更多数据挖掘代码:https://github.com/linyiqun/DataMiningAlgorithm
介绍
与GSP一样,PrefixSpan算法也是序列模式分析算法的一种,不过与前者不同的是PrefixSpan算法不产生任何的侯选集,在这点上可以说已经比GSP好很多了。PrefixSpan算法可以挖掘出满足阈值的所有序列模式,可以说是非常经典的算法。序列的格式就是上文中提到过的类似于<a, b, (de)>这种的。
算法原理
PrefixSpan算法的原理是采用后缀序列转前缀序列的方式来构造频繁序列的。举个例子,
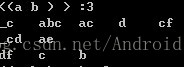
比如原始序列如上图所示,4条序列,1个序列中好几个项集,项集内有1个或多个元素,首先找出前缀为a的子序列,此时序列前缀为<a>,后缀就变为了:
"_"下标符代表前缀为a,说明是在项集中间匹配的。这就相当于从后缀序列中提取出1项加入到前缀序列中,变化的规则就是从左往右扫描,找到第1个此元素对应的项,然后做改变。然后根据此规则继续递归直到后续序列不满足最小支持度阈值的情况。所以此算法的难点就转变为了从后缀序列变为前缀序列的过程。在这个过程要分为2种情况,第1种是单个元素项的后缀提前,比如这里的a,对单个项的提前有分为几种情况,比如:
<b a c ad>,就会变为<c ad>,如果a是嵌套在项集中的情况<b c dad r>,就会变为< _d r>,_代表的就是a.如果a在一项的最末尾,此项也会被移除<b c dda r>变为<r>。但是如果是这种情况<_da d d>a包含在下标符中,将会做处理,应该此时的a是在前缀序列所属的项集内的。
还有1个大类的分类就是对于组合项的后缀提取,可以分为2个情况,1个是从_X中寻找,一个从后面找出连续的项集,比如在这里<a>的条件下,找出前缀<(ab)>的后缀序列
第一种在_X中寻找还有没有X=a的情况,因为_已经代表1个a了,还有一个是判断_X != _a的情况,从后面的项集中找到包含有连续的aa的那个项集,然后做变换处理,与单个项集的变换规则一致。
算法的递归顺序
想要实现整个的序列挖掘,算法的递归顺序就显得非常重要了。在探索递归顺序的路上还是犯了一些错误的,刚刚开始的递归顺序是<a>---><a a>----><a a a>,假设<a a a>找不到对应的后缀模式时,然后回溯到<a (aa)>进行递归,后来发现这样会漏掉情况,为什么呢,因为如果 <a a >没法进行到<a a a>,那么就不可能会有前缀<a (aa)>,顶多会判断到<(aa)>,从<a a>处回调的。于是我发现了这个问题,就变为了下面这个样子,经测试是对的。:
加入所有的单个元素的类似为a-f,顺序为
<a>,---><a a>.同时<(aa)>,然后<ab>同时<(ab)>,就是在a添加a-f的元素的时候,检验a所属项集添加a-f元素的情况。这样就不会漏掉情况了,用了2个递归搞定了这个问题。这个算法的整体实现可以对照代码来看会理解很多。最后提醒一点,在每次做出改变之后都会判断一下是否满足最小支持度阈值的。
PrefixSpan实例
这里举1个真实一点的例子,下面是输入的初始序列:
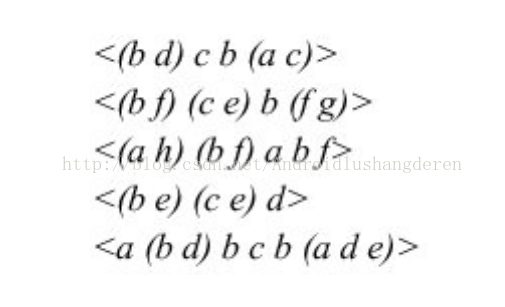
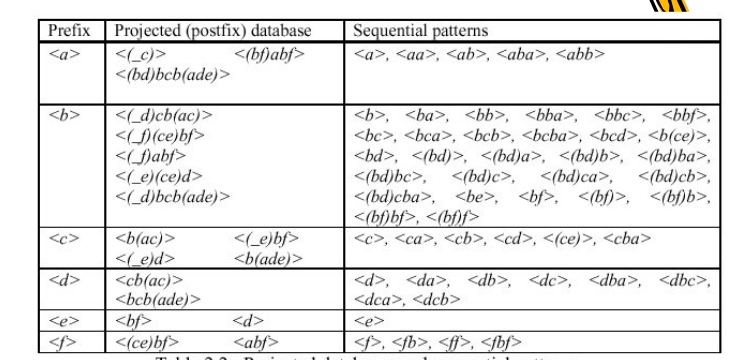
挖掘出的所有的序列模式为,下面是一个表格的形式
在<b>的序列模式中少了1个序列模式。可以与后面程序算法测试的结果做对比。
算法的代码实现
代码实现同样以这个为例子,这样会显得更有说服性。
测试数据:
bd c b ac
bf ce b fg
ah bf a b f
be ce d
a bd b c b adepackage DataMining_PrefixSpan;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 序列类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Sequence {
// 序列内的项集
private ArrayList<ItemSet> itemSetList;
public Sequence() {
this.itemSetList = new ArrayList<>();
}
public ArrayList<ItemSet> getItemSetList() {
return itemSetList;
}
public void setItemSetList(ArrayList<ItemSet> itemSetList) {
this.itemSetList = itemSetList;
}
/**
* 判断单一项是否包含于此序列
*
* @param c
* 待判断项
* @return
*/
public boolean strIsContained(String c) {
boolean isContained = false;
for (ItemSet itemSet : itemSetList) {
isContained = false;
for (String s : itemSet.getItems()) {
if (itemSet.getItems().contains("_")) {
continue;
}
if (s.equals(c)) {
isContained = true;
break;
}
}
if (isContained) {
// 如果已经检测出包含了,直接挑出循环
break;
}
}
return isContained;
}
/**
* 判断组合项集是否包含于序列中
*
* @param itemSet
* 组合的项集,元素超过1个
* @return
*/
public boolean compoentItemIsContain(ItemSet itemSet) {
boolean isContained = false;
ArrayList<String> tempItems;
String lastItem = itemSet.getLastValue();
for (int i = 0; i < this.itemSetList.size(); i++) {
tempItems = this.itemSetList.get(i).getItems();
