一、 用grep在文件中搜索文本
grep能够接受正则表达式,生成各种格式的输出。除此之外,它还有大量有趣的选项。
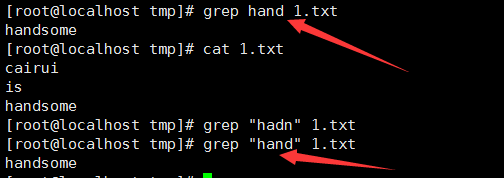
1、 搜索包含特定模式的文本行:
2、 从stdin中读取:

3、 单个grep命令可以对多个文件进行搜索:

4、 --color选项在输出行中着重标记出匹配到的单词:

5、 grep中使用正则表达式时使用(grep -E或者egrep)

6、 只输出文件中匹配到的文本部分,可以使用-o:

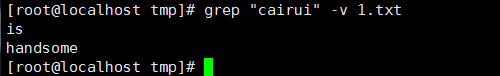
7、 要显示除匹配行外的所有行用-v选项:
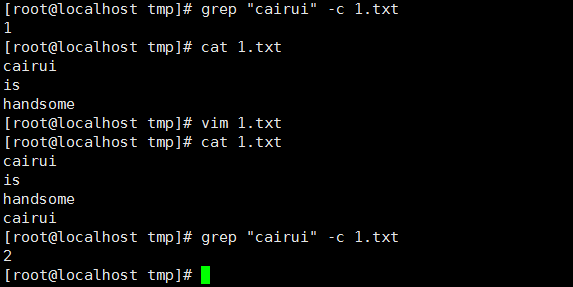
8、 统计文件或文本中包含匹配字符串的行数,-c(在单行出现多个匹配,只匹配一次):
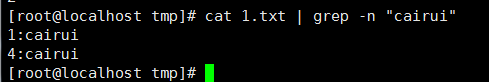
9、 打印出包含匹配字符串的行号,-n:
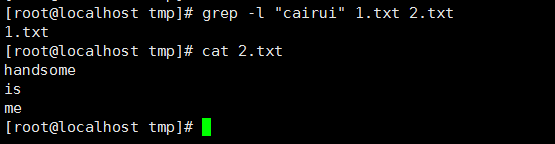
10、 搜索多个文件并找出匹配文本位于哪一个文件,-l(-L与之作用相反):
11、 递归搜素文件,-r(-R与之作用相同):

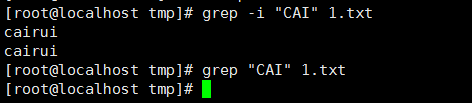
12、 忽略样式中的大小写,-i:
13、 用grep匹配多个样式,-e:

14、 在grep搜索中指定(--include)或排除(--exclude)文件:
目录中递归搜索所有的.c和.cpp文件

在搜索中排除所有的README文件

如果需要排除目录,使用--exclude-dir选项
15、 grep静默输出,-q:
不输出任何内容,如果成功匹配返回0,如果失败返回非0值。
16、 打印出匹配文本之前或之后的行:
[root@localhost tmp]# seq 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [root@localhost tmp]# seq 10 | grep 5 -A 3 #打印匹配的后指定行数 5 6 7 8 [root@localhost tmp]# seq 10 | grep 5 -B 3 #打印匹配前指定行数 2 3 4 5 [root@localhost tmp]# seq 10 | grep 5 -C 3 #打印匹配前后指定行数 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
二、 使用sed进行文本替换
sed是流编辑器(stream editor)的缩写。sed一个用法为文本替换。
[root@cairui ~]# sed --help Usage: sed [OPTION]... {script-only-if-no-other-script} [input-file]... -n, --quiet, --silent suppress automatic printing of pattern space #取消自动打印模式空间 -e script, --expression=script add the script to the commands to be executed #添加“脚本”到程序的运行列表 -f script-file, --file=script-file add the contents of script-file to the commands to be executed #添加“脚本文件”到程序的运行列表 --follow-symlinks follow symlinks when processing in place; hard links will still be broken. -i[SUFFIX], --in-place[=SUFFIX] edit files in place (makes backup if extension supplied). The default operation mode is to break symbolic and hard links. This can be changed with --follow-symlinks and --copy. -c, --copy use copy instead of rename when shuffling files in -i mode. While this will avoid breaking links (symbolic or hard), the resulting editing operation is not atomic. This is rarely the desired mode; --follow-symlinks is usually enough, and it is both faster and more secure. -l N, --line-length=N specify the desired line-wrap length for the `l' command --posix disable all GNU extensions. -r, --regexp-extended use extended regular expressions in the script. -s, --separate consider files as separate rather than as a single continuous long stream. -u, --unbuffered load minimal amounts of data from the input files and flush the output buffers more often --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit If no -e, --expression, -f, or --file option is given, then the first non-option argument is taken as the sed script to interpret. All remaining arguments are names of input files; if no input files are specified, then the standard input is read. GNU sed home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/sed/>. General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>. E-mail bug reports to: <bug-gnu-utils@gnu.org>. Be sure to include the word ``sed'' somewhere in the ``Subject:'' field.
1、 sed可以替换给定文本的字符串:


