上周五和周末,工作忙里偷闲,在看java cocurrent中也顺便再温故了一下Thread.interrupt和java 5之后的LockSupport的实现。
在介绍之前,先抛几个问题。
Thread.interrupt()方法和InterruptedException异常的关系?是由interrupt触发产生了InterruptedException异常?
Thread.interrupt()会中断线程什么状态的工作? RUNNING or BLOCKING?
一般Thread编程需要关注interrupt中断不?一般怎么处理?可以用来做什么?
LockSupport.park()和unpark(),与object.wait()和notify()的区别?
LockSupport.park(Object blocker)传递的blocker对象做什么用?
LockSupport能响应Thread.interrupt()事件不?会抛出InterruptedException异常?
Thread.interrupt()处理是否有对应的回调函数?类似于钩子调用?
如果你都都能很明确的答上来了,说明你已经完全懂Thread.interrupt,可以不用往下看那了。
那如果不清楚的,带着这几个问题,一起来梳理下。
Thread的interrupt处理的几个方法:
public void interrupt() : 执行线程interrupt事件
public boolean isInterrupted() : 检查当前线程是否处于interrupt
public static boolean interrupted() : check当前线程是否处于interrupt,并重置interrupt信息。类似于resetAndGet()
理解:
1. 每个线程都有一个interrupt status标志位,用于表明当前线程是否处于中断状态
2. 一般调用Thread.interrupt()会有两种处理方式
遇到一个低优先级的block状态时,比如object.wait(),object.sleep(),object.join()。它会立马触发一个unblock解除阻塞,并throw一个InterruptedException。
其他情况,Thread.interrupt()仅仅只是更新了status标志位。然后你的工作线程通过Thread.isInterrrupted()进行检查,可以做相应的处理,比如也throw InterruptedException或者是清理状态,取消task等。
在interrupt javadoc中描述: 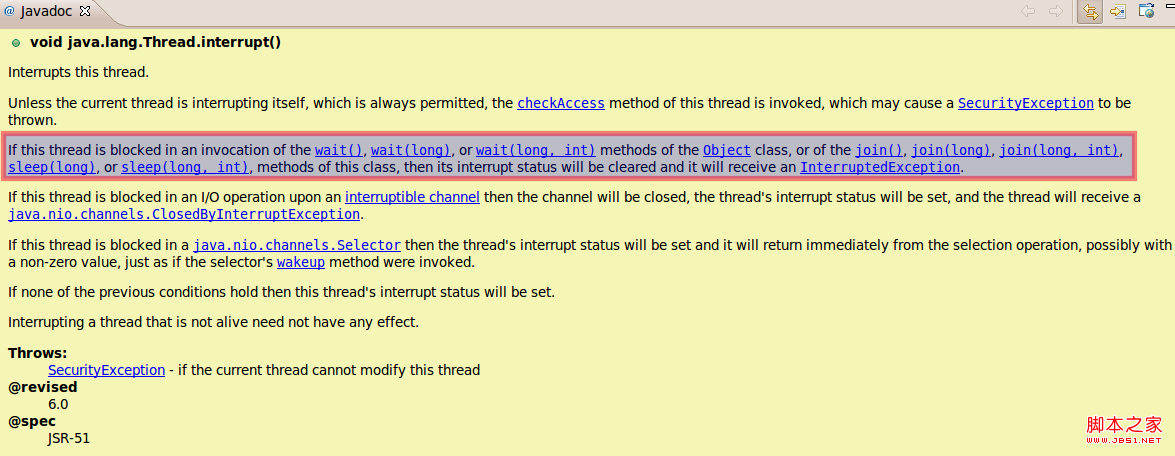
最佳实践
IBM上有篇文章写的挺不错。Java theory and practice: Dealing with InterruptedException , 里面提到了Interrupt处理的几条最佳实践。
Don't swallow interrupts (别吃掉Interrupt,一般是两种处理: 继续throw InterruptedException异常。 另一种就是继续设置Thread.interupt()异常标志位,让更上一层去进行相应处理。
public class TaskRunner implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<Task> queue;
public TaskRunner(BlockingQueue<Task> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
Task task = queue.take(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
task.execute();
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Restore the interrupted status
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
Implementing cancelable tasks with Interrupt (使用Thread.interrupt()来设计和支持可被cancel的task)
public class PrimeProducer extends Thread {
private final BlockingQueue<BigInteger> queue;
PrimeProducer(BlockingQueue<BigInteger> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
try {
BigInteger p = BigInteger.ONE;
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted())
queue.put(p = p.nextProbablePrime());
} catch (InterruptedException consumed) {
/* Allow thread to exit */
}
}
public void cancel() { interrupt(); } // 发起中断
}<SPAN style="WHITE-SPACE: normal"> </SPAN>
注册Interrupt处理事件(非正常用法)
一般正常的task设计用来处理cancel,都是采用主动轮询的方式检查Thread.isInterrupt(),对业务本身存在一定的嵌入性,还有就是存在延迟,你得等到下一个检查点(谁知道下一个检查点是在什么时候,特别是进行一个socket.read时,遇到过一个HttpClient超时的问题)。
来看一下,主动抛出InterruptedException异常的实现,借鉴于InterruptibleChannel的设计,比较取巧。
interface InterruptAble { // 定义可中断的接口
public void interrupt() throws InterruptedException;
}
abstract class InterruptSupport implements InterruptAble {
private volatile boolean interrupted = false;
private Interruptible interruptor = new Interruptible() {
public void interrupt() {
interrupted = true;
InterruptSupport.this.interrupt(); // 位置3