// 分2种情况查找,第一种从_X中找出x等于项集最后的元素,因为_前缀已经为原本的元素
if (tempItems.size() > 1 && tempItems.get(0).equals("_")
&& tempItems.get(1).equals(lastItem)) {
isContained = true;
break;
} else if (!tempItems.get(0).equals("_")) {
// 从没有_前缀的项集开始寻找,第二种为从后面的后缀中找出直接找出连续字符为ab为同一项集的项集
if (strArrayContains(tempItems, itemSet.getItems())) {
isContained = true;
break;
}
}
if (isContained) {
break;
}
}
return isContained;
}
/**
* 删除单个项
*
* @param s
* 待删除项
*/
public void deleteSingleItem(String s) {
ArrayList<String> tempItems;
ArrayList<String> deleteItems = new ArrayList<>();
for (ItemSet itemSet : this.itemSetList) {
tempItems = itemSet.getItems();
deleteItems = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < tempItems.size(); i++) {
if (tempItems.get(i).equals(s)) {
deleteItems.add(tempItems.get(i));
}
}
tempItems.removeAll(deleteItems);
}
}
/**
* 提取项s之后所得的序列
*
* @param s
* 目标提取项s
*/
public Sequence extractItem(String s) {
Sequence extractSeq = this.copySeqence();
ItemSet itemSet;
ArrayList<String> items;
ArrayList<ItemSet> deleteItemSets = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> tempItems = new ArrayList<>();
for (int k = 0; k < extractSeq.itemSetList.size(); k++) {
itemSet = extractSeq.itemSetList.get(k);
items = itemSet.getItems();
if (items.size() == 1 && items.get(0).equals(s)) {
//如果找到的是单项,则完全移除,跳出循环
extractSeq.itemSetList.remove(k);
break;
} else if (items.size() > 1 && !items.get(0).equals("_")) {
//在后续的多元素项中判断是否包含此元素
if (items.contains(s)) {
//如果包含把s后面的元素加入到临时字符数组中
int index = items.indexOf(s);
for (int j = index; j < items.size(); j++) {
tempItems.add(items.get(j));
}
//将第一位的s变成下标符"_"
tempItems.set(0, "_");
if (tempItems.size() == 1) {
// 如果此匹配为在最末端,同样移除
deleteItemSets.add(itemSet);
} else {
//将变化后的项集替换原来的
extractSeq.itemSetList.set(k, new ItemSet(tempItems));
}
break;
} else {
deleteItemSets.add(itemSet);
}
} else {
// 不符合以上2项条件的统统移除
deleteItemSets.add(itemSet);
}
}
extractSeq.itemSetList.removeAll(deleteItemSets);
return extractSeq;
}
/**
* 提取组合项之后的序列
*
* @param array
* 组合数组
* @return
*/
public Sequence extractCompoentItem(ArrayList<String> array) {
// 找到目标项,是否立刻停止
boolean stopExtract = false;
Sequence seq = this.copySeqence();
String lastItem = array.get(array.size() - 1);
ArrayList<String> tempItems;
ArrayList<ItemSet> deleteItems = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < seq.itemSetList.size(); i++) {
if (stopExtract) {
break;
}
tempItems = seq.itemSetList.get(i).getItems();
// 分2种情况查找,第一种从_X中找出x等于项集最后的元素,因为_前缀已经为原本的元素
if (tempItems.size() > 1 && tempItems.get(0).equals("_")
&& tempItems.get(1).equals(lastItem)) {
if (tempItems.size() == 2) {
seq.itemSetList.remove(i);
} else {
// 把1号位置变为下标符"_",往后移1个字符的位置
tempItems.set(1, "_");
// 移除第一个的"_"下划符
