ThreadLocal是什么呢?其实ThreadLocal并非是一个线程的本地实现版本,它并不是一个Thread,而是threadlocalvariable(线程局部变量)。也许把它命名为ThreadLocalVar更加合适。线程局部变量(ThreadLocal)其实的功用非常简单,就是为每一个使用该变量的线程都提供一个变量值的副本,是Java中一种较为特殊的线程绑定机制,是每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会和其它线程的副本冲突。是能够解决多线程的实例变量的问题。
API是这样介绍的:
* This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from * their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its * {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized * copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private * static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., * a user ID or Transaction ID).
该类提供了线程局部 (thread-local) 变量。这些变量不同于它们的普通对应物,因为访问某个变量(通过其 get 或 set 方法)的每个线程都有自己的局部变量,它独立于变量的初始化副本。 ThreadLocal实例通常是类中的 private static 字段,它们希望将状态与某一个线程(例如,用户 ID 或事务 ID)相关联。
所以ThreadLocal与线程同步机制不同,线程同步机制是多个线程共享同一个变量,而ThreadLocal是为每一个线程创建一个单独的变量副本,故而每个线程都可以独立地改变自己所拥有的变量副本,而不会影响其他线程所对应的副本。可以说ThreadLocal为多线程环境下变量问题提供了另外一种解决思路。
ThreadLocal定义了四个方法:
get():返回此线程局部变量的当前线程副本中的值。
initialValue():返回此线程局部变量的初始值。
remove():移除此线程局部变量当前线程的值。
set(T value):将此线程局部变量的当前线程副本中的值设置为指定的值。
除了这四个方法,ThreadLocal内部还有一个静态内部类ThreadLocalMap,该内部类才是实现该线程隔离机制的关键,get(),set(),remove() 都是基于该内部类操作。ThreadLocalMap提供了一种用键值对存储方式存储每个线程的变量副本,key为当前ThreadLocal对象,value则是对应线程的变量副本。
对于ThreadLocal需要注意的有两点:
1.ThreadLocal实例本身是不存储值,它只是提供了一个在当前线程中找到副本值的一个key。
2.是ThreadLocal包含在Thread中,而不是Thread包含在ThreadLocal中,不要弄错它们之间的关系。
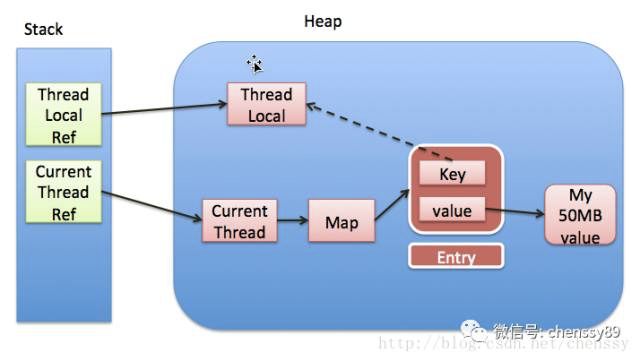
ThreadLocalMap的内部实现,ThreadLocalMap其内部利用Entry来实现key-value的存储,如下:
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } }
从上面代码中可以看出Entry的key就是ThreadLocal,而value就是值。同时,Entry也继承WeakReference,所以说Entry
所对应的key(ThrealLocal实例)的引用为一个弱引用(关于弱引用这里就多说了)。
下面开始分析具体代码:
看一下set 方法的源码:
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//根据当前线程 得到 ThreadLocapMap实例
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
//当前的ThreadLocal实例为键,当前value为值进行赋值
map.set(this, value);
else
//如果map=null,新建一个ThreadLocalMap实例,其实就是绑定当前的线程 threadLocals 赋值,然后可以通过thread获取ThreadLocalMap
//同时/当前的ThreadLocal实例为键,当前value为值进行赋值
createMap(t, value);
}
getMap方法:
/** * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @return the map */ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { //根据当前线程获取ThreadLocalMap 实例 return t.threadLocals; }
ThreadLocalMap.set()方法:
/**
* Set the value associated with key.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @param value the value to be set
*/
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
//通过 hash表来维护这种数据
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//通过hash值,和数组长度&计算,定位出该key在hash表中的位置,threadLocal的hash值是计算好的,直接引用,不必重新计算得到
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//该键存在 就覆盖该值 并结束当前循环
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
//该键null,覆盖替换掉陈腐的值 结束掉当前循环
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
//如果值没找到,就继续循环查找,因为这里采用的是开放地址法来解决hash冲突,所以通过hash值没有定位到指定的实例很正常.(不了解开放地址法,可以自行google)
}
//如果该键不存在hash表中,就重新实例化一个,存入hash表中
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
//实例的值大于阀值,重新进行hash
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
get() 方法的实现:
/** * Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this * thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the * current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned * by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method. * * @return the current thread's value of this thread-local */ public T get() { //获得当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //通过当前线程取出其中的局部变量ThreadLocalMap,其实就是实例变量 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { //当前t threadLocal作为key 取出Entry实例 ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } //如果当前线程没有设置值,返回初始值 return setInitialValue(); }
getEntry()解析:
/**
* Get the entry associated with key. This method
* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing
* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is
* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part
* by making this method readily inlinable.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//通过hash值和数组长度求余(通过位运算实现相同的效果,当然数组的大小必须为2的次方),定位到数组
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
//通过下表获取相应实例
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//因为采用的是开放地址法,通过hash值,不一定能够获得相应的Entrt实例
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
getEntryAfterMiss() 方法解析:
/**
* Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in
* its direct hash slot.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @param i the table index for key's hash code
* @param e the entry at table[i]
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//e!=null 其实就是证明该hash值必须存在,只有存在才能发生冲突,才会选择一个空的值重新填入
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
//肯定选择依次最近的值,如果当前值为空结束循环,因为开放地址也是按顺序选择第一个为空的值,填入,如果有空值,结束当前循环
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
remove()方法解析:
/** * Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local * variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently * {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be * reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method, * unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread * in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the * {@code initialValue} method in the current thread. * * @since 1.5 */ public void remove() { //根据线程获取ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); if (m != null) //用当前threadLocal 作为键,移除该项 m.remove(this); }
remove() 方法
/**
* Remove the entry for key.
*/
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
//删除该对象不会进入队列(弱引用被垃圾回收会进入临时队列)
e.clear();
//清空当前对象
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}