本人文笔较差,语文从来不及格,基础不好,写此类文章仅供自己学习,理解队列及其他知识,高手大神请略过。参考书籍 《数据结构与算法分析-Java语言描述》
1.1 单链表简介
线性表的最大的缺点就是插入和删除操作需要移动大量的元素,这是它在内存中的连续存储结构造成的。为了弥补这2个缺点,就出现了链表,即线性表的链式存储。
链表是由一系列的节点组成,这些节点不必在内存中相连。这就意味着元素可以存在内存未被占用的任意位置。如图
这个存储可以想象成元素在内存中成三维空间存储,他们之间可没有像数组那样的下标标记。他们之间的联系是靠图中的箭头。与顺序存储结构不同的是,链表的
每一个节点不仅仅保存着元素本身,还包含另一块区域,而这块区域保存着它的直接后即元素节点的链儿,也叫next链儿(next引用,其实就是节点的引用变量),
顶头的节点存储的不是元素,是一个只有指向第一个元素节点的链儿(头指针),最后一个节点的next链儿是引用null。(C语言中貌似叫指针,原谅我这个没学过C语言的土鳖)。

所以单链表的存储是从头指针开始的,之后的每一个节点都是上一个next链儿指向的位置。这种方式的存储使得要获取某一个节点变得困难。如要获取单链表
a1,a2,...ai...,an的元素ai,必须得先获取ai-1,因为只有ai-1存储了指向ai的next链儿。同样获取ai-1必须先获取ai-2
若从头指针开始,获取第一个元素耗时将是O(1)(与线性表类似,假设获取某一个元素时间是t[t是固定不变的常数]),最费时的情况将是获取最后一个元素。
O(N),则整个链表的获取元素的平均耗时就是O(N)/2,时间复杂度即O(N)。
看起来确实不如顺序存储。但在这个二元对立的世界,任何行为都是具有两面性的。对于单链表的插入,若将节点 P 插入上图的节点a3的位置,只需要将a2的
next链儿指向节点P(若P不是空节点),P的next链儿指向a3就完事儿了。其它元素节点不需要任何移动。如图
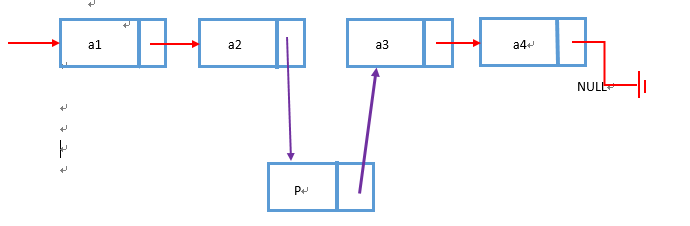
对于删除节点a3也是同一个道理,只需要将节点a2的next链儿指向a4,然后移除a3就可以了。单纯就插入和删除的操作来说,时间复杂度是O(1)。可是这真的
就节省时间了么?仔细看,插入和删除都是由两部分组成的:第一部分是遍历获取元素,第二部分才是插入或删除的操作。整体来说时间复杂度还是O(N),这
看起来与顺序存储确实没有太大的优势。但如果插入或删除元素较多,如从ai元素位置插入10个,100个,甚至上10000(当然表的最大存储空间要足够大),或者
更多个元素,对于顺序存储每一次插入(删除)都要移动n-i个节点元素,也就是每一次时间复杂度都是O(N),但对于单链表而言只是简单的赋值和next链的移动,
时间复杂度都是O(1)。
总结:插入或删除节点元素操作频繁的,单链表的效率要高于顺序存储的线性表。
1.2 单链表的Java简单实现
1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 import java.util.List; 4 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 5 6 /** 7 * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. 8 * CreateUser: blentle 9 * Email: renhuan@milipp.com 10 * CreateTime: 2014/11/6 23:20 11 * ModifyUser: blentle 12 * ModifyTime: 2014/11/6 23:20 13 * Class Description: 14 * To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. 15 */ 16 public class SingleLinkedList<T> { 17 //链表的存储大小 18 private int size; 19 //链表的头结点 20 private Node<T> firstNode; 21 //链表的最后一个元素,里面的nextChain指向引用null 22 private Node<T> lastNode; 23 24 public SingleLinkedList() { 25 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * 不指定位置,插入到最后一个元素的后面 30 * @param t 31 * @return 32 */ 33 public boolean add(T t) { 34 //存储插入前最后一个元素,便于后面修改next链儿 35 Node<T> node = this.lastNode; 36 Node<T> newNode = new Node(t,null); 37 //修改最后一个元素的值 38 this.lastNode = newNode; 39 if(node == null) { 40 //原来是空表,头指针也是最后一个节点 41 this.firstNode = this.lastNode; 42 } else { 43 //将插入之前最后一个节点的next链儿指向新的节点元素 44 node.nextChain = newNode; 45 } 46 //增加链表的长度 47 size++; 48 return true; 49 } 50 51 /** 52 * 指定位置,插入到指定位置 53 * @param index 54 * @param t 55 * @return 56 */ 57 public boolean add(int index,T t) { 58 if(index == this.size) { 59 //若指定位置刚好在最后一个元素(从0开始)后面 60 add(t); 61 } else { 62 Node<T> node = get(index); 63 //插入的新元素节点next链儿指向原来位置的元素节点 64 Node newNode = new Node(t, node); 65 //新元素节点前驱元素的next链儿指向新元素 66 if(index > 0) { 67 //插入的不是第一个节点 68 Node<T> prevousNode = get(index - 1) ; 69 prevousNode.nextChain = newNode; 70 } else { 71 //插入到第一个节点 72 firstNode = newNode; 73 } 74 75 } 76 size++; 77 return true; 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * 这个方法才能体现出单链表的优势 82 * todo:待优化 83 * @param index 84 * @param collection 85 * @return 86 */ 87 public boolean addAll(int index,Collection<? extends T> collection) { 88 //检查序号越界 89 if(index < 0 || index > size) { 