Problem A: 输出数组
题面:
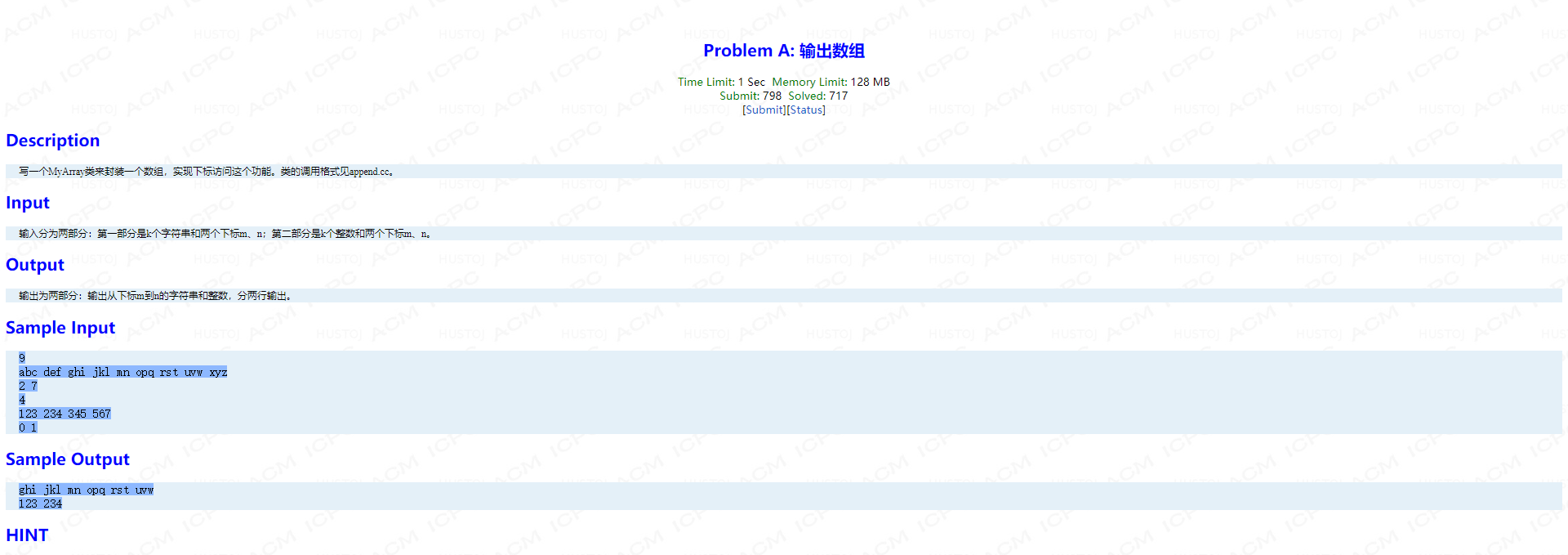
main函数:
int main() { int k, m, n; cin >> k; MyArray<string> s(k); for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) cin >> s[i]; cin >> m >> n; cout << s[m]; for(int i = m + 1; i <= n; i++) cout << " " << s[i]; cout << endl; cin >> k; MyArray<int> a(k); for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) cin >> a[i]; cin >> m >> n; cout << a[m]; for(int i = m + 1; i <= n; i++) cout << " " << a[i]; cout << endl; }
考点:下标运算符的重载,vector的使用。
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; template<class T> class MyArray { vector<T> arr; public: MyArray(int k){arr.resize(k);} T& operator [](int k) { return arr[k]; } };
Problem B: 循环交换
题面:

main函数:
int main() { int a, b, c, k; cin >> a >> b >> c; while(cin >> k) { if(k == 0) swp(a, b, c); else swp(a, b, c, k); cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << endl; } }
考点:传引用,默认参数,还有算是swap的灵活应用吧,对于a,b,c三个数,左移 = (swap(a,b)+swap(b,c));右移 = (swap(b,c)+swap(a,b))。
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; void swp(int &a,int &b,int &c,int k = 0 ) { if(k==0) { swap(a,b); swap(b,c); } else { for(int i = 0;i<k;i++) { swap(b,c); swap(a,b); } } }
Problem C: 薪酬计算 之二
题面:
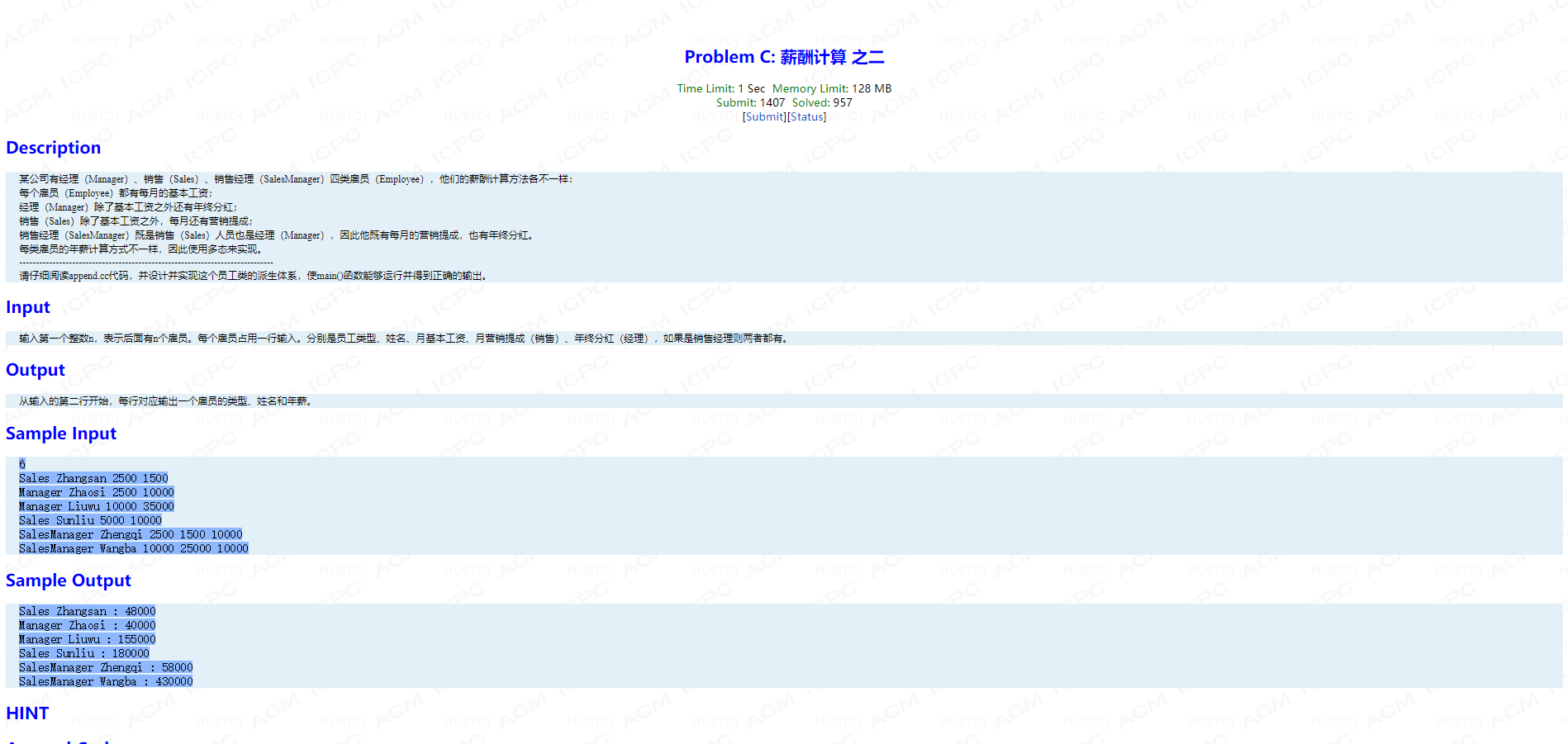
main函数:
int main() { string label, name; Employee* p[100]; int n; int base, royalty, bonus; cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> label >> name; if(label == "Sales") { cin >> base >> royalty; p[i] = new Sales(name, base, royalty); } if(label == "Manager") { cin >> base >> bonus; p[i] = new