顺序访问文件
一个文件是由一个字节序列构成的。操作系统维护一个叫做文件指针(file pointer)的特殊标记,指向序列中的某个位置。读写操作都是在文件指针指向的位置进行。当文件打开时,文件指针被设置在文件开始位置。当读写数据时,文件指针会移动到下一个数据项。例如,如果使用get()函数读取一个字节,C++从文件指针指向的位置读出一个字节,文件指针会向前移动一个字节,如下图所示:
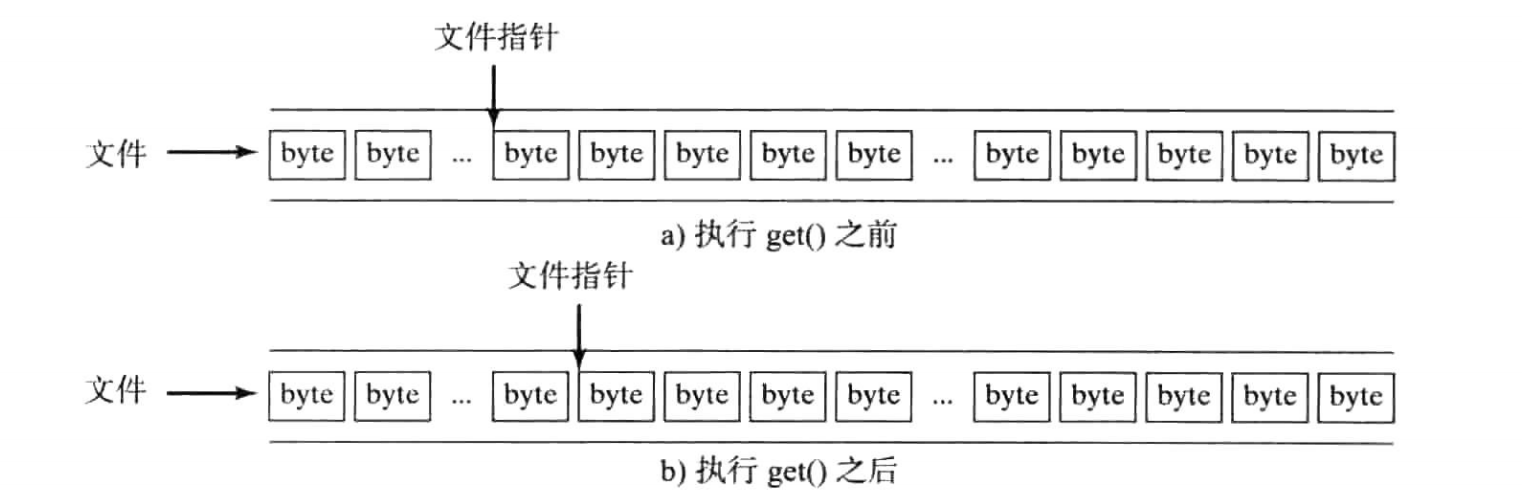
(注:前是向文件结尾的方向,而后是向文件开始的方向)
我们之前写过的程序都是顺读写数据的,即文件指针一直向前移动,这被称为顺序访问文件。如果一个文件以输入的方式打开,将从其文件开始位置向文件结尾读取数据。如果一个文件以输出方式打开,则从其开始位置(默认)或末尾位置(ios::app)开始一个接一个地写入数据项。
随机访问文件
顺序访问的问题在于,如果我们想要读取一个特定位置的字节,那么必须读取它前面所有的字节,这样做效率太低了。所以C++引入了随机访问文件的概念,也就是说可以任意地向前或向后移动文件指针,而使用的函数是seekp和seekg函数。
seekp,即seek put,用于输出流。
seekg,即seek get,用于输入流。
seekp和seekg都有两个版本,分别是有一个参数的和有两个参数的。
一个参数的:参数指出绝对位置,例如:
input.seekg(0); output.seekp(0);
以上两句代码都将文件指针移动到了文件开始的位置。
两个参数的:第一个参数是长整数,指出偏移量,正数为向前,负数为向后;第二个参数被称为定位基址(seek base),指出偏移量是相对于哪个位置而偏移的。下表给出了三个支持的定位基址参数。
| 定位基址 | 描述 |
| ios::beg | 偏移量相对于文件开始位置 |
| ios::end | 偏移量相当于文件结尾位置 |
| ios::cur | 偏移量相当于文件指针当前位置 |
下表给出一些使用seekp和seekg函数的例子。
| 语句 | 描述 |
| seekg(100, ios::beg); | 将文件指针移动到从文件开始第100个字节处 |
| seekg(-100, ios::end); | 将文件指针移动到文件末尾向后100个字节处 |
| seekp(42, ios::cur); | 将文件指针从当前位置向前移动42个字节 |
| seekp(-42, ios::cur); | 将文件指针从当前位置向后移动42个字节 |
| seekp(100); | 将文件指针移动到文件第100个字节处 |
我们可以使用tellp和tellg函数返回文件指针的当前位置。
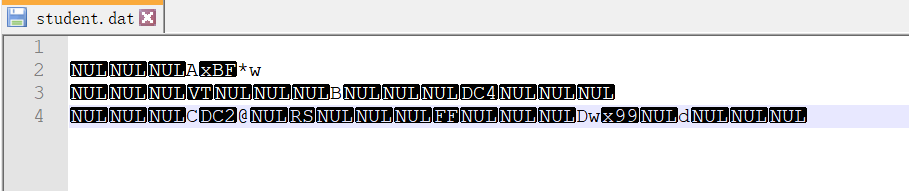
下面给出一个例子。这个例子先将4个Student对象写入到student.dat文件中。然后从student.dat文件中读取第三个同学的信息(一个Student对象占据的空间是12,int=4,char=1,但是char占4):
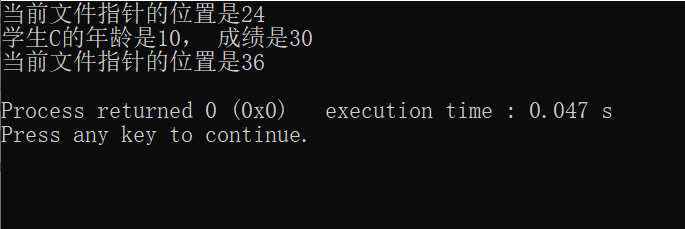
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> using namespace std; class Student { public: Student(){} Student(char name, int age, int score){ this->age = age; this->name = name; this->score = score; } int getAge() const{ return this->age; } char getName() const{ return this->name; } int getScore() const{ return this->score; } private: int age; char name; int score; }; void displayStudent(const Student student){ cout << "学生" << student.getName() << "的年龄是" << student.getAge() << ", 成绩是" << student.getScore() << endl; } int main() { fstream binaryio; binaryio.open("student.dat", ios::out|ios::binary); Student student1('A', 10, 10); Student student2('B', 11, 20); Student student3('C', 10, 30); Student student4('D', 12, 100); binaryio.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&student1),sizeof(Student)); binaryio.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&student2),sizeof(Student)); binaryio.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&student3),sizeof(Student)); binaryio.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&student4),sizeof(Student)); binaryio.close(); binaryio.open("student.dat", ios::in|ios::binary); Student studentNew; binaryio.seekg(2*sizeof(Student)); cout << "当前文件指针的位置是" << binaryio.tellg() << endl; binaryio.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&studentNew),sizeof(Student)); displayStudent(studentNew); cout << "当前文件指针的位置是" << binaryio.tellg() << endl; binaryio.close(); return 0; }
运行结果:
student.dat文件: