubstring(data.template().queries(), varName) && 24 !searchMapValuesContainsSubstring(data.template().headers(), varName)) { 25 //如果参数不在path里面,不在query里面,不在header里面,就设置到formParam中 26 data.formParams().add(name); 27 } 28 } else if (annotationType == QueryMap.class) { 29 //@QueryMap注解,注解参数对象时,将该参数转换为http请求参数格式发送 30 //... 31 data.queryMapIndex(paramIndex); 32 data.queryMapEncoded(QueryMap.class.cast(annotation).encoded()); 33 isHttpAnnotation = true; 34 } else if (annotationType == HeaderMap.class) { 35 //@HeaderMap注解,注解一个Map类型的参数,放入http header中发送 36 //... 37 data.headerMapIndex(paramIndex); 38 isHttpAnnotation = true; 39 } 40 } 41 return isHttpAnnotation; 42 }
Spring.Contract-SpringMvcContract
feign默认的解析器是SpringMvcContract继承了Contract.BaseContract,解析生成MethodMetadata方法入口:
1 @Override 2 public MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method) { 3 this.processedMethods.put(Feign.configKey(targetType, method), method); 4 MethodMetadata md = super.parseAndValidateMetadata(targetType, method); 5 6 RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(targetType, 7 RequestMapping.class); 8 if (classAnnotation != null) { 9 // produces - use from class annotation only if method has not specified this 10 // 如果Accept为空,则设置@RequestMapping的produces 11 if (!md.template().headers().containsKey(ACCEPT)) { 12 parseProduces(md, method, classAnnotation); 13 } 14 15 // consumes -- use from class annotation only if method has not specified this 16 // 如果Content-Type为空,则设置@RequestMapping的consumes 17 if (!md.template().headers().containsKey(CONTENT_TYPE)) { 18 parseConsumes(md, method, classAnnotation); 19 } 20 21 // headers -- class annotation is inherited to methods, always write these if 22 // present 设置heerders 23 parseHeaders(md, method, classAnnotation); 24 } 25 return md; 26 }
这里parseAndValidateMetadata调用了父类即BaseContract的方法,如上,也会分为3部来处理,这里只分析有区别的部分。解析完成之后,会根据在class上注解的@RequestMapping的属性值来设置到MethodMetadata中。
1.处理Class上的注解
这里主要处理@RequestMapping
1 protected void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> clz) { 2 if (clz.getInterfaces().length == 0) { 3 RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(clz, 4 RequestMapping.class); 5 if (classAnnotation != null) { 6 // Prepend path from class annotation if specified 7 if (classAnnotation.value().length > 0) { 8 String pathValue = emptyToNull(classAnnotation.value()[0]); 9 pathValue = resolve(pathValue); 10 if (!pathValue.startsWith("/")) { 11 pathValue = "/" + pathValue; 12 } 13 //插入url 14 data.template().insert(0, pathValue); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 }
2.处理方法上的注解
这里主要处理@RequestMapping,和处理class时差不多
1 protected void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data, 2 Annotation methodAnnotation, Method method) { 3 if (!RequestMapping.class.isInstance(methodAnnotation) && !methodAnnotation 4 .annotationType().isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) { 5 return; 6 } 7 8 RequestMapping methodMapping = findMergedAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class); 9 // 设置HTTP Method 10 RequestMethod[] methods = methodMapping.method(); 11 if (methods.length == 0) { 12 methods = new RequestMethod[] { RequestMethod.GET }; 13 } 14 checkOne(method, methods, "method"); 15 data.template().method(methods[0].name()); 16 17 // path 18 checkAtMostOne(method, methodMapping.value(), "value"); 19 if (methodMapping.value().length > 0) { 20 String pathValue = emptyToNull(methodMapping.value()[0]); 21 if (pathValue != null) { 22 pathValue = resolve(pathValue); 23 // Append path from @RequestMapping if value is present on method 24 if (!pathValue.startsWith("/") 25 && !data.template().toString().endsWith("/")) { 26 pathValue = "/" + pathValue; 27 } 28 data.template().append(pathValue); 29 } 30 } 31 32 // produces 33 parseProduces(data, method, methodMapping); 34 35 // consumes 36 parseConsumes(data, method, methodMapping); 37 38 // headers 39 parseHeaders(data, method, methodMapping); 40 41 data.indexToExpander(new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Param.Expander>()); 42 }
3.处理参数上的注解
这里主要处理@Param、@QueryMap、@HeaderMap
1 protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data, 2 Annotation[] annotations, int paramIndex) { 3 boolean isHttpAnnotation = false; 4 5 AnnotatedParameterProcessor.AnnotatedParameterContext context = new SimpleAnnotatedParameterContext( 6 data, paramIndex); 7 Method method = this.processedMethods.get(data.configKey()); 8 for (Annotation parameterAnnotation : annotations) { 9 AnnotatedParameterProcessor processor = this.annotatedArgumentProcessors 10 .get(parameterAnnotation.annotationType()); 11 if (processor != null) { 12 Annotation processParameterAnnotation; 13 // synthesize, handling @AliasFor, while falling back to parameter name on 14 // missing String #value(): 15 processParameterAnnotation = synthesizeWithMethodParameterNameAsFallbackValue( 16 parameterAnnotation, method, paramIndex); 17 //调用不同策略处理不同的注解 18 isHttpAnnotation |= processor.processArgument(context, 19 processParameterAnnotation, method); 20 } 21 } 22 if (isHttpAnnotation && data.indexToExpander().get(paramIndex) == null 23 && this.conversionService.canConvert( 24 method.getParameterTypes()[paramIndex], String.class)) { 25 data.indexToExpander().put(paramIndex, this.expander); 26 } 27 return isHttpAnnotation; 28 }
这里spring提供了三种参数上的注解解析
- RequestHeaderParameterProcessor:处理@RequestHeader
- PathVariableParameterProcessor:处理@PathVariable
- RequestParamParameterProcessor:处理@RequestParam
代码稍微有点多,但是逻辑很清晰,先处理类上的注解,再处理方法上注解,最后处理方法参数注解,把所有注解的情况都处理到就可以了。
生成的MethodMetadata的结构如下:
1 public final class MethodMetadata implements Serializable { 2 //标识方法的key,接口名加方法签名:GitHub#contributors(String,String) 3 private String configKey; 4 //方法返回值类型 5 private transient Type returnType; 6 //uri参数的位置,方法中可以写个uri参数,发请求时直接使用这个参数 7 private Integer urlIndex; 8 //body参数的位置,只能有一个注解的参数为body,否则报错 9 private Integer bodyIndex; 10 //headerMap参数的位置 11 private Integer headerMapIndex; 12 //@QueryMap注解参数位置 13 private Integer queryMapIndex; 14 //@QueryMap注解里面encode参数,是否已经urlEncode编码过了 15 private boolean queryMapEncoded; 16 //body的类型 17 private transient Type bodyType; 18 //RequestTemplate 19 private RequestTemplate template = new RequestTemplate(); 20 //form请求参数 21 private List<String> formParams = new ArrayList<String>(); 22 //方法参数位置和名称的map 23 private Map<Integer, Collection<String>> indexToName ; 24 //@Param中注解的expander方法,可以指定解析参数类 25 private Map<Integer, Class<? extends Expander>> indexToExpanderClass ; 26 //参数是否被urlEncode编码过了,@Param中encoded方法 27 private Map<Integer, Boolean> indexToEncoded ; 28 //自定义的Expander 29 private transient Map<Integer, Expander> indexToExpander;
调用
ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHanlder 的 invoke 方法
1 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 2 //通过动态代理实现了几个通用方法,比如 equals、toString、hasCode 3 if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) { 4 try { 5 Object 6 otherHandler = 7 args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null; 8 return equals(otherHandler); 9 } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { 10 return false; 11 } 12 } else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) { 13 return hashCode(); 14 } else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) { 15 return toString(); 16 } 17 //找到具体的 method 的 Handler,然后调用 invoke 方法。这样就又进入了SynchronousMethodHandler对象的 invoke 方法。 18 return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args); 19 }
SynchronousMethodHandler 的 invoke 方法主要是应用 encoder,decoder 以及 retry 等配置, 并执行http请求及返回结果的处理
1 public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable { 2 RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv); 3 Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone(); 4 while (true) { 5 try { 6 return executeAndDecode(template); 7 } catch (RetryableException e) { 8 retryer.continueOrPropagate(e); 9 if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) { 10 logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel); 11 } 12 continue; 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 17 Object executeAndDecode(RequestTemplate template) throws Throwable { 18 //通过RequestTemplate生成Request,这里会首先执行RequestInterceptors 19 Request request = targetRequest(template); 20 21 if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) { 22 logger.logRequest(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, request); 23 } 24 25 Response response; 26 long start = System.nanoTime(); 27 try { 28 //通过 client 获得请求的返回值 29 response = client.execute(request, options); 30 // ensure the request is set. TODO: remove in Feign 10 31 response.toBuilder().request(request).build(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) { 34 logger.logIOException(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, e, elapsedTime(start)); 35 } 36 throw errorExecuting(request, e); 37 } 38 long elapsedTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - start); 39 40 boolean shouldClose = true; 41 try { 42 if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) { 43 response = 44 logger.logAndRebufferResponse(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, response, elapsedTime); 45 // ensure the request is set. TODO: remove in Feign 10 46 //将request设置到response中 47 response.toBuilder().request(request).build(); 48 } 49 if (Response.class == metadata.returnType()) { 50 if (response.body() == null) { 51 return response; 52 } 53 if (response.body().length() == null || 54 response.body().length() > MAX_RESPONSE_BUFFER_SIZE) { 55 shouldClose = false; 56 return response; 57 } 58 // Ensure the response body is disconnected 59 byte[] bodyData = Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream()); 60 return response.toBuilder().body(bodyData).build(); 61 } 62 if (response.status() >= 200 && response.status() < 300) { 63 if (void.class == metadata.returnType()) { 64 return null; 65 } else { 66 //解码 67 return decode(response); 68 } 69 } else if (decode404 && response.status() == 404 && void.class != metadata.returnType()) { 70 return decode(response); 71 } else { 72 throw errorDecoder.decode(metadata.configKey(), response); 73 } 74 } 75 //...