90 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("single linked list size is :" + size + ",but index is:" + index); 91 } 92 int insertSize = collection.size(); 93 if(index == size) { 94 //序号和表的长度相同,即插入到最后一个元素后面,保存插入前的最后一个元素节点,用于后面移动next链儿 95 Node<T> previosNode = this.lastNode; 96 for(T oneTarget: collection) { 97 Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(oneTarget,null); 98 if(previosNode == null) { 99 //插入的是空表 100 firstNode = newNode; 101 } else { 102 previosNode.nextChain = newNode; 103 } 104 //插入下一个元素时的,previousNode就变成了当前插入的元素 105 previosNode = newNode; 106 } 107 } else { 108 //插入到其他位置 109 Node<T> indexNodeBeforeInsert = get(index); 110 Node<T> previosNode = null; 111 if(index > 0) { 112 previosNode = get(index-1); 113 } 114 for(T oneTarget: collection) { 115 Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(oneTarget,null); 116 if(previosNode == null) { 117 //插入的是空表 118 firstNode = newNode; 119 } else { 120 previosNode.nextChain = newNode; 121 } 122 //插入下一个元素时的,previousNode就变成了当前插入的元素 123 previosNode = newNode; 124 previosNode.nextChain = indexNodeBeforeInsert; 125 } 126 127 } 128 size += insertSize; 129 return true; 130 } 131 132 /** 133 * 删除指定位置的元素 134 * @param index 135 * @return 136 */ 137 public boolean remove(int index) { 138 if(size == 0) { 139 return false; 140 } 141 //检查标号越界 142 if(index < 0 || index >= size ) { 143 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("single linked list size is :" + size + ",but index is:" + index); 144 } 145 Node<T> target = get(index); 146 Node<T> nextNode = target.nextChain; 147 Node<T> previousNode = null; 148 if(index > 0) { 149 previousNode = get(index - 1); 150 previousNode.nextChain = nextNode; 151 } else { 152 firstNode = nextNode; 153 } 154 if(nextNode == null) { 155 //删除的是最后一个元素,改变表尾元素节点 156 lastNode = previousNode; 157 } else { 158 //删除后自身的next链儿引用null 159 target.nextChain = null; 160 } 161 target.item = null; 162 size--; 163 return true; 164 } 165 166 /** 167 * 清理链表 168 */ 169 public void clear() { 170 if(size > 0) { 171 //第一个节点开始遍历,依次引用null 172 Node<T> node = firstNode; 173 while(node != null) { 174 Node<T> next = node.nextChain; 175 node.nextChain = null; 176 node.item = null; 177 node = next; 178 } 179 firstNode = lastNode = null; 180 size = 0; 181 } 182 } 183 184 /** 185 * 获取链表的元素长度 186 * @return 187 */ 188 public int size() { 189 return this.size; 190 } 191 192 /** 193 * 根据标号获取元素节点,从第头指针(第一个next链儿指向第一个节点元素)开始遍历, 194 * 每遍历一个元素正在活跃的next链儿向后移动一位 195 * @param index 196 * @return 197 */ 198 private Node<T> get(int index) { 199 //这里next链是可以移动到最后一个元素size-1的 200 if(index < size && index >= 0) { 201 //从第一个节点开始遍历 202 Node<T> current = this.firstNode; 203 for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i++) { 204 current = current.nextChain; 205 } 206 return current; 207 } 208 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 209 } 210 211 /** 212 * 链表中的每一个节点元素【参考LinkedList源码】 213 * @param <T> 214 */ 215 private static class Node<T> { 216 //节点元素 217 private T item; 218 //next链儿(下一节点的引用变量) 219 private Node<T> nextChain; 220 221 Node(T item, Node<T> nextChain) { 222 this.item = item; 223 this.nextChain = nextChain; 224 } 225 } 226 227 }