就像其他的编程语言一样,shell也有三种基本的结构:顺序结构、分支结构、循环结构。顺序结构就是按照命令的出现顺序依次执行,比较简单。如下分别介绍分支结构和循环结构。
分支结构
格式1:
if command then commands fi # 或者 if command: then commands fi
说明:在其他编程语言中,if后面的command是一个等式,用来判断是true还是false;但是在bash shell中,该command是一个命令,if语句根据command执行结果的退出状态码是否为0来判断then部分是否需要执行[返回0表明命令执行成功,则执行then部分]。
如下使用grep命令在/etc/passwd文件中查找某个特定用户名是否在当前系统上使用,如果存在该用户,则显示该用户主目录的bash文件:
#! /bin/bash # function: This script is to test structured commands # author: benxintuzi # date: 2015-07-13 user=benxintuzi if grep $user /etc/passwd then echo "The bash files for user $user are:" ls -a /home/$user/.b* fi
格式2:
if command then commands else commands fi
user=123456 if grep $user /etc/passwd then echo "The bash files for user $user are:" ls -a /home/$user/.b* else echo "The user $user does not exist on this system" fi
格式3:
if command1 then commands elif command2 then commands elif ... then ... fi
注:if-then语句不能测试与命令退出码无关的条件,这个任务可以通过test命令来完成。
test命令的格式非常简单:test condition,用在if-then语句块中时,格式如下:
if test condition then commands fi # 或者 # bash shell中可以使用方括号: if [ condition ] then commands fi 说明:方括号定义了test命令,但是括号内两侧必须有空格
test命令可以用于3类条件:数值比较、字符串比较、文件比较。
1 数值比较
|
操 作 |
描 述 |
|
n1 –eq n2 |
判断n1是否等于n2 |
|
n1 –ge n2 |
判断n1是否大于或等于n2 |
|
n1 –gt n2 |
判断n1是否大于n2 |
|
n1 –le n2 |
判断n1是否小于或等于n2 |
|
n1 –lt n2 |
判断n1是否小于n2 |
|
n1 –ne n2 |
判断n1是否不等于n2 |
val=10 if [ $val -gt 5 ] then echo "The test value $val is greater than 5" else echo "sorry, you are so little" fi
2 字符串比较
|
比 较 |
描 述 |
|
str1 = str2 |
是否相同 |
|
str1 != str2 |
是否不同 |
|
str1 < str2 |
是否小于 |
|
str1 > str2 |
是否大于 |
|
-n str1 |
str1的长度是否非0 |
|
-z str1 |
str1的长度是否为0 |
2.1 【=、!=】
user=benxintuzi if [ $USER = $user ] then echo "Welcome $user" else echo "The user $user is not exist" fi
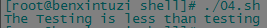
2.2 【>、<】这两个比较操作使用时必须转义,否则shell将其解释为重定向符号。
val1=Testing val2=testing if [ $val1 > $val2 ] then echo "The $val1 is greater than $val2" else echo "The $val1 is less than $val2" fi
2.3 【-n、-z】
val1=testing val2='' if [ -n val1 ] then echo "The string '$val1' is not empty" else echo "The string '$val1' is empty" fi if [ -z val2 ] then echo "The string '$val2' is not empty" else echo "The string '$val2' is empty" fi
3 文件比较
|
-d file |
检查file目录是否存在 |
|
-e file |
检查file是否存在 |
|
-f file |
检查file文件是否存在 |
|
-r file |
检查file是否存在并可读 |
|
-s file |
检查file是否存在并非空 |
|
-w file |
检查file是否存在并可写 |
|
-x file |
检查file是否存在并可执行 |
|
-O file |
检查file是否存在并属于当前用户所有 |
|
-G file |
检查file是否存在并且默认组与当前用户相同 |
|
file1 –nt file2 |
检查file1是否比file2新 |
|
file1 –ot file2 |
检查file1是否比file2旧 |
复合条件的编写
if-then语句可以使用布尔逻辑来组合测试,格式如下:
[ condition1 ] && [ condition2 ]
[ condition1 ] || [ condition2 ]
if-then高级特性
(( expression )) 用于对expression进行简单比较或计算,其中的比较操作符>等不需要转义
[[ expression ]] 主要用于字符串模式匹配
val1=10 if (( $val1 ** 2 > 90 )) then (( val2=$val1 ** 2 )) echo "The square of $val1 is $val2" fi
if [[ $USER == benxin* ]] then echo "Hello, $USER" else echo "Sorry, I do not know you" fi
当分支情况比较多时,可能需要编写多条if-then-elif-then-...语句,此时,可以使用case语句,格式如下:
case variable in pattern1 | pattern2) command1;; pattern3) commands;; *) commands;; esac
说明:在一行中使用|来分割多个模式。
val=benxin case $val in benxin | tuzi) echo "You are alone";; benxintuzi) echo "Congratulations";; *) echo "go out now!";; esac
循环结构
for命令
for var in list do commands done # 或者 for var in list; do commands done
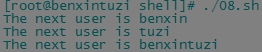
for var in benxin tuzi benxintuzi do echo "The next user is $var" done
说明:for命令使用空格来划分列表中的不同值,如果单个数据值中也有空格,此时需要用双引号将这个值括起来,如下:
for var in benxin tuzi "benxin tuzi" do echo "The next user is $var" done
通常的情况下,我们将一系列的值都存储在一个变量中,如:
list="benxin tuzi benxintuzi" for var in $list do echo "The next user is $var" done
bash shell中使用IFS(Internal Field Separator)环境变量作为字段分隔符,默认情况下IFS使用如下字符:空格符,制表符,换行符。
如果要将冒号:设定为分隔符,可以如下设置:
IFS=:
IFS=: list="benxin:tuzi:benxintuzi" for var in $list do echo "The next user is $var" done
如果需要指定多个IFS字符,只要将它们在赋值行中串起来就行了:
(IFS=$' :;')表示可以使用换行符、冒号、分号作为字段之间的分隔符。
IFS=$' :;' list="benxin tuzi:benxintuzi tuzi;123" for var in $list do echo "The next user is $var" done
注:我们修改默认IFS一般只是为了处理一段特殊的脚本,因此处理完成后必须恢复默认值,如下:
IFS.OLD=$IFS IFS=$’ ’ # user processing... IFS=$IFS.OLD
while命令
while test command do commands done
val=10 while [ $val -gt 0 ] do echo $val val=$[ $val - 1 ] done
until命令
until test command do commands done
说明:until命令的执行刚好与while相反,其测试条件不成立时才执行。
循环控制命令
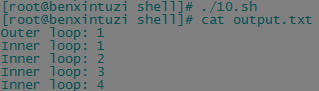
1 break命令 终止并退出循环; break n 默认情况下,n为1,表示跳出当前循环;如果n为2,表示跳出上一级循环 for a in 1 2 3 4 do echo "Outer loop: $a" for (( b = 1; b < 100; b++ )) do if [ $b -gt 4 ] then break 2 fi echo "Inner loop: $b" done done

2 continue命令 跳过本次循环中的其余命令,继续执行下一轮循环 同理也有continue n
循环重定向
for a in 1 2 3 4 do echo "Outer loop: $a" for (( b = 1; b < 100; b++ )) do if [ $b -gt 4 ] then break 2 fi echo "Inner loop: $b" done done > output.txt
即直接在done后加上重定向符号即可,当然,也可以直接将循环输出重定向到一个命令的输入中:
for state in apple orange pear banana pineapple do echo "$state is my favourite fruit" done | sort