Manager(name, base, bonus); } if(label == "SalesManager") { cin >> base >> royalty >> bonus; p[i] = new SalesManager(name, base, royalty, bonus); } } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) p[i]->print(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) delete p[i]; }
考点:类的继承,虚基类
AC代码:
#include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Employee { friend class Sales; friend class Manager; friend class SalesManager; string name ; int base; public: Employee(string _name,int _b):name(_name),base(_b){} virtual void print()=0; }; class Sales:public Employee { int ti; public: Sales(string _n,int _b,int _r):Employee(_n,_b),ti(_r){} void print() { cout << "Sales "; cout << name; cout << " : " <<(ti+base)*12 << endl; } }; class Manager:public Employee { int ti; public: Manager(string _n,int _b,int _r):Employee(_n,_b),ti(_r){} void print() { cout << "Manager "; cout << name; cout << " : " <<base*12+ti << endl; } }; class SalesManager:public Employee { int ti,b; public: SalesManager(string _n,int _b,int _r,int _s):Employee(_n,_b),ti(_r),b(_s){} void print() { cout << "SalesManager "; cout << name; cout << " : " <<(ti+base)*12+b << endl; } };
Problem D: 儿童绘画游戏
题面:
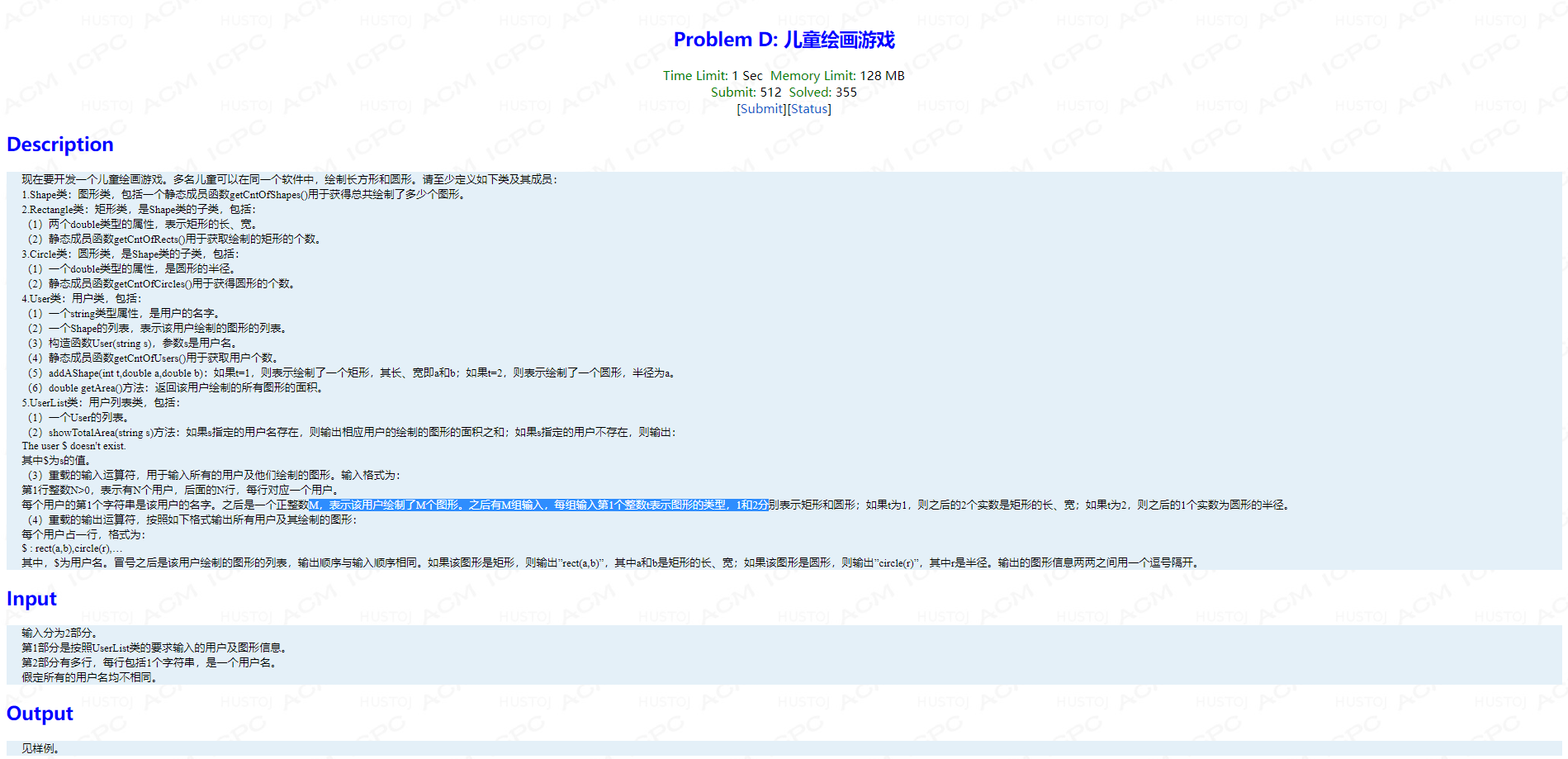

main函数:
int main() { cout<<"In beginning, "<<User::getCntOfUsers()<<" users,"; cout<<Shape::getCntOfShapes()<<" shapes."<<endl; User tmp("C++"); tmp.addAShape(1, 1, 2); tmp.addAShape(2, 3); cout<<tmp.getArea()<<endl; UserList lst; string s1; cin>>lst; cout<<"Now, "<<User::getCntOfUsers()<<" users,"; cout<<Shape::getCntOfShapes()<<" shapes, including "; cout<<Circle::getCntOfCircles()<<" circles, and "; cout<<Rectangle::getCntOfRects()<<" rectangles."<<endl; cout<<lst; while(cin>>s1) { lst.showTotalArea(s1); } return 0; }