tempItems.remove(0);
}
stopExtract = true;
break;
} else if (!tempItems.get(0).equals("_")) {
// 从没有_前缀的项集开始寻找,第二种为从后面的后缀中找出直接找出连续字符为ab为同一项集的项集
if (strArrayContains(tempItems, array)) {
// 从左往右找出第一个给定字符的位置,把后面的部分截取出来
int index = tempItems.indexOf(lastItem);
ArrayList<String> array2 = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int j = index; j < tempItems.size(); j++) {
array2.add(tempItems.get(j));
}
array2.set(0, "_");
if (array2.size() == 1) {
//如果此项在末尾的位置,则移除该项,否则进行替换
deleteItems.add(seq.itemSetList.get(i));
} else {
seq.itemSetList.set(i, new ItemSet(array2));
}
stopExtract = true;
break;
} else {
deleteItems.add(seq.itemSetList.get(i));
}
} else {
// 这种情况是处理_X中X不等于最后一个元素的情况
deleteItems.add(seq.itemSetList.get(i));
}
}
seq.itemSetList.removeAll(deleteItems);
return seq;
}
/**
* 深拷贝一个序列
*
* @return
*/
public Sequence copySeqence() {
Sequence copySeq = new Sequence();
ItemSet tempItemSet;
ArrayList<String> items;
for (ItemSet itemSet : this.itemSetList) {
items = (ArrayList<String>) itemSet.getItems().clone();
tempItemSet = new ItemSet(items);
copySeq.getItemSetList().add(tempItemSet);
}
return copySeq;
}
/**
* 获取序列中最后一个项集的最后1个元素
*
* @return
*/
public String getLastItemSetValue() {
int size = this.getItemSetList().size();
ItemSet itemSet = this.getItemSetList().get(size - 1);
size = itemSet.getItems().size();
return itemSet.getItems().get(size - 1);
}
/**
* 判断strList2是否是strList1的子序列
*
* @param strList1
* @param strList2
* @return
*/
public boolean strArrayContains(ArrayList<String> strList1,
ArrayList<String> strList2) {
boolean isContained = false;
for (int i = 0; i < strList1.size() - strList2.size() + 1; i++) {
isContained = true;
for (int j = 0, k = i; j < strList2.size(); j++, k++) {
if (!strList1.get(k).equals(strList2.get(j))) {
isContained = false;
break;
}
}
if (isContained) {
break;
}
}
return isContained;
}
}
package DataMining_PrefixSpan;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 字符项集类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class ItemSet {
// 项集内的字符
private ArrayList<String> items;
public ItemSet(String[] str) {
items = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : str) {
items.add(s);
}
}
public ItemSet(ArrayList<String> itemsList) {
this.items = itemsList;
}
public ItemSet(String s) {
items = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
items.add(s.charAt(i) + "");
}
}
public ArrayList<String> getItems() {
return items;
}
public void setItems(ArrayList<String> items) {
this.items = items;
}
/**
* 获取项集最后1个元素
*
* @return
*/
public String getLastValue() {
int size = this.items.size();
return this.items.get(size - 1);
}
}
package DataMining_PrefixSpan;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* PrefixSpanTool序列模式分析算法工具类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class PrefixSpanTool {