Client也有两种,一种直连,一种负载均衡,这里主要分析直连,负载均衡最后也要调用这里。
Client.Default#execute
调用HttpURLConnection进行http请求
1 public Response execute(Request request, Options options) throws IOException { 2 HttpURLConnection connection = convertAndSend(request, options); 3 return convertResponse(connection).toBuilder().request(request).build(); 4 } 5 6 HttpURLConnection convertAndSend(Request request, Options options) throws IOException { 7 final HttpURLConnection 8 connection = 9 (HttpURLConnection) new URL(request.url()).openConnection(); 10 if (connection instanceof HttpsURLConnection) { 11 HttpsURLConnection sslCon = (HttpsURLConnection) connection; 12 if (sslContextFactory != null) { 13 sslCon.setSSLSocketFactory(sslContextFactory); 14 } 15 if (hostnameVerifier != null) { 16 sslCon.setHostnameVerifier(hostnameVerifier); 17 } 18 } 19 connection.setConnectTimeout(options.connectTimeoutMillis()); 20 connection.setReadTimeout(options.readTimeoutMillis()); 21 connection.setAllowUserInteraction(false); 22 connection.setInstanceFollowRedirects(options.isFollowRedirects()); 23 connection.setRequestMethod(request.method()); 24 25 Collection<String> contentEncodingValues = request.headers().get(CONTENT_ENCODING); 26 boolean 27 gzipEncodedRequest = 28 contentEncodingValues != null && contentEncodingValues.contains(ENCODING_GZIP); 29 boolean 30 deflateEncodedRequest = 31 contentEncodingValues != null && contentEncodingValues.contains(ENCODING_DEFLATE); 32 33 boolean hasAcceptHeader = false; 34 Integer contentLength = null; 35 for (String field : request.headers().keySet()) { 36 if (field.equalsIgnoreCase("Accept")) { 37 hasAcceptHeader = true; 38 } 39 for (String value : request.headers().get(field)) { 40 if (field.equals(CONTENT_LENGTH)) { 41 if (!gzipEncodedRequest && !deflateEncodedRequest) { 42 contentLength = Integer.valueOf(value); 43 connection.addRequestProperty(field, value); 44 } 45 } else { 46 connection.addRequestProperty(field, value); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 // Some servers choke on the default accept string. 51 if (!hasAcceptHeader) { 52 connection.addRequestProperty("Accept", "*/*"); 53 } 54 55 if (request.body() != null) { 56 if (contentLength != null) { 57 connection.setFixedLengthStreamingMode(contentLength); 58 } else { 59 connection.setChunkedStreamingMode(8196); 60 } 61 connection.setDoOutput(true); 62 OutputStream out = connection.getOutputStream(); 63 if (gzipEncodedRequest) { 64 out = new GZIPOutputStream(out); 65 } else if (deflateEncodedRequest) { 66 out = new DeflaterOutputStream(out); 67 } 68 try { 69 out.write(request.body()); 70 } finally { 71 try { 72 out.close(); 73 } catch (IOException suppressed) { // NOPMD 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 return connection; 78 } 79 80 Response convertResponse(HttpURLConnection connection) throws IOException { 81 int status = connection.getResponseCode(); 82 String reason = connection.getResponseMessage(); 83 84 if (status < 0) { 85 throw new IOException(format("Invalid status(%s) executing %s %s", status, 86 connection.getRequestMethod(), connection.getURL())); 87 } 88 89 Map<String, Collection<String>> headers = new LinkedHashMap<String, Collection<String>>(); 90 for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> field : connection.getHeaderFields().entrySet()) { 91 // response message 92 if (field.getKey() != null) { 93 headers.put(field.getKey(), field.getValue()); 94 } 95 } 96 97 Integer length = connection.getContentLength(); 98 if (length == -1) { 99 length = null; 100 } 101 InputStream stream; 102 if (status >= 400) { 103 stream = connection.getErrorStream(); 104 } else { 105 stream = connection.getInputStream(); 106 } 107 return Response.builder() 108 .status(status) 109 .reason(reason) 110 .headers(headers) 111 .body(stream, length) 112 .build(); 113 }
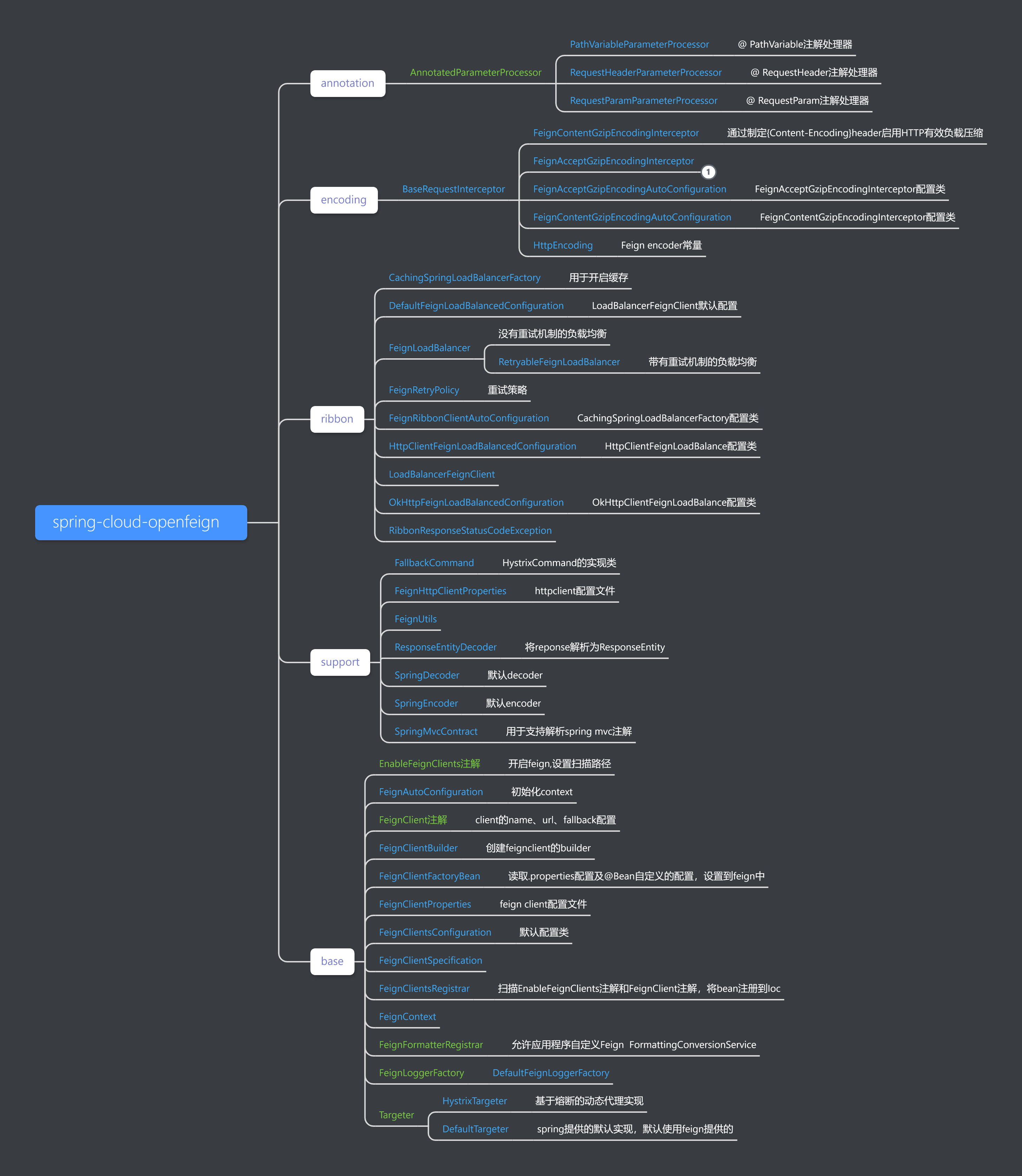
最后放一张读源码时画的脑图。
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_29899265/article/details/86577997