网站:https://www.jianshu.com/p/52dc85668d00
也算记录自己的学习篇=。= 适合入门看 这里简单介绍下MethodInfo和他基本的几个方法
简介
MethodInfo就是通过反射指定类获取到的 属性并提供对方法函数数据的访问。
1.如何获取?
Type.GetMethod(String) 获取该类的指定的名字String公开的函数方法 如果私有会为空
Type.GetMethod(String,BindingFlags) 获取该类的指定的名字String,和指定类型BindingFlags的函数方法
Type.GetMethods() 获取该类的所有公开的函数方法
Type.GetMethods(BindingFlags) 获取该类的所有指定类型BindingFlags的函数方法
例子
先定义个类型
public class Method
{
public int A;
public string B;
public void M(string data)
{
Console.WriteLine(data);
}
public void M1()
{
Console.WriteLine("M1");
}
private void M2()
{
Console.WriteLine("M2");
}
}
Type.GetMethod(String) 获取该类的指定的名字String公开的函数方法 如果私有会为空
typeof(Method).GetMethod("M1").Invoke(method,null);
typeof(Method).GetMethod("M").Invoke(method, new string[] { "凉_开果"});
Console.ReadKey();
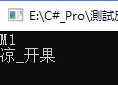
image.png
可以看出来invoke就是启动函数的 第一个是触发的类,第二个是要代入的参数
Type.GetMethod(String,BindingFlags) 获取该类的指定的名字String,和指定类型BindingFlags的函数方法
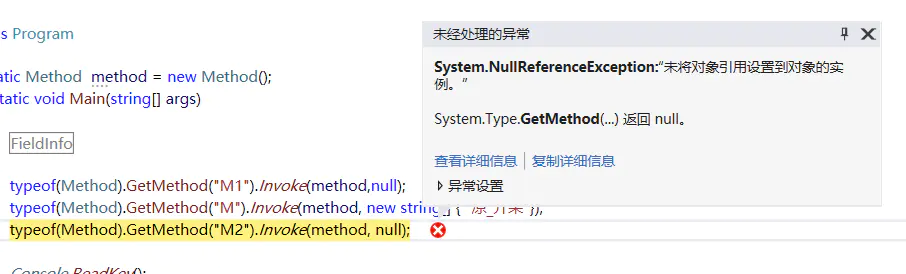
image.png
可以看出来如果不指定BindingFlags是搜索不到了
看看加上之后的
typeof(Method).GetMethod("M1").Invoke(method,null);
typeof(Method).GetMethod("M").Invoke(method, new string[] { "凉_开果"});
typeof(Method).GetMethod("M2",BindingFlags.Instance|BindingFlags.NonPublic).Invoke(method, null);//BindingFlags.Instance(对象) 和 BindingFlags.Static(静态) 必须有一个,
Console.ReadKey();

image.png
Type.GetMethods() 获取该类的所有公开的函数方法
Type.GetMethods(BindingFlags) 获取该类的所有指定类型BindingFlags的函数方法
MethodInfo[] Methods1= typeof(Method).GetMethods();
MethodInfo[] Methods2 = typeof(Method).GetMethods(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
foreach (var item in Methods1)
{
Console.WriteLine("不加BindingFlags" + item.Name);
}
foreach (var item in Methods2)
{
Console.WriteLine("加BindingFlags" + item.Name);
}
Console.ReadKey();

image.png
2.属性
这里就列几个基础的=。=完全的可以自己 去看c#的API
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ReturnType | 获取这个函数方法返回的类型 |
| MemberType | 返回一个MemberTypes枚举表示 他是个方法。 |
| DeclaringType | 获取是谁声明该模块成员的类的Type |
| 还有一堆is开头的bool属性 | 都是字面意思 就是判断是否含有 |
3.方法 =。=我就写下基础的几个
-
接着上面声明的类就好
-
运行函数Invoke(object obj, object[] parameters);
- 上面已经用过了
-
typeof(Method).GetMethod("M1").Invoke(method,null); typeof(Method).GetMethod("M").Invoke(method, new string[] { "凉_开果"}); -
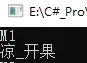 image.png
image.png - 可以看出来invoke就是启动函数的 第一个是触发的类,第二个是要代入的参数
-
转成委托 Delegate CreateDelegate(Type delegateType, object target);
-
和Delegate的CreateDelegate一样的就是少写了个指定MethodInfo 大概用途是 注册事件时候,需要反射出函数的委托进行注册,
-
static event Action A1; static event Action<string> A2; static void Main(string[] args) { Method Instance = Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(Method)) as Method; A1?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("没注册之前"); A1+= Instance.GetType().GetMethod("M1").CreateDelegate(typeof(Action), Instance) as Action; A1?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("注册之后"); Console.ReadKey(); } -
结果
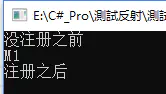 image.png
image.png- 可以看出 事件注册之前没东西的通过转化成的委托进行注册 就有了 第二个赋值的是包含这个函数的实例化对象
-
-
找到拥有该函数初始父类 MethodInfo GetBaseDefinition();
- 当在派生类中被重写时,为直接或间接的基类上的方法返回MethodInfo 就是找到他的 谁创建的这个函数
-
先声明代码
-
public class BaseMethod { public virtual void M3() { } } public class Method: BaseMethod { public int A; public string B; public void M( string data) { Console.WriteLine(data); } public void M1() { Console.WriteLine("M1"); } private void M2(int data) { Console.WriteLine("M2"); } public override void M3() { base.M3(); } }
-
-
例子
-
Console.WriteLine(typeof(Method).GetMethod("M3").ReflectedType.Name); Console.WriteLine("创建他的父类"+typeof(Method).GetMethod("M3").GetBaseDefinition().ReflectedType.Name); Console.WriteLine(typeof(Method).GetMethod("ToString").ReflectedType.Name); Console.WriteLine("创建他的父类" + typeof(Method).GetMethod("ToString").GetBaseDefinition().ReflectedType.Name); Console.ReadKey(); -
结果
 image.png
image.png
-
作者:懒_开果
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/52dc85668d00
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。