聚合
考虑这样一个场景,如果我们要开发一个电商系统,按照现在流行的微服务架构,肯定是希望前端和后端独立成两个项目分别进行开发和部署,但前端和后端很多时候有共同的业务。比如,笔者就曾经遇到后端可以帮助用户下单,逻辑与前端用户下单的业务逻辑一致,如果两个项目独立开发,那么下单的代码势必要在两个项目中重复编写,未来如果下单的逻辑有变化,两个项目也要进行修改。Maven的聚合特性能够把不同项目的各个模块聚合在一起构件,让我们避免上面的烦恼。
我们还是用代码来举例,假设我们有个hello项目,我们在这个项目划分三个层:pojo、service和app。pojo层中有个User对象,用来装载用户的姓名,service层有个HelloService类,提供一个返回String类型的sayHello(User user)业务方法,app层负责调用service层的业务方法。现在我们将通过这个hello项目来实现Maven的聚合。
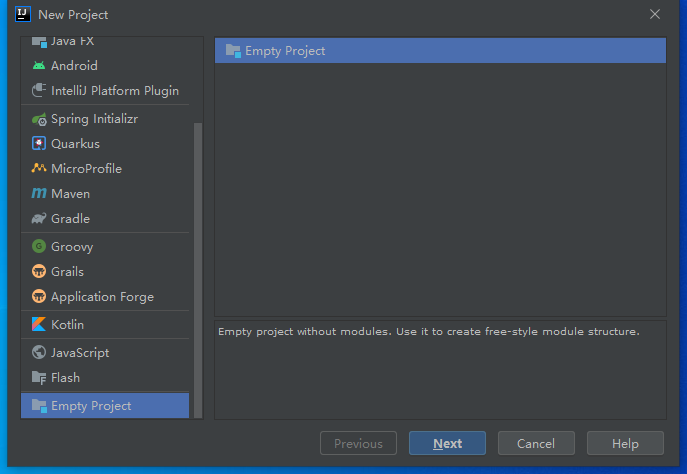
我们先创建一个名为hello的空项目:
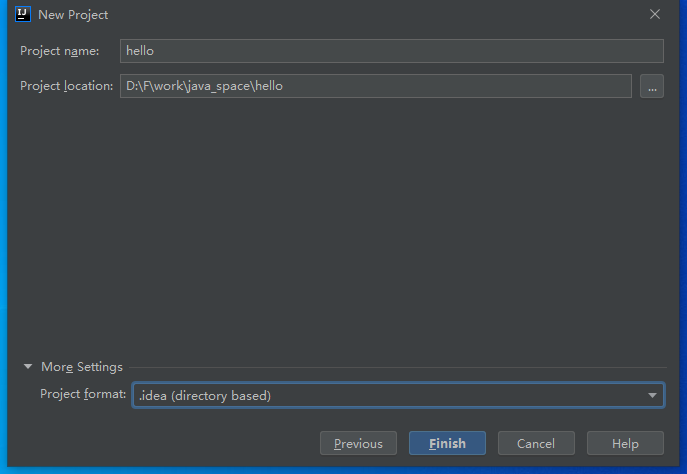
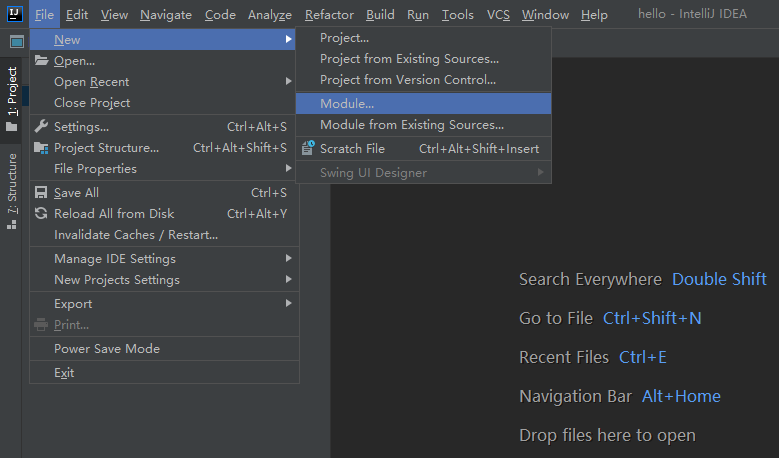
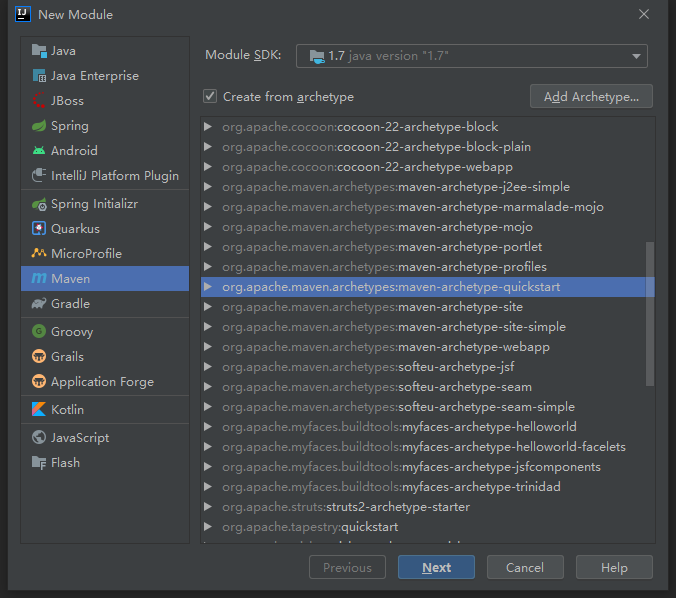
然后选择Module,创建quickstart为骨架创建一个名为hello-parent的Maven项目:
hello-parent项目创建完毕后,我们在pom.xml文件中的坐标处加入<packaging>pom</packaging>:
<groupId>com.leolin.mvnbook</groupId> <artifactId>hello-parent</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>pom</packaging>
然后,我们再按照之前的方式创建一个新的Module,名为hello-pojo:
我们在hello-pojo项目pom.xml文件的坐标处,加入<packaging>jar</packaging>:
<artifactId>hello-pojo</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging>
我们对hello-pojo项目进行Maven→Reimport,然后删除com.leolin.mvnbook下的App文件,并创建pojo包,在pojo包下新建User类:
package com.leolin.mvnbook.pojo;
public class User {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
我们再建立一个名为hello-service的Module:

hello-service创建完毕后,我们pom.xml文件中加入packaging元素,并加入对hello-pojo的依赖:
<artifactId>hello-service</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.leolin.mvnbook</groupId> <artifactId>hello-pojo</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
然后对hello-service进行Maven→Reimport,我们删除该项目原先的App.java文件,并创建service目录,在service目录下创建HelloService.java文件:
package com.leolin.mvnbook.service;
import com.leolin.mvnbook.pojo.User;
public class HelloService {
public String sayHello(User user) {