}
};
public final boolean execute() throws InterruptedException {
try {
blockedOn(interruptor); // 位置1
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { // 立马被interrupted
interruptor.interrupt();
}
// 执行业务代码
bussiness();
} finally {
blockedOn(null); // 位置2
}
return interrupted;
}
public abstract void bussiness() ;
public abstract void interrupt();
// -- sun.misc.SharedSecrets --
static void blockedOn(Interruptible intr) { // package-private
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().blockedOn(Thread.currentThread(), intr);
}
}
代码说明,几个取巧的点:
位置1:利用sun提供的blockedOn方法,绑定对应的Interruptible事件处理钩子到指定的Thread上。
位置2:执行完代码后,清空钩子。避免使用连接池时,对下一个Thread处理事件的影响。
位置3:定义了Interruptible事件钩子的处理方法,回调InterruptSupport.this.interrupt()方法,子类可以集成实现自己的业务逻辑,比如sock流关闭等等。
使用:
class InterruptRead extends InterruptSupport {
private FileInputStream in;
@Override
public void bussiness() {
File file = new File("/dev/urandom"); // 读取linux黑洞,永远读不完
try {
in = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (in.read(bytes, 0, 1024) > 0) {
// Thread.sleep(100);
// if (Thread.interrupted()) {// 以前的Interrupt检查方式
// throw new InterruptedException("");
// }
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public FileInputStream getIn() {
return in;
}
@Override
public void interrupt() {
try {
in.getChannel().close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
final InterruptRead test = new InterruptRead();
Thread t = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
System.out.println("InterruptRead start!");
test.execute();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("InterruptRead end! cost time : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t.start();
// 先让Read执行3秒
Thread.sleep(3000);
// 发出interrupt中断
t.interrupt();
}
jdk源码介绍:
1. sun提供的钩子可以查看System的相关代码, line : 1125
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.setJavaLangAccess(new sun.misc.JavaLangAccess(){
public sun.reflect.ConstantPool getConstantPool(Class klass) {
return klass.getConstantPool();
}
public void setAnnotationType(Class klass, AnnotationType type) {
klass.setAnnotationType(type);
}
public AnnotationType getAnnotationType(Class klass) {
return klass.getAnnotationType();
}
public <E extends Enum<E>>
E[] getEnumConstantsShared(Class<E> klass) {
return klass.getEnumConstantsShared();
}
public void blockedOn(Thread t, Interruptible b) {
t.blockedOn(b);
}
});
2. Thread.interrupt()
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread())
checkAccess();
synchronized (blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = blocker;
if (b != null) {
interrupt0(); // Just to set the interrupt flag
b.interrupt(); //回调钩子
return;
}
}
interrupt0();
}
更多
更多关于Thread.stop,suspend,resume,interrupt的使用注意点,可以看一下sun的文档,比如http://download.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/guides/concurrency/threadPrimitiveDeprecation.html
最后来解答一下之前的几个问题:
问题1: Thread.interrupt()方法和InterruptedException异常的关系?是由interrupt触发产生了InterruptedException异常?