考点:静态数据成员,虚基类,输入输出流的重载。
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <typeinfo> using namespace std; const double PI = 3.14; class Shape { static int CntOfShapes; public: Shape(){CntOfShapes++;} virtual double getArea()=0; static int getCntOfShapes() { return CntOfShapes; } virtual void print()=0; virtual ~Shape(){}; }; class UserList; class Rectangle:public Shape { double length,width; static int CntOfRects; public: Rectangle(double _length,double _width):Shape(),length(_length),width(_width){CntOfRects++;} double getArea() { return length*width; } static int getCntOfRects() { return CntOfRects; } void print() { cout << "rect(" << length << "," << width << ")"; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); ~Rectangle(){} }; class Circle:public Shape { double radius; static int CntOfCircles; public: Circle(double _radius):Shape(),radius(_radius){CntOfCircles++;} static int getCntOfCircles() { return CntOfCircles; } double getArea() { return PI*radius*radius; } void print() { cout << "Circle(" << radius << ")"; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); ~Circle(){} }; class User { friend class UserList; string name; vector<Shape*> ShapeList; static int CntOfUsers; public: User(){} User(string _name):name(_name){CntOfUsers++;} static int getCntOfUsers() { return CntOfUsers; } void addAShape(int t,double a,double b = 0) { if(t==1) ShapeList.push_back(new