说过ReentrantLock的大概操作之后,再来看一下它的源码。
首先说一下几个概念
JUC:java.util.concurrent 包的缩写,计算机方面有时候真的很莫名其妙,总给你弄很多看起来高大上的缩写。
AQS:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的缩写,翻译过来就是抽象队列同步器,是ReentrantLock的基础。

AQS里面有一个int类型的state,state用volatile修饰来达到它的可见性,用来表示资源的状态,Node类型的head,tail维护一个双向的线程等待队列。
接下来开始看ReentrantLock,
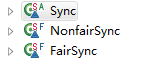
可以看到ReentrantLock有三个内部类,它们的继承关系是,Sync继承刚才所说的AQS,其他两个,一个公平锁,一个非公平锁都继承与Sync。
private final Sync sync;
ReentrantLock的操作,基本就是对sync的操作,通过多态的方式使用公平锁或者非公平锁。
public ReentrantLock() { sync = new NonfairSync(); } public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) { sync = (fair)? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync(); }
ReentrantLock有两个构造函数,默认构造非公平锁。
接下来看它的最常用方法,lock,unlock。
public void lock() { sync.lock(); }
调用sync的lock,这里我们看非公平锁的。
final void lock() { if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1); }
先用AQS里的方法compareAndSetState判断现在的状态,如果现在状态为0,线程直接进入锁,状态改为1。具体实现依赖于Java的unsafe类。
状态为0当然是最理想的状态,这里假设已经有线程占用了,进入else,
进入acquire,acquire是AQS里面的方法
public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }
回到不公平锁里的tryAcquire()方法:
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); }
继续进入nonfairTryAcquire,这个方法在sync里面,
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; }
兴许在错过第一次compareAndSetState之后,资源被重新释放,状态归零,所以再判断一次,判断失败进入else if,如果现在占用资源的线程就是现在想要操作的线程,也能获取成功,状态每次加一,线程重入了,所以重入锁叫重入锁。
如果返回true的话,在 if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&这里因为是短路与,方法直接结束,继续假设是其他线程在进行操作,返回false,进入 acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))。
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; }
如果在方法中,队列没有更改,线程插到队尾,如果有其他线程也在同样操作导致队列更改,进入enq()方法,总之就是把线程放进队列的合适位置,返回node,继续看acquireQueued,
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } catch (RuntimeException ex) { cancelAcquire(node); throw ex; } }
这里有些不懂,经过查询大概归纳它的意思是,轮流检查状态看能不能获取资源,获取不了就park()阻塞,等待唤醒继续检查。然后循环。
大概流程如下:

图片转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/waterystone/p/4920797.html
lock完之后看unlock:
public void unlock() { sync.release(1); }
进入ASQ的release
public final boolean release(int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h); return true; } return false; }
回到sync的tryRelease
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); boolean free = false; if (c == 0) { free = true; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); } setState(c); return free; }
因为可以重入,也要释放重入次数才能使状态重新归零。
当资源彻底被释放之后,ASQ的release里面unparkSuccessor(h),使阻塞的线程停止阻塞状态。
自此,告一段落。