答: Thread.interrupt()只是在Object.wait() .Object.join(), Object.sleep()几个方法会主动抛出InterruptedException异常。而在其他的的block常见,只是通过设置了Thread的一个标志位信息,需要程序自我进行处理。
if (Thread.interrupted()) // Clears interrupted status!
throw new InterruptedException();
问题2:Thread.interrupt()会中断线程什么状态的工作? RUNNING or BLOCKING?
答:Thread.interrupt设计的目的主要是用于处理线程处于block状态,比如wait(),sleep()状态就是个例子。但可以在程序设计时为支持task cancel,同样可以支持RUNNING状态。比如Object.join()和一些支持interrupt的一些nio channel设计。
问题3: 一般Thread编程需要关注interrupt中断不?一般怎么处理?可以用来做什么?
答: interrupt用途: unBlock操作,支持任务cancel, 数据清理等。
问题4: LockSupport.park()和unpark(),与object.wait()和notify()的区别?
答:
1. 面向的主体不一样。LockSuport主要是针对Thread进进行阻塞处理,可以指定阻塞队列的目标对象,每次可以指定具体的线程唤醒。Object.wait()是以对象为纬度,阻塞当前的线程和唤醒单个(随机)或者所有线程。
2. 实现机制不同。虽然LockSuport可以指定monitor的object对象,但和object.wait(),两者的阻塞队列并不交叉。可以看下测试例子。object.notifyAll()不能唤醒LockSupport的阻塞Thread.
问题5: LockSupport.park(Object blocker)传递的blocker对象做什么用?
答: 对应的blcoker会记录在Thread的一个parkBlocker属性中,通过jstack命令可以非常方便的监控具体的阻塞对象.
public static void park(Object blocker) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
setBlocker(t, blocker); // 设置Thread.parkBlocker属性的值
unsafe.park(false, 0L);
setBlocker(t, null); // 清除Thread.parkBlocker属性的值
}
具体LockSupport的javadoc描述也比较清楚,可以看下: 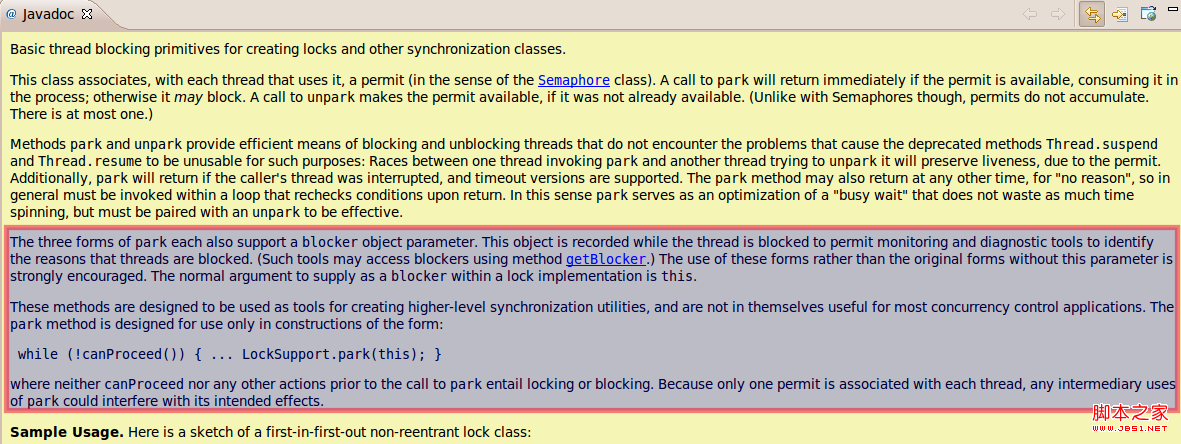
问题6: LockSupport能响应Thread.interrupt()事件不?会抛出InterruptedException异常?
