数据
2019-6-1 39 2019-5-21 33 2019-6-1 38 2019-6-2 31 2018-3-11 18 2018-4-23 22 1970-8-23 23 1970-8-8 32
方法一:
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("over") setMaster ("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val line = sc.textFile("data/date.txt") // 1970-8-8 32 val tuple2 = line.map(x => { val lines = x.split(" ") val dates = lines(0).split("-") ((dates(0).toInt, dates(1).toInt), (dates(2).toInt, lines(1).toInt)) }) //(1970 8) ,(8 32) val res = tuple2.groupByKey().mapValues(arr => { val hashMap = new mutable.HashMap[Int, Int]() arr.foreach(x => { if (hashMap.get(x._1).getOrElse(0) < x._2) hashMap.put(x._1, x._2) }) // hashMap去重 hashMap.toList.sorted(new Ordering[(Int, Int)] { override def compare(x: (Int, Int), y: (Int, Int)): Int = y._2.compareTo(x._2) }) // hashMap根据温度排序 }) res.foreach(println) 结果: ((2018,3),List((11,18))) ((2019,5),List((21,33))) ((2018,4),List((23,22))) ((1970,8),List((8,32), (23,23))) ((2019,6),List((1,39), (2,31)))
stage:
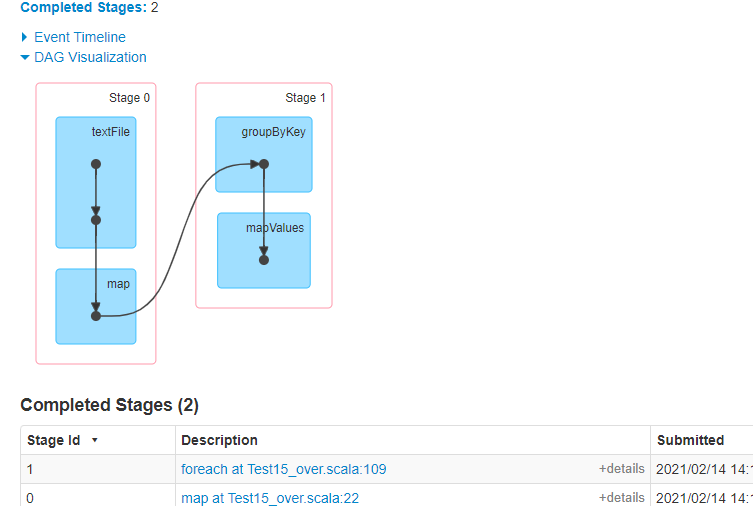
问题:
1.HashMap有内存溢出问题,可能会发生OOM
2.groupByKey也有内存溢出问题(因为可能一开始数据量大,可以先把数据过滤出来,在进行分组)
方法二
implicit val dsfgsdfg = new Ordering[(Int, Int)] { override def compare(x: (Int, Int), y: (Int, Int)): Int = y._2.compareTo(x._2) } val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("over") setMaster ("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val line = sc.textFile("data/date.txt") // 1970-8-8 32 val tuple2 = line.map(x => { val lines = x.split(" ") val dates = lines(0).split("-") ((dates(0).toInt, dates(1).toInt, dates(2).toInt), lines(1).toInt) }) // ((1970 8 8), 32) 先去重(去掉同一天的数据,取一天中最大的值) val distinct_tuple2 = tuple2.reduceByKey((x, y) => if(y > x) y else x) // ((1970 8 8), 32) val kv = distinct_tuple2.map(t2 => ((t2._1._1, t2._1._2),(t2._1._3, t2._2))) // ((1970 8) (8, 32)) val groupDate = kv.groupByKey() groupDate.mapValues(arr=> arr.toList.sorted.take(2)).foreach(println)
结果:
((2018,3),List((11,18)))
((2019,5),List((21,33)))
((2018,4),List((23,22)))
((1970,8),List((8,32), (23,23)))
((2019,6),List((1,39), (2,31)))
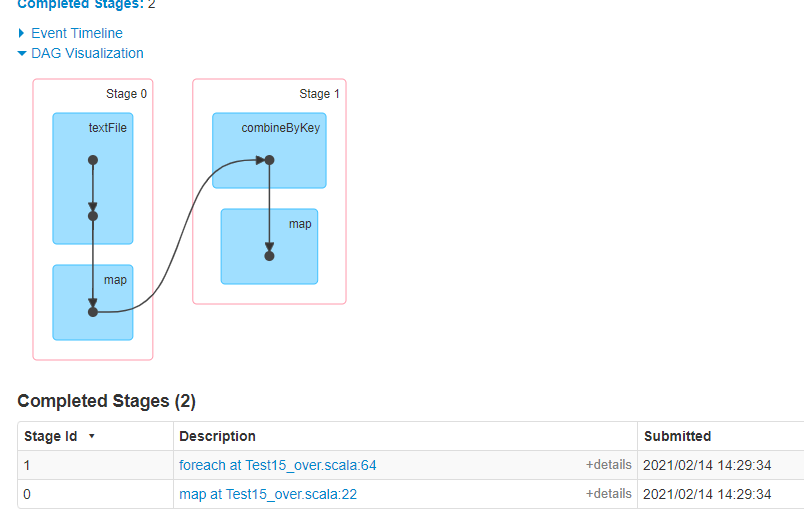
stage:

问题:
1.多次shuffle
有没有一种方式既不存在内存溢出风险、又不多次shuffle
方式三: combineByKey: 源码中的combineByKey只是在这里将数据value不断地堆积,没有做任何处理,所以我们需要在这里进行处理,压缩(过滤数据)
implicit val dsfgsdfg = new Ordering[(Int, Int)] { override def compare(x: (Int, Int), y: (Int, Int)): Int = y._2.compareTo(x._2) } val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("over") setMaster ("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val line = sc.textFile("data/date.txt") // 1970-8-8 32 val tuple2 = line.map(x => { val lines = x.split(" ") val dates = lines(0).split("-") ((dates(0).toInt, dates(1).toInt), (dates(2).toInt, lines(1).toInt)) }) // 根据年月key来压缩 ((1970,8),(8,32)) val res = tuple2.combineByKey( // 第一条记录怎么放: 设置三个格子,1.第一个格子用来去重、2.剩下的两个格子给两位数进行排序。 举例:当循环两次以后Array = (1,33),(2,30) 当第三个次的时候来一个(3,20)则会把最后一个替换掉,造成数据错误,所以需要占位两个格子用来排序 (v1: (Int, Int)) => { Array(v1, (0, 0)) }, // 第二条:及以后后续的怎么放、 (oldv: Array[(Int, Int)], newV: (Int, Int)) => { // 去重、排序 var flg = 0; // 按月遍历上一个一条数据的数组 for (i <- 0 until oldv.length) { // a)key相同 1)温度大 2)温度小 b)key不同 0 key是日期 if (oldv(i)._1 == newV._1) { //日期一样去重 if (oldv(i)._2 < newV._2) { flg = 1 oldv(i) = newV } else { flg = 2 } } } if (flg == 0) { //日期不一样 排序 oldv(oldv.length - 1) = newV } scala.util.Sorting.quickSort(oldv) oldv }, // 溢写合并 (v1: Array[(Int, Int)], v2: Array[(Int, Int)]) => { val union = v1.union(v2) scala.util.Sorting.quickSort(union) union }) // 数组需要转换成List res.map(x => (x._1, x._2.toList)).foreach(println)
结果:
((2018,3),List((11,18), (0,0)))
((2019,5),List((21,33), (0,0)))
((2018,4),List((23,22), (0,0)))
((1970,8),List((8,32), (23,23)))
((2019,6),List((1,39), (2,31)))
stage:
总结:分布式计算的核心思想: 调优天下无敌,combineByKey 分布式是并行的,离线批量计算有个特征就是后续步骤(stage) 如果前一步骤(stage)能够加上正确的combineByKey的函数,是尽量压缩内存中的数据。
map和mapValue区别
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("topN") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc.setLogLevel("ERROR") val data: RDD[String] = sc.parallelize(List( "hello world", "hello spark", "hello world", "hello hadoop", "hello world", "hello msb", "hello world" )) val words: RDD[String] = data.flatMap(_.split(" ")) val kv: RDD[(String, Int)] = words.map((_,1)) val res: RDD[(String, Int)] = kv.reduceByKey(_+_) // val res01: RDD[(String, Int)] = res.map(x=>(x._1,x._2*10)) val res01: RDD[(String, Int)] = res.mapValues(x=>x*10) val res02: RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = res01.groupByKey() res02.foreach(println) map结果:
(spark,CompactBuffer(10))
(hadoop,CompactBuffer(10))
(hello,CompactBuffer(70))
(msb,CompactBuffer(10))
(world,CompactBuffer(40))
map-stage:
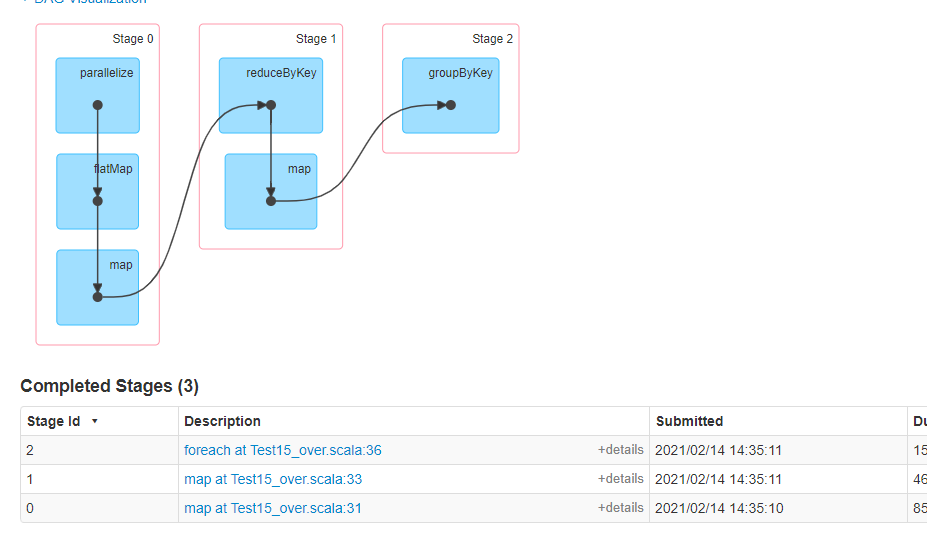
mapValues结果: (spark,CompactBuffer(10)) (hadoop,CompactBuffer(10)) (hello,CompactBuffer(70)) (msb,CompactBuffer(10)) (world,CompactBuffer(40)) mapValues-stage:

解析:
1.map和mapValue在这之前都有一次hash取模的意思,hash的值永远不变,也就是不论map和mapValue取模的值都在同一个分区内(同一台机器内),所以没必要在进行一次shuffle拉取,所以mapValue更优
建议:
1.key没有发生变化、分区器没有发生变化、分区数没有发生变化、且你是KV的、那么就是用mapValues、flatMapValues