// 测试数据文件地址
private String filePath;
// 最小支持度阈值比例
private double minSupportRate;
// 最小支持度,通过序列总数乘以阈值比例计算
private int minSupport;
// 原始序列组
private ArrayList<Sequence> totalSeqs;
// 挖掘出的所有序列频繁模式
private ArrayList<Sequence> totalFrequentSeqs;
// 所有的单一项,用于递归枚举
private ArrayList<String> singleItems;
public PrefixSpanTool(String filePath, double minSupportRate) {
this.filePath = filePath;
this.minSupportRate = minSupportRate;
readDataFile();
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*/
private void readDataFile() {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
minSupport = (int) (dataArray.size() * minSupportRate);
totalSeqs = new ArrayList<>();
totalFrequentSeqs = new ArrayList<>();
Sequence tempSeq;
ItemSet tempItemSet;
for (String[] str : dataArray) {
tempSeq = new Sequence();
for (String s : str) {
tempItemSet = new ItemSet(s);
tempSeq.getItemSetList().add(tempItemSet);
}
totalSeqs.add(tempSeq);
}
System.out.println("原始序列数据:");
outputSeqence(totalSeqs);
}
/**
* 输出序列列表内容
*
* @param seqList
* 待输出序列列表
*/
private void outputSeqence(ArrayList<Sequence> seqList) {
for (Sequence seq : seqList) {
System.out.print("<");
for (ItemSet itemSet : seq.getItemSetList()) {
if (itemSet.getItems().size() > 1) {
System.out.print("(");
}
for (String s : itemSet.getItems()) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
if (itemSet.getItems().size() > 1) {
System.out.print(")");
}
}
System.out.println(">");
}
}
/**
* 移除初始序列中不满足最小支持度阈值的单项
*/
private void removeInitSeqsItem() {
int count = 0;
HashMap<String, Integer> itemMap = new HashMap<>();
singleItems = new ArrayList<>();
for (Sequence seq : totalSeqs) {
for (ItemSet itemSet : seq.getItemSetList()) {
for (String s : itemSet.getItems()) {
if (!itemMap.containsKey(s)) {
itemMap.put(s, 1);
}
}
}
}
String key;
for (Map.Entry entry : itemMap.entrySet()) {
count = 0;
key = (String) entry.getKey();
for (Sequence seq : totalSeqs) {
if (seq.strIsContained(key)) {
count++;
}
}
itemMap.put(key, count);
}
for (Map.Entry entry : itemMap.entrySet()) {
key = (String) entry.getKey();
count = (int) entry.getValue();
if (count < minSupport) {
// 如果支持度阈值小于所得的最小支持度阈值,则删除该项
for (Sequence seq : totalSeqs) {
seq.deleteSingleItem(key);
}
} else {
singleItems.add(key);
}
}
Collections.sort(singleItems);
}
/**
* 递归搜索满足条件的序列模式
*
* @param beforeSeq
* 前缀序列
* @param afterSeqList
* 后缀序列列表
*/
private void recursiveSearchSeqs(Sequence beforeSeq,
ArrayList<Sequence> afterSeqList) {
ItemSet tempItemSet;
Sequence tempSeq2;
Sequence tempSeq;
ArrayList<Sequence> tempSeqList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : singleItems) {
// 分成2种形式递归,以<a>为起始项,第一种直接加入独立项集遍历<a,a>,<a,b> <a,c>..