Rectangle(a,b)); else ShapeList.push_back(new Circle(a)); } double getArea() { double ans = 0; int len = ShapeList.size(); for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { ans += ShapeList[i]->getArea(); } return ans; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); ~User(){} }; class UserList { vector<User*> Userlist; public: void showTotalArea(string name) { int len = Userlist.size(); for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { if(Userlist[i]->name == name) { cout << Userlist[i]->getArea() << endl; return ; } } cout << "The user "; cout << name; cout << " doesn't exist." << endl; return ; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); }; istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul) { int N,M,t; double a,b; in >> N; ul.Userlist.resize(N); for(int i = 0;i<N;i++) { ul.Userlist[i] = new User; in >> ul.Userlist[i]->name; in >> M; for(int j = 0;j<M;j++) { //cout << "Begin" << endl; in >> t; if(t==1) { in >> a >> b; ul.Userlist[i]->addAShape(t,a,b); } else { in >> a; ul.Userlist[i]->addAShape(t,a); } // cout << "END" << endl; } } return in; } ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul) { int len = ul.Userlist.size(); for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { out << ul.Userlist[i]->name; out << " : "; int len1 = ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList.size(); for(int j = 0;j<len1;j++) { ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList[j]->print(); if(j!=len1-1) out << ","; else out << " "; } } return out; } int Shape::CntOfShapes = 0; int Rectangle::CntOfRects = 0; int Circle::CntOfCircles = 0; int User::CntOfUsers = 0;