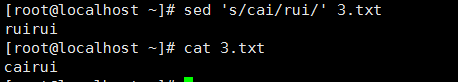
该使用从stdin中读取输入,不影响原本的内容
2、默认情况下sed命令打印替换后的文本,如果想连原文本一起修改加-i命令,-i:
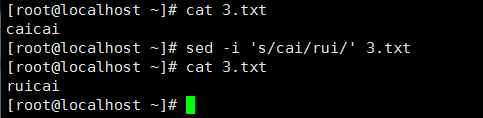
3、 之前的sed都是替换第一个匹配到的内容,想要全部替换就要在末尾加g:
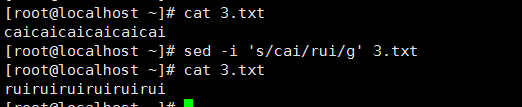
从第N个匹配开始替换
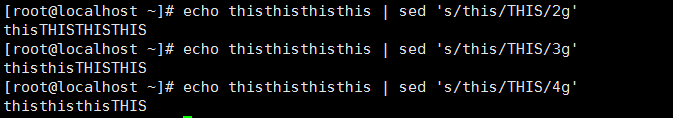
sed中的/为定界符,使用任何其他符号都可以替代

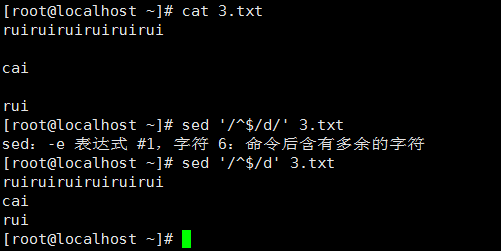
4、 移除空白行
三、 使用awk进行高级文本处理
awk是一款设计用于数据流的工具。它对列和行进行操作。awk有很多内建的功能,比如数组、函数等,和C有很多相同之处。awk最大的优势是灵活性。
[root@cairui ~]# awk --help Usage: awk [POSIX or GNU style options] -f progfile [--] file ... Usage: awk [POSIX or GNU style options] [--] 'program' file ... POSIX options: GNU long options: -f progfile --file=progfile -F fs --field-separator=fs -v var=val --assign=var=val -m[fr] val -O --optimize -W compat --compat -W copyleft --copyleft -W copyright --copyright -W dump-variables[=file] --dump-variables[=file] -W exec=file --exec=file -W gen-po --gen-po -W help --help -W lint[=fatal] --lint[=fatal] -W lint-old --lint-old -W non-decimal-data --non-decimal-data -W profile[=file] --profile[=file] -W posix --posix -W re-interval --re-interval -W source=program-text --source=program-text -W traditional --traditional -W usage --usage -W use-lc-numeric --use-lc-numeric -W version --version To report bugs, see node `Bugs' in `gawk.info', which is section `Reporting Problems and Bugs' in the printed version. gawk is a pattern scanning and processing language. By default it reads standard input and writes standard output. Examples: gawk '{ sum += $1 }; END { print sum }' file gawk -F: '{ print $1 }' /etc/passwd
awk脚本的结构基本如下所示:
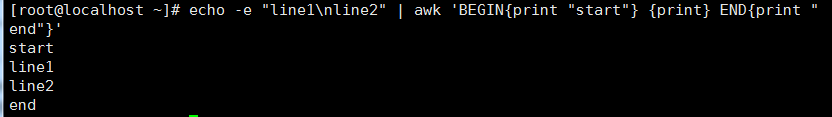
awk ' BEGIN{ print "start" } pattern { commands } END { print "end" }' file
awk脚本通常由3部分组成。BEGIN,END和带模式匹配选项的常见语句块。这3个部分都是可选的。
1、工作原理
(1)执行BEGIN { commands }语句块中的语句。
(2)从文件或stdin中读取一行,然后执行pattern { commands }。重复这个过程,直到文件全部被读取完毕。
(3)当读至输入流末尾时,执行END { commands }语句块。
其中最重要的部分就是pattern语句块中的通用命令。这个语句块同样是可选的。如果不提供该语句块,则默认执行{ print },即打印所读取到的每一行。awk对于每一行,都会执行这个语句块。这就像一个用来读取行的while循环,在循环中提供了相应的语句。