if (isLargerThanMinSupport(s, afterSeqList)) {
tempSeq = beforeSeq.copySeqence();
tempItemSet = new ItemSet(s);
tempSeq.getItemSetList().add(tempItemSet);
totalFrequentSeqs.add(tempSeq);
tempSeqList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Sequence seq : afterSeqList) {
if (seq.strIsContained(s)) {
tempSeq2 = seq.extractItem(s);
tempSeqList.add(tempSeq2);
}
}
recursiveSearchSeqs(tempSeq, tempSeqList);
}
// 第二种递归为以元素的身份加入最后的项集内以a为例<(aa)>,<(ab)>,<(ac)>...
// a在这里可以理解为一个前缀序列,里面可能是单个元素或者已经是多元素的项集
tempSeq = beforeSeq.copySeqence();
int size = tempSeq.getItemSetList().size();
tempItemSet = tempSeq.getItemSetList().get(size - 1);
tempItemSet.getItems().add(s);
if (isLargerThanMinSupport(tempItemSet, afterSeqList)) {
tempSeqList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Sequence seq : afterSeqList) {
if (seq.compoentItemIsContain(tempItemSet)) {
tempSeq2 = seq.extractCompoentItem(tempItemSet
.getItems());
tempSeqList.add(tempSeq2);
}
}
totalFrequentSeqs.add(tempSeq);
recursiveSearchSeqs(tempSeq, tempSeqList);
}
}
}
/**
* 所传入的项组合在所给定序列中的支持度是否超过阈值
*
* @param s
* 所需匹配的项
* @param seqList
* 比较序列数据
* @return
*/
private boolean isLargerThanMinSupport(String s, ArrayList<Sequence> seqList) {
boolean isLarge = false;
int count = 0;
for (Sequence seq : seqList) {
if (seq.strIsContained(s)) {
count++;
}
}
if (count >= minSupport) {
isLarge = true;
}
return isLarge;
}
/**
* 所传入的组合项集在序列中的支持度是否大于阈值
*
* @param itemSet
* 组合元素项集
* @param seqList
* 比较的序列列表
* @return
*/
private boolean isLargerThanMinSupport(ItemSet itemSet,
ArrayList<Sequence> seqList) {
boolean isLarge = false;
int count = 0;
if (seqList == null) {
return false;
}
for (Sequence seq : seqList) {
if (seq.compoentItemIsContain(itemSet)) {
count++;
}
}
if (count >= minSupport) {
isLarge = true;
}
return isLarge;
}
/**
* 序列模式分析计算
*/
public void prefixSpanCalculate() {
Sequence seq;
Sequence tempSeq;
ArrayList<Sequence> tempSeqList = new ArrayList<>();
ItemSet itemSet;
removeInitSeqsItem();
for (String s : singleItems) {
// 从最开始的a,b,d开始递归往下寻找频繁序列模式
seq = new Sequence();
itemSet = new ItemSet(s);
seq.getItemSetList().add(itemSet);
if (isLargerThanMinSupport(s, totalSeqs)) {
tempSeqList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Sequence s2 : totalSeqs) {
// 判断单一项是否包含于在序列中,包含才进行提取操作
if (s2.strIsContained(s)) {
tempSeq = s2.extractItem(s);
tempSeqList.add(tempSeq);
}
}
totalFrequentSeqs.add(seq);
recursiveSearchSeqs(seq, tempSeqList);
}
}
printTotalFreSeqs();
}
/**
* 按模式类别输出频繁序列模式
*/
private void printTotalFreSeqs() {
System.out.println("序列模式挖掘结果:");