略有不同的另一个版本:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <typeinfo> using namespace std; const double PI = 3.14; class Shape { static int CntOfShapes; public: Shape(){CntOfShapes++;} virtual double getArea()=0; static int getCntOfShapes() { return CntOfShapes; } virtual ~Shape(){}; }; class UserList; class Rectangle:public Shape { double length,width; static int CntOfRects; public: Rectangle(double _length,double _width):Shape(),length(_length),width(_width){CntOfRects++;} double getArea() { return length*width; } static int getCntOfRects() { return CntOfRects; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); ~Rectangle(){} }; class Circle:public Shape { double radius; static int CntOfCircles; public: Circle(double _radius):Shape(),radius(_radius){CntOfCircles++;} static int getCntOfCircles() { return CntOfCircles; } double getArea() { return PI*radius*radius; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); ~Circle(){} }; class User { friend class UserList; string name; vector<Shape*> ShapeList; static int CntOfUsers; public: User(){} User(string _name):name(_name){CntOfUsers++;} static int getCntOfUsers() { return CntOfUsers; } void addAShape(int t,double a,double b = 0) { if(t==1) ShapeList.push_back(new Rectangle(a,b)); else ShapeList.push_back(new Circle(a)); //cout << 1 << endl; } double getArea() { double ans = 0; int len = ShapeList.size(); for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { ans += ShapeList[i]->getArea(); } return