springboot监听器的设计
1、首先先了解一下设计模式---》观察者模式,因为springboot的监听器用到了观察者模式。
观察者模式(发布/订阅模式):对象的关系是一(发布者/目标对象)对多(观察者),当一个对象发生改变,依赖他的其他对象会收到通知到并自动更新。
(jdk9以后放弃了Observer和Observable,用PropertyChangeEvent和PropertyChangeListener来代替)具体的可以自己搜搜为什么不用了。
目标对象:
package com.observer; import java.beans.PropertyChangeListener; import java.beans.PropertyChangeSupport; public class Publisher { private int state; private PropertyChangeSupport changeSupport = new PropertyChangeSupport(this); public int getState() { return state; } public void setState(int state) { int oldState = this.state; this.state = state;
//添加对bean内某个变量的监听,第一个参数最好是变量名,第二个是变量改变前的值,第二个是变量改变后的值 changeSupport.firePropertyChange("state", oldState, state); } public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) { changeSupport.addPropertyChangeListener(listener); } public void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) { changeSupport.removePropertyChangeListener(listener); } }
firePropertyChange源码:
private PropertyChangeListenerMap map = new PropertyChangeListenerMap();
public void firePropertyChange(String propertyName, Object oldValue, Object newValue) {
if (oldValue == null || newValue == null || !oldValue.equals(newValue)) {
firePropertyChange(new PropertyChangeEvent(this.source, propertyName, oldValue, newValue));
}
}
public void firePropertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent event) { Object oldValue = event.getOldValue(); Object newValue = event.getNewValue(); if (oldValue == null || newValue == null || !oldValue.equals(newValue)) { String name = event.getPropertyName(); PropertyChangeListener[] common = this.map.get(null);
//获取所有订阅者对象 PropertyChangeListener[] named = (name != null) ? this.map.get(name) : null; fire(common, event); fire(named, event); } }
private static void fire(PropertyChangeListener[] listeners, PropertyChangeEvent event) {
if (listeners != null) {
for (PropertyChangeListener listener : listeners) {
//调用Subscriber的propertyChange()
listener.propertyChange(event);
}
}
}
观察对象:
package com.observer; import java.beans.PropertyChangeEvent; import java.beans.PropertyChangeListener; public class Subscriber implements PropertyChangeListener{ private int state; @Override public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt) { state = (int) evt.getNewValue(); } public int getState() { return state; } public void setState(int state) { this.state = state; } }
测试:
package com.observer; import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Publisher publisher = new Publisher(); Subscriber s1 = new Subscriber(); Subscriber s2 = new Subscriber(); Subscriber s3 = new Subscriber(); publisher.addPropertyChangeListener(s1); publisher.addPropertyChangeListener(s2); publisher.addPropertyChangeListener(s3); System.out.println("目标对象开始修改"); publisher.setState(100); System.out.println("s1的state值:"+s1.getState()); System.out.println("s2的state值:"+s2.getState()); System.out.println("s3的state值:"+s3.getState()); System.out.println("-----------------"); System.out.println("目标对象开始修改"); publisher.setState(200); System.out.println("s1的state值:"+s1.getState()); System.out.println("s2的state值:"+s2.getState()); System.out.println("s3的state值:"+s3.getState()); System.out.println("-----------------"); publisher.removePropertyChangeListener(s3); System.out.println("目标对象开始修改"); publisher.setState(500); System.out.println("s1的state值:"+s1.getState()); System.out.println("s2的state值:"+s2.getState()); System.out.println("s3的state值:"+s3.getState()); } }
结果:
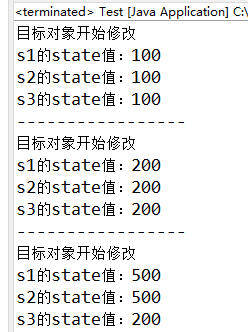
移除了s3之后,s3的state值仍是200,没有更新成最新的500.
