In the following equation x, y, and n are positive integers.

For n = 4 there are exactly three distinct solutions:
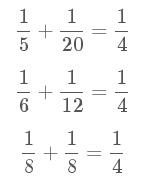
What is the least value of n for which the number of distinct solutions exceeds one-thousand?
NOTE: This problem is an easier version of Problem 110; it is strongly advised that you solve this one first.
在如下方程中,x、y、n均为正整数。

对于n = 4,上述方程恰好有3个不同的解:
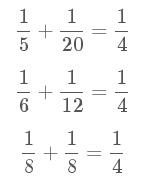
使得不同的解的数目超过1000的最小n值是多少?
注意:这个问题是第110题的简单版本;强烈推荐先解决这一题。
解题
这是一道很难的题目
先说暴力解法,普通暴力不行
1/x + 1/y = 1/n -> y = (n*x)/(x -n) 可以发现 只要 n*x能够整除(x-n)就是一个解了
能够找出x的范围就可以暴力解决
y = (n*x)/(x -n) 可以发现 x一定大于n,由于x y一定要是正数。
x=y=2n的时候上面等式也成了
假设x<=y 则y/x>=1 n/(x-n)>=1
2n>=x
x的取值范围就是n 到 2n
用javalong出现溢出的情况,Python好像时间很长,我用180180验证能够出来的
# coding=gbk def run(): for n in range(10,180181): count = 0 for x in range(n+1,2*n+1): if (n*x)%(x-n)==0: count+=1 if count>1000: print n if __name__ == '__main__': run()
技巧性解题
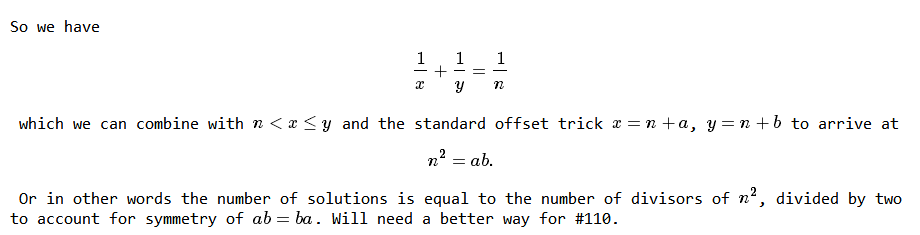

截图于mathblog
问题就转化为求d(N) 下面就很简单了
1,如何求许多素数,筛选法求素数
2,其他根据上面的就可以直接求解了
学会分析问题很重要,根据已学到的知识,解决没有见过的问题

package Level4; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set; public class PE0108{ public static void run(){ ArrayList<Integer> prime = getPrime(20); int n=2; while(true){ int count = getDiophantine(n,prime); count = (count+1)/2; if(count> 500){ System.out.println(n+" "+count); if(count>1000) break; } n++; } } // 174720 608 // 175560 851 // 176400 563 // 177840 608 // 179520 527 // 180180 1013 public static int getDiophantine(int n,ArrayList<Integer> prime){ int count = 1; int i=0; for(i=0;i<prime.size();i++){ int p = prime.get(i); int exp = 1; while(n %p ==0){ exp+=2; n=n/p; } count *=exp; if(n==1) return count; } return count; } // 求 前num个素数 public static ArrayList<Integer> getPrime(int num){ ArrayList<Integer> prime=new ArrayList<Integer>(); prime.add(2); // 除以已经判断是素数的数 boolean isPrime = true; for(int i=3;prime.size()<num;i++){ isPrime = true; for(int j=0;j<prime.size();j++){ if(i%prime.get(j) ==0){ isPrime = false; break; } } if(isPrime == true){ prime.add(i); } } return prime; } public static void run1(){ int MAX = 1000; int n=4; // 内存溢出使得程序运行错误 System.out.println(getCount(180180)); while(true){ int count =getCount(n); if(count >=600){ System.out.println(n+" "+count); if(count>MAX) break; } n++; } } public static int getCount(int n){ int count =0; for(int x=n+1;x<=2*n;x++){ long nx = n*x; System.out.println(nx); if( nx%(x-n)==0){ count++; } } return count; } public static void main(String[] args){ long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis(); run1(); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); long t = t1 - t0; System.out.println("running time="+t/1000+"s"+t%1000+"ms"); } }