ans; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); ~User(){} }; class UserList { vector<User*> Userlist; public: void showTotalArea(string name) { int len = Userlist.size(); for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { if(Userlist[i]->name == name) { cout << Userlist[i]->getArea() << endl; return ; } } cout << "The user "; cout << name; cout << " doesn't exist." << endl; return ; } friend istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul); friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul); }; istream& operator >> (istream& in,UserList& ul) { int N,M,t; double a,b; in >> N; ul.Userlist.resize(N); for(int i = 0;i<N;i++) { ul.Userlist[i] = new User; in >> ul.Userlist[i]->name; in >> M; for(int j = 0;j<M;j++) { //cout << "Begin" << endl; in >> t; if(t==1) { in >> a >> b; ul.Userlist[i]->addAShape(t,a,b); } else { in >> a; ul.Userlist[i]->addAShape(t,a); } // cout << "END" << endl; } } return in; } ostream& operator << (ostream& out,const UserList& ul) { int len = ul.Userlist.size(); for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { out << ul.Userlist[i]->name; out << " : "; int len1 = ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList.size(); for(int j = 0;j<len1;j++) { if(typeid(*(ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList[j]))==typeid(Rectangle)) { out << "rect(" << ((Rectangle*)(ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList[j]))->length << "," << ((Rectangle*)(ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList[j]))->width << ")"; } else { out << "circle(" << ((Circle*)(ul.Userlist[i]->ShapeList[j]))->radius << ")" ; } if(j!=len1-1) out << ","; else out << " "; } } return out; } int Shape::CntOfShapes = 0; int Rectangle::CntOfRects = 0; int Circle::CntOfCircles = 0; int User::CntOfUsers = 0;