ArrayList<Sequence> seqList;
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Sequence>> seqMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String s : singleItems) {
seqList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Sequence seq : totalFrequentSeqs) {
if (seq.getItemSetList().get(0).getItems().get(0).equals(s)) {
seqList.add(seq);
}
}
seqMap.put(s, seqList);
}
int count = 0;
for (String s : singleItems) {
count = 0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
seqList = (ArrayList<Sequence>) seqMap.get(s);
for (Sequence tempSeq : seqList) {
count++;
System.out.print("<");
for (ItemSet itemSet : tempSeq.getItemSetList()) {
if (itemSet.getItems().size() > 1) {
System.out.print("(");
}
for (String str : itemSet.getItems()) {
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
if (itemSet.getItems().size() > 1) {
System.out.print(")");
}
}
System.out.print(">, ");
// 每5个序列换一行
if (count == 5) {
count = 0;
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
}
package DataMining_PrefixSpan;
/**
* PrefixSpan序列模式挖掘算法
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] agrs){
String filePath = "C:\Users\lyq\Desktop\icon\input.txt";
//最小支持度阈值率
double minSupportRate = 0.4;
PrefixSpanTool tool = new PrefixSpanTool(filePath, minSupportRate);
tool.prefixSpanCalculate();
}
}
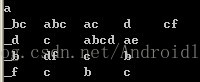
原始序列数据:
<(b d )c b (a c )>
<(b f )(c e )b (f g )>
<(a h )(b f )a b f >
<(b e )(c e )d >
<a (b d )b c b (a d e )>
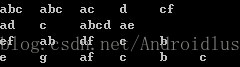
序列模式挖掘结果:
<a >, <a a >, <a b >, <a b a >, <a b b >,
<b >, <b a >, <b b >, <b b a >, <b b c >,
<b b f >, <b c >, <b c a >, <b c b >, <b c b a >,
<b c d >, <b (c e )>, <b d >, <(b d )>, <(b d )a >,
<(b d )b >, <(b d )b a >, <(b d )b c >, <(b d )c >, <(b d )c a >,
<(b d )c b >, <(b d )c b a >, <b e >, <b f >, <(b f )>,
<(b f )b >, <(b f )b f >, <(b f )f >,
<c >, <c a >, <c b >, <c b a >, <c d >,
<(c e )>,
<d >, <d a >, <d b >, <d b a >, <d b c >,
<d c >, <d c a >, <d c b >, <d c b a >,
<e >,
<f >, <f b >, <f b f >, <f f >, 算法实现时的难点
我在实现这个算法时确实碰到了不少的问题,下面一一列举。
1、Sequence序列在判断或者提取单项和组合项的时候,情况少考虑了,还有考虑到了处理的方式又可能错了。
2、递归的顺序在最早的时候考虑错了,后来对递归的顺序进行了调整。
3、在算法的调试时遇到了,当发现某一项出现问题时,不能够立即调试,因为里面陷入的递归层次实在太深,只能自己先手算此情况下的前缀,后缀序列,然后自己模拟出1个Seq调试,在纠正extract方法时用的比较多。
我对PrefixSpan算法的理解
实现了这个算法之后,再回味这个算法,还是很奇妙的,一个序列,通过从左往右的扫描,通过各个项集的子集,能够组合出许许多多的的序列模式,然后进行挖掘,PrefixSpan通过递归的形式全部找出,而且效率非常高,的确是个很强大的算法。
PrefixSpan算法整体的特点
首先一点,他不会产生候选序列,在产生投影数据库的时候(也就是产生后缀子序列),他的规模是不断减小的。PrefixSpan采用分治法进行序列的挖掘,十分的高效。唯一比较会有影响的开销就是在构造后缀子序列的过程,专业上的名称叫做构造投影数据库的时候。