一、字符串类型
判断字符串是否相等
String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = new String("abc"); String s3 = "abc"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); System.out.println(s1 == s3); System.out.println(s2 == s3);
内存布局:
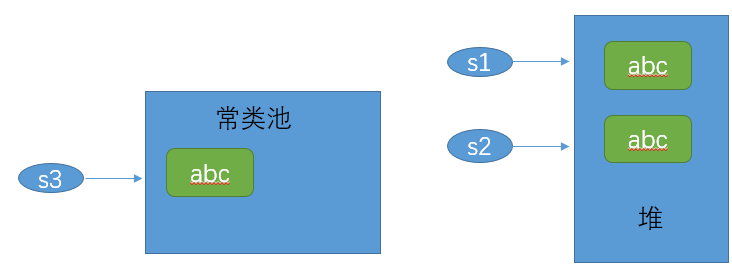
因此,三个字符结果都是 false
String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = new String("abc"); String s3 = "abc"; String b = "ab"; String s4 = "ab"+"c"; String s5 = b+"c"; System.out.println(s1 == s4 ); System.out.println(s2 == s4); System.out.println(s3 == s4); System.out.println(s5 == s4);
此处只有 S3 与 S4 返回 true ,均在编译时就确定的常类。注意 S5 与 S4 并不相等,b 为变量,与“c” 通过StringBuilder拼接实现,最后调用toString 返回一个新的 String 对象
二、Integer/int 类型
该类型特殊的地方是,当数字范围在 -128 ~ 127 ,值都是从缓存中获取,地址相等,当值大于改范围,Integer 就会在堆上创建对象
三、浮点型比较
浮点类型不适合用等值比较,而因该是用插值比较,给定一定的误差范围
四、0被除的情况
整数除法中,0作为被除数,将抛出算术异常 ArithmeticException
// int i = 10/0; ArithmeticException // byte i = (byte)(10/0); ArithmeticException ,如果不强制转换,则编译不通过 // short i = (short)(10/0); ArithmeticException ,如果不转换,编译无法通过 // long i = 10/0; ArithmeticException
浮点数比较特殊
//float f = 10/0; ArithmeticException // float f = 10/0.0f; 如果不加 f ,则为double 类型,无法通过校验。 可以整除,值为 Infinity // double d = 10/0; ArithmeticException //double d = 10/0.0; Infinity //double d = 10.0/0; Infinity // double d = 0.0/0.0; 此时 d 的值为 NaN // double d = 10.0/0.0; Infinity // double d = 0/0.0; NaN // float f = 0/0f; nan // double d = 0/0; ArithmeticException
分析:
1.float f = 10/0 或者double 都会抛出异常,是因为10/0 都是整数运算,将结果赋值给浮点数,还算整数运算
2.浮点数定义了无穷值 Infinity 与非数字的值 NaN
3.当除数与被除数都是0,则会产生 NaN ,非数字值
4.当只有被除数是0,则会产生无穷大的值 Infinity
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/4679618fd28c