springboot中嵌入tomcat原理分析
首先要了解tomcat本身,否则springboot内嵌tomcat就很难分析。关于tomcat的源码会后续更新。
本文主要先简单分析一下springboot内嵌tomcat的源码,深入了解以后再更新。
还是先从springboot的启动入口run()方法开始分析。。。。。。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); //创建应用上下文 context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新应用上下文,完成spring容器的初始化,也会加载tomcat refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
进入refreshContext()----》ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refreshContext()方法:
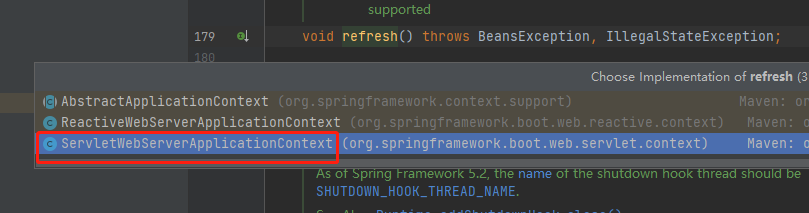
进入super.refresh()方法后,进入到spring的源码中了,在进入onRefreshContext()方法---》ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefreshContext()方法
@Override protected void onRefresh() { super.onRefresh(); try {
//创建web实例 createWebServer(); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex); } }
进入createWebServer()方法:
private void createWebServer() { WebServer webServer = this.webServer; ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//获取webServer的工厂对象 ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
//获得具体的webServer对象------>TomcatWebServer this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()); getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown", new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer)); getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop", new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer)); } else if (servletContext != null) { try { getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext); } catch (ServletException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex); } } initPropertySources(); }
再看一下getWebServer()里的逻辑---》直接进入TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer()中
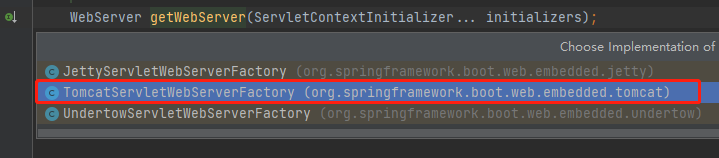
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) { Registry.disableRegistry(); }
//创建tomcat对象 Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat"); tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
//创建连接器 Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
//service关联连接器 tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); customizeConnector(connector); tomcat.setConnector(connector); tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
//配置Engin configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine()); for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); } prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//返回获取的TomcatWebServer对象 return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat); }
然后进入到getTomcatWebServer()方法中
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
//直接创建,我们需要看构造方法 return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0, getShutdown()); }
TomcatWebServer的构造方法:
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) { Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null"); this.tomcat = tomcat; this.autoStart = autoStart; this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null;
//初始化 重点 initialize(); }
进入initialize()方法:
private void initialize() throws WebServerException { logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false)); synchronized (this.monitor) { try { addInstanceIdToEngineName(); Context context = findContext(); context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> { if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) { // Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't // happen when the service is started. removeServiceConnectors(); } }); // Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
//启动Tomcat通过发布事件触发一些Listener的初始化
this.tomcat.start(); //启动tomcat // We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions(); try { ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader()); } catch (NamingException ex) { // Naming is not enabled. Continue } // Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a // blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown startDaemonAwaitThread(); } catch (Exception ex) { stopSilently(); destroySilently(); throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex); } } }
进入start()方法:
public void start() throws LifecycleException { this.getServer(); this.server.start(); }
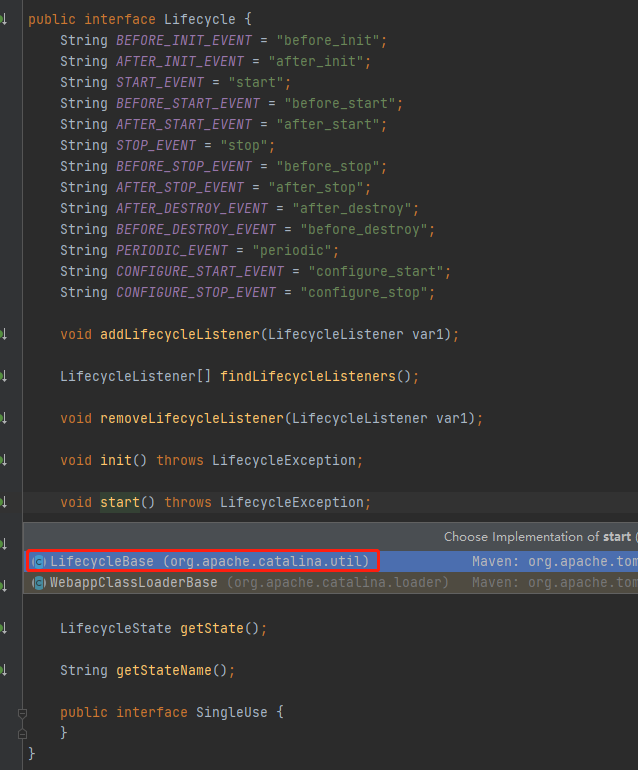
到这儿后面的逻辑其实就是Tomcat自身启动的逻辑了。这就需要你的Tomcat基础了,到这SpringBoot启动是如何内嵌Tomcat容器的到这儿就结束了哦。
springboot源码大致流程也就结束了。后面会有一些细节补充的内容。