return "hello " + user.getName();
}
}
我们可以看到,虽然hello-service和hello-pojo都是独立的Maven项目,但hello-service在pom中加入hello-pojo的依赖,就可以引用hello-pojo了。那么按照之前所说的,我们还有个app项目,这个app项目会依赖service,调用service的方法。现在,我们动手创建app:
在pom.xml文件中加入对packaging和hello-service的依赖:
<artifactId>hello-app</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.leolin.mvnbook</groupId> <artifactId>hello-service</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
对项目Reimport之后,我们可以在App.java文件中尝试调用HelloService中的sayHello(User user)方法:
package com.leolin.mvnbook;
import com.leolin.mvnbook.pojo.User;
import com.leolin.mvnbook.service.HelloService;
/**
* Hello world!
*/
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User("Jack");
HelloService service = new HelloService();
System.out.println(service.sayHello(user));
}
}
运行App文件,可以看到控制台打印出:
hello Jack
至此,我们通过Maven的聚合解决了同一个系统,不同模块独立运行部署时产生的代码冗余的问题。
继承
现在,让我们在回到开头提的电商系统,如果我们的领导,希望电商系统不仅做到前端后端分离,且前端不同模块,比如:订单模块、商品模块、物流模块,也要独立部署运行。这看上去并不是什么难题,无非就是多建几个Maven项目而已,但我们细细一想,如果我们使用的是Spring Framework框架,那么在订单、商品、物流等模块的pom文件是不是引入相同的groupId和version。也有人说,我们可以在专门在一个Maven项目中存放我们的依赖,然后将那个Maven项目引入进来,这个办法确实可行,但如果有一个项目,它仅依赖spring-core,却因为引入那个Maven项目也间接引入spring-context、spring-beans,这是不是造成没必要的冗余?
因此,Maven提供的depenencyManagement元素既能让子模块继承到父模块的元素,又能保证子模块的灵活性。代码如下:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.10</junit.version>
<spring.version>4.1.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
这里使用depenencyManagement声明的依赖不会给子模块间接引入依赖,不过这段配置是会被继承的。现在,修改hello-service的pom文件如下:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.leolin.mvnbook</groupId> <artifactId>hello-pojo</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
我们可以看到,spring-context和junit我们都没引入版本号,但Maven会去依赖hello-parent所定义的版本号。