了解了观察者模式后,接下来进入springboot监听器的源码。
2、springboot监听器源码分析
根据上一篇spingboot启动入口run方法的分析后,知道了
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); 将所有的监听器(观察者)都绑定到了EventPublishingRunlistener(发布者)中。
接下来分析run()方法中如何发布对应的事件:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//触发启动事件 listeners.starting(); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//准备环境事件,此时ConfigFileApplicationListener对该事件进行了处理 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); }
//启动完成事件 listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) {
//启动出错事件 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
以listener.starting()为例,监听器以ConfigFileApplicationListener为例。
void starting() { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.starting(); } }
进入到了EventPublishingRunlistener的starting()
@Override public void starting() {
//创建了一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件 this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args)); }
@Override public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event)); } @Override public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event)); Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
//循环遍历所有的监听器(spring.factories中的所有ApplicationListener) for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { if (executor != null) {
//异步执行监听器 executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event)); } else {
//同步执行监听器 invokeListener(listener, event); } } }
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) { ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler(); if (errorHandler != null) { try {
//真正开始执行监听器 doInvokeListener(listener, event); } catch (Throwable err) { errorHandler.handleError(err); } } else { doInvokeListener(listener, event); } }
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) { try {
//进入到具体的监听器中执行里面的onApplicationEvent方法,以configFileApplicationListener为例 listener.onApplicationEvent(event); } catch (ClassCastException ex) { String msg = ex.getMessage(); if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) { // Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for // -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message. Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex); } } else { throw ex; } } }
configFileApplicationListener类中的onApplicationEvent()
@Override
//判断事件类型
//没有对ApplicationStartingEvent事件的处理 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//对准备环境的事件进行了处理
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) { onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event); } if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) { onApplicationPreparedEvent(event); } }
总结:
图中是官方内置的事件、触发器等,依赖的包中也可以有别的,当然也可以自定义监听器,下一篇会来说一下如何自定义监听器
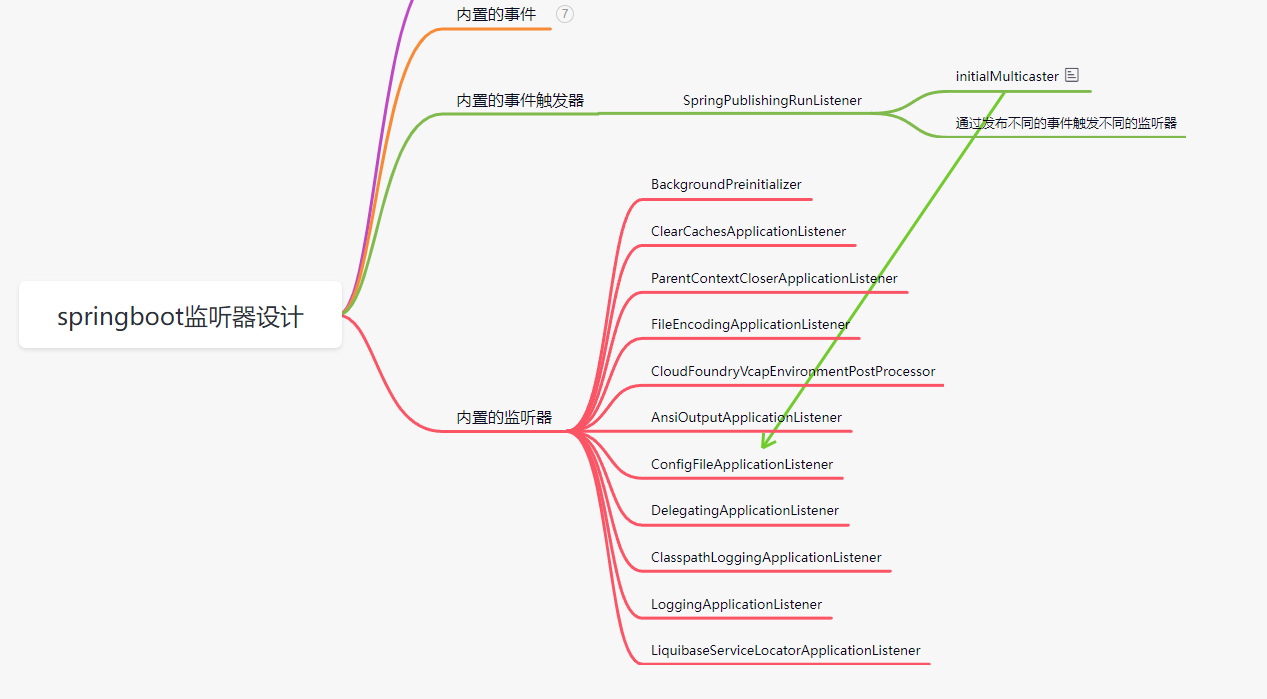
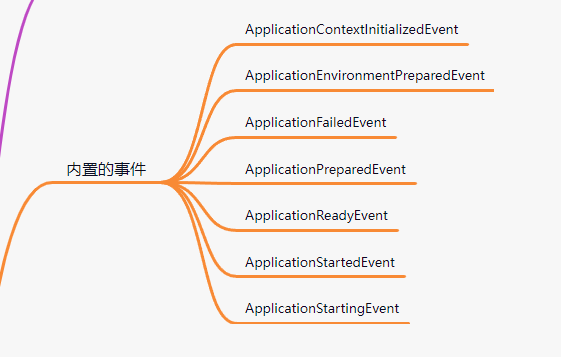
到这儿对应SpringBoot中的监听器这块就分析的差不错了。像SpringBoot的属性文件中的信息什么时候加载的就是在这些内置的监听器中完成的。