答:能响应interrupt事件,但不会抛出InterruptedException异常。针对LockSupport对Thread.interrupte支持,也先看一下javadoc中的描述: 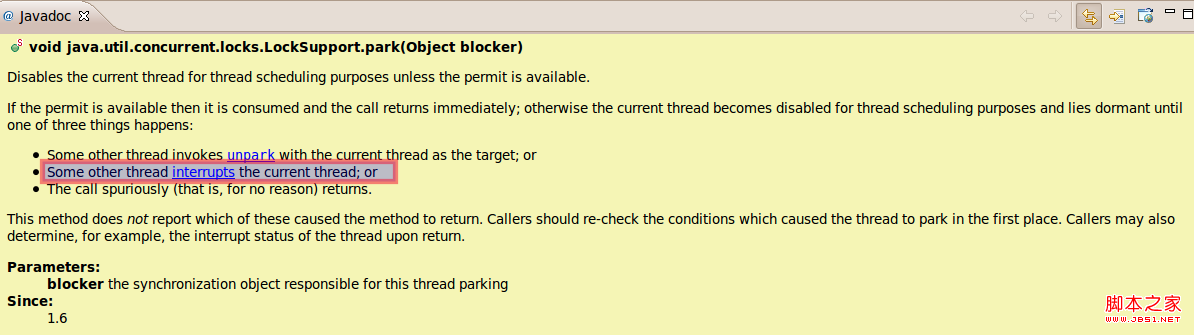
相关测试代码
package com.agapple.cocurrent;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class LockSupportTest {
private static LockSupportTest blocker = new LockSupportTest();
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
lockSupportTest();
parkTest();
interruptParkTest();
interruptSleepTest();
interruptWaitTest();
}
/**
* LockSupport.park对象后,尝试获取Thread.blocker对象,调用其single唤醒
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private static void lockSupportTest() throws Exception {
Thread t = doTest(new TestCallBack() {
@Override
public void callback() throws Exception {
// 尝试sleep 5s
System.out.println("blocker");
LockSupport.park(blocker);
System.out.println("wakeup now!");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "lockSupportTest";
}
});
t.start(); // 启动读取线程
Thread.sleep(150);
synchronized (blocker) {
Field field = Thread.class.getDeclaredField("parkBlocker");
field.setAccessible(true);
Object fBlocker = field.get(t);
System.out.println(blocker == fBlocker);
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("notifyAll");
blocker.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 尝试去中断一个object.wait(),会抛出对应的InterruptedException异常
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private static void interruptWaitTest() throws InterruptedException {
final Object obj = new Object();
Thread t = doTest(new TestCallBack() {
@Override
public void callback() throws Exception {
// 尝试sleep 5s
obj.wait();
System.out.println("wakeup now!");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "interruptWaitTest";
}
});
t.start(); // 启动读取线程
Thread.sleep(2000);
t.interrupt(); // 检查下在park时,是否响应中断
}
/**
* 尝试去中断一个Thread.sleep(),会抛出对应的InterruptedException异常
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private static void interruptSleepTest() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = doTest(new TestCallBack() {
@Override
public void callback() throws Exception {
// 尝试sleep 5s
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("wakeup now!");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "interruptSleepTest";
}
});
t.start(); // 启动读取线程
Thread.sleep(2000);
t.interrupt(); // 检查下在park时,是否响应中断
}
/**
* 尝试去中断一个LockSupport.park(),会有响应但不会抛出InterruptedException异常
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private static void interruptParkTest() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = doTest(new TestCallBack() {
@Override
public void callback() {
// 尝试去park 自己线程
LockSupport.parkNanos(blocker, TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(5));
System.out.println("wakeup now!");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "interruptParkTest";
}
});
t.start(); // 启动读取线程
Thread.sleep(2000);
t.interrupt(); // 检查下在park时,是否响应中断
}
/**
* 尝试去中断一个LockSupport.unPark(),会有响应
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private static void parkTest() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = doTest(new TestCallBack() {
@Override
public void callback() {
// 尝试去park 自己线程
LockSupport.park(blocker);
System.out.println("wakeup now!");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "parkTest";
}
});
t.start(); // 启动读取线程
Thread.sleep(2000);
LockSupport.unpark(t);
t.interrupt();
}
public static Thread doTest(final TestCallBack call) {
return new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
File file = new File("/dev/urandom"); // 读取linux黑洞
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (in.read(bytes, 0, 1024) > 0) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException("");
}
System.out.println(bytes[0]);
Thread.sleep(100);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
call.callback();
System.out.println(call.getName() + " callback finish cost : "
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}
}
interface TestCallBack {
public void callback() throws Exception;
public String getName();
}
最后
发觉文章越写越长,那就索性发到了论坛,大家一起讨论下.毕竟文章中描述的都是一些使用层面的东东,并没有从操作系统或者sun native实现上去介绍Thread的一些机制,熟悉这块的大牛门也可以出来发表下高见.