Problem E: 向量的删除
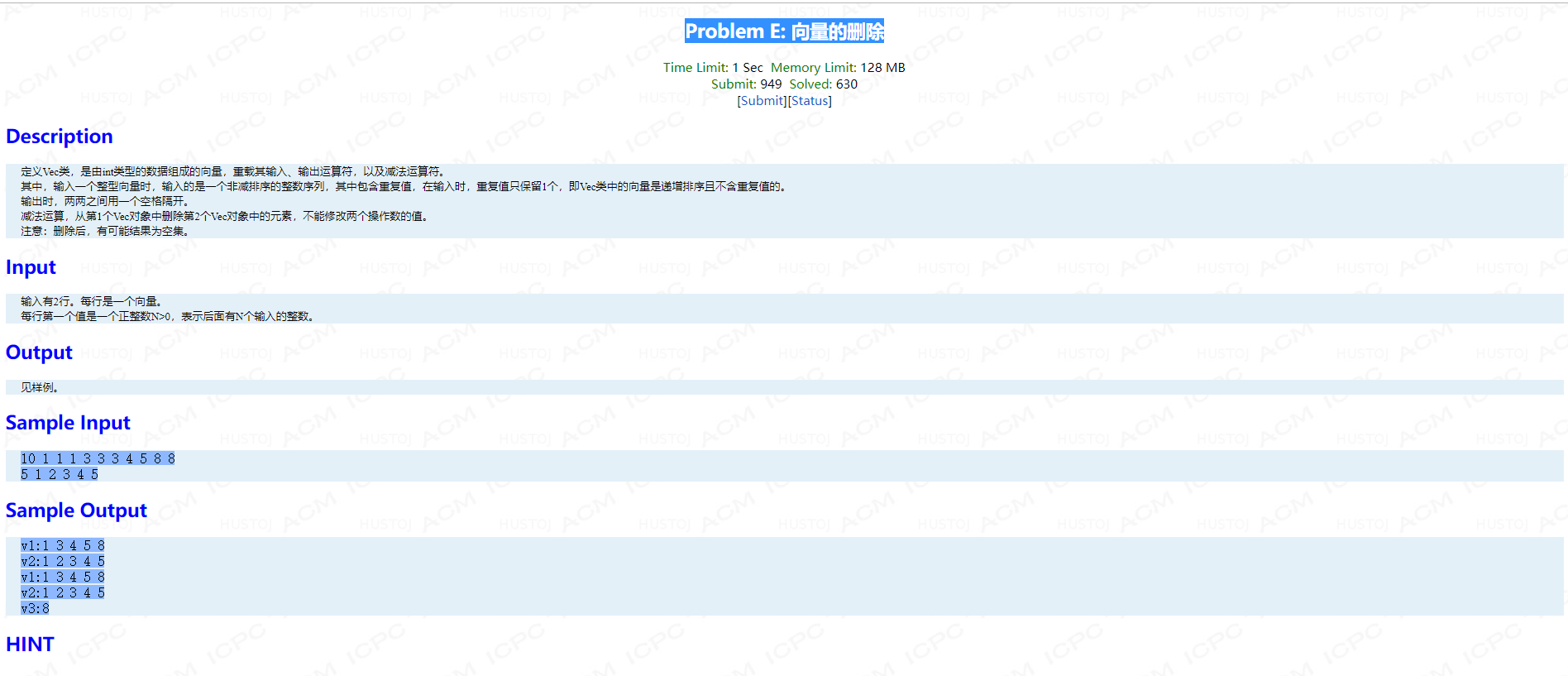
main函数:
int main() { Vec v1, v2, v3; cin>>v1; cin>>v2; cout<<"v1:"<<v1; cout<<"v2:"<<v2; v3 = v1 - v2; cout<<"v1:"<<v1; cout<<"v2:"<<v2; cout<<"v3:"<<v3; return 0; }
考点:set的使用,输入输出运算符的重载。
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <set> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; class Vec { public: Vec() {} set<int> s; Vec(set<int>c):s(c) {}; friend istream &operator >> (istream &is,Vec&b); friend ostream& operator<< (ostream &os,Vec &b); Vec operator -(Vec &b) { set<int>c; set_difference(s.begin(),s.end(),b.s.begin(),b.s.end(),inserter(c, c.begin())); return Vec(c); } }; istream &operator >> (istream &is,Vec&b) { int a,k; is >> a; for(int i = 0; i<a; i++) { is>> k; b.s.insert(k); } return is; } ostream& operator<< (ostream &os,Vec &b) { if(b.s.size()==0) { os<< endl; return os; } set<int>::iterator it = b.s.begin(); os << *it; it++; for(it; it!=b.s.end(); ++it) os << " " << *it; os << endl; return os; }
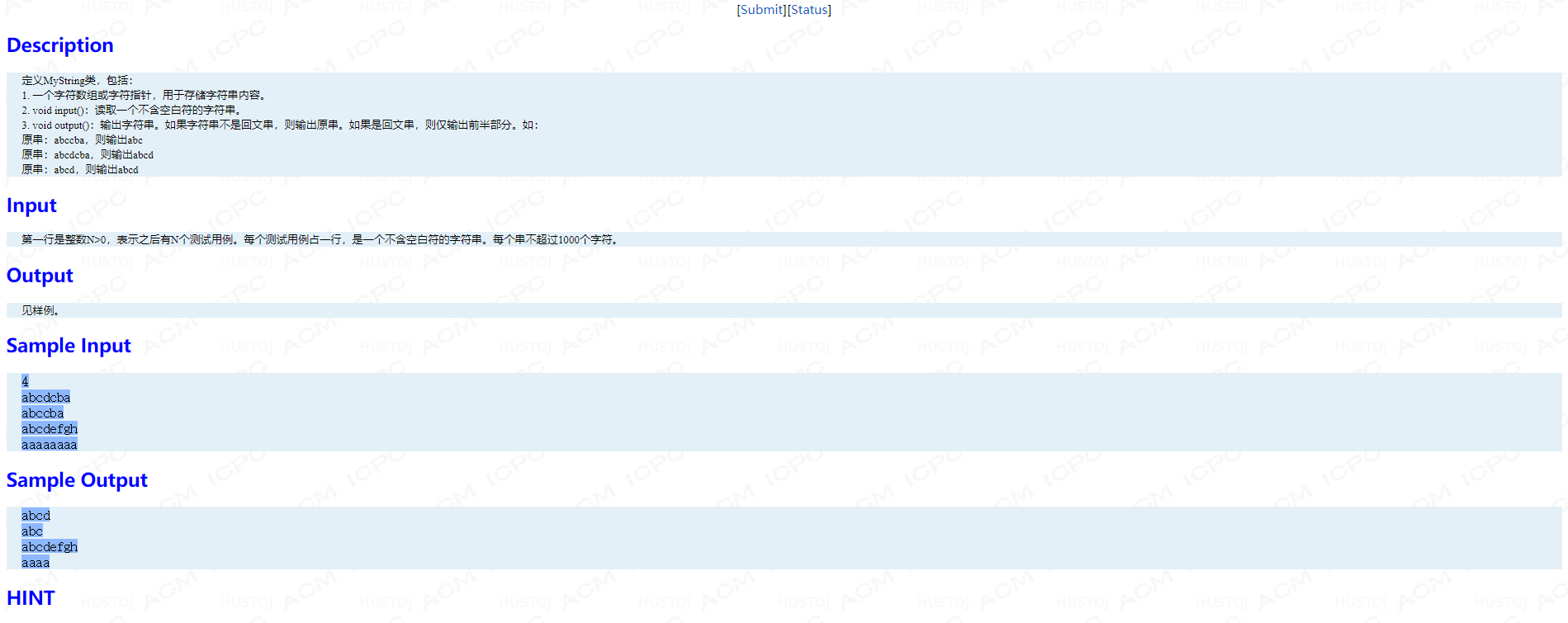
Problem F: 字符串折叠
题面:
main函数:
int main() { MyString str; int n, i; cin>>n; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { str.input(); str.output(); } return 0; }
考点:回文串的判断。
AC代码:
#include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; bool ok(string s) { int len = s.size(); for(int i = 0,j=len-1;i<=j;i++,j--) if(s[i]!=s[j]) return false; return true; } class MyString { public: string s; void input() { cin >> s; } void output() { if(ok(s)) { int len =s.size(); for(int i = 0 ;i<(len+1)/2;i++) cout << s[i]; cout << endl; } else cout << s << endl; } };
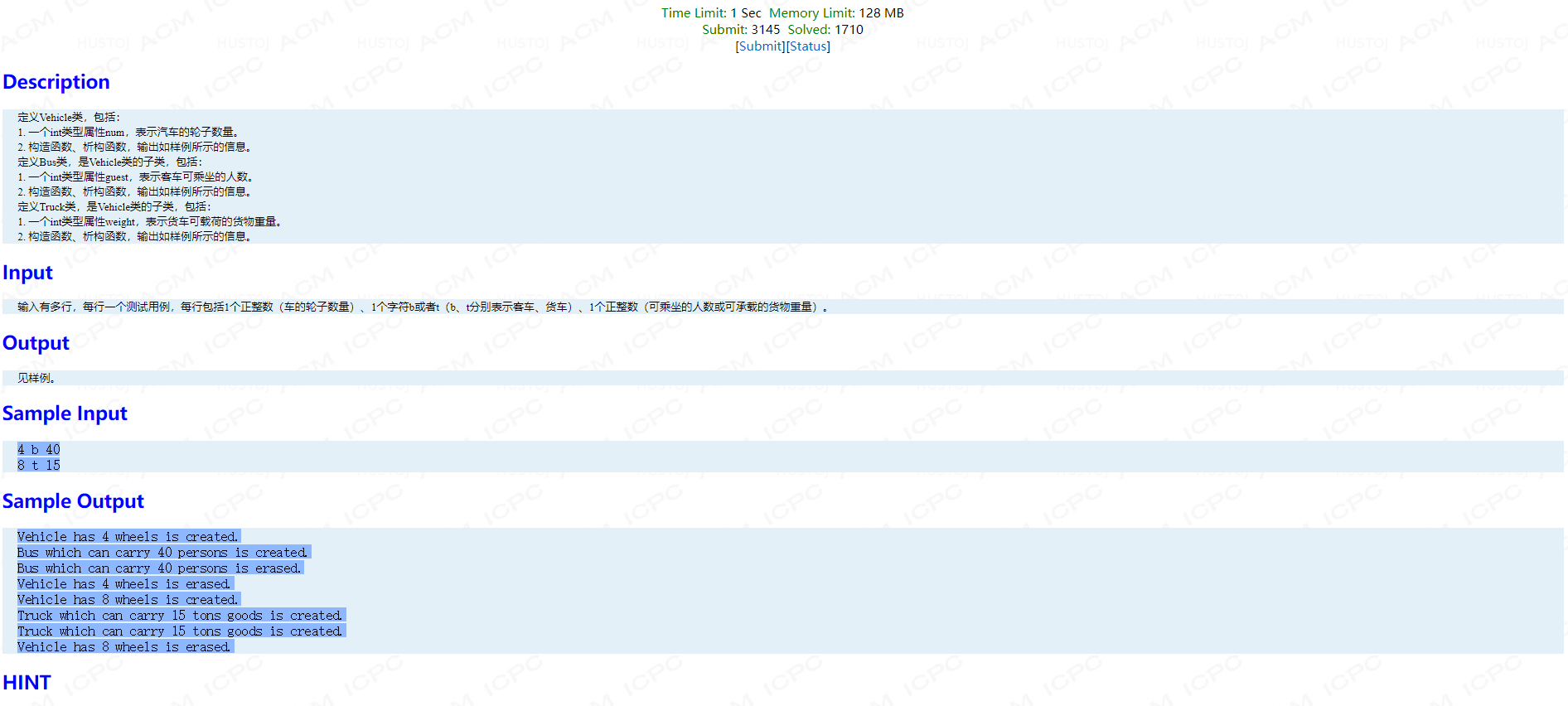
Problem G: 汽车、客车、货车
题面:
main函数:
int main() { int w, g; char t; Vehicle *veh; while (cin>>w>>t>>g) { if (t == 'b') { veh = new Bus(w, g); } else { veh = new Truck(w, g); } delete veh; } return 0; }
考点:类的继承
AC代码:
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Vehicle { public: int num; Vehicle(int n):num(n) { printf("Vehicle has %d wheels is created. ",num); } virtual ~Vehicle() { printf("Vehicle has %d wheels is erased. ",num); } }; class Bus:public Vehicle { public: int w; Bus(int _n,int _w):Vehicle(_n),w(_w) { printf("Bus which can carry %d persons is created. ",w); } ~Bus() { printf("Bus which can carry %d persons is erased. ",w); } }; class Truck:public Vehicle { public: int w; Truck(int _n,int _w):Vehicle(_n),w(_w) { printf("Truck which can carry %d tons goods is created. ",w); } ~Truck() { printf("Truck which can carry %d tons goods is created. ",w); } };
Problem H: 不一样的奇偶性

main函数:
int main() { int i; while(cin>>i) { Integer INT(i); if (INT.judge()) cout<<"YES"<<endl; else cout<<"NO"<<endl; } return 0; }
考点:类的使用
AC代码:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Integer { public: int data; Integer(int _d):data(_d){} bool judge() { int d = data; int num = 0; while(d) { num+=(d%10); d/=10; } if(num%2==0) return false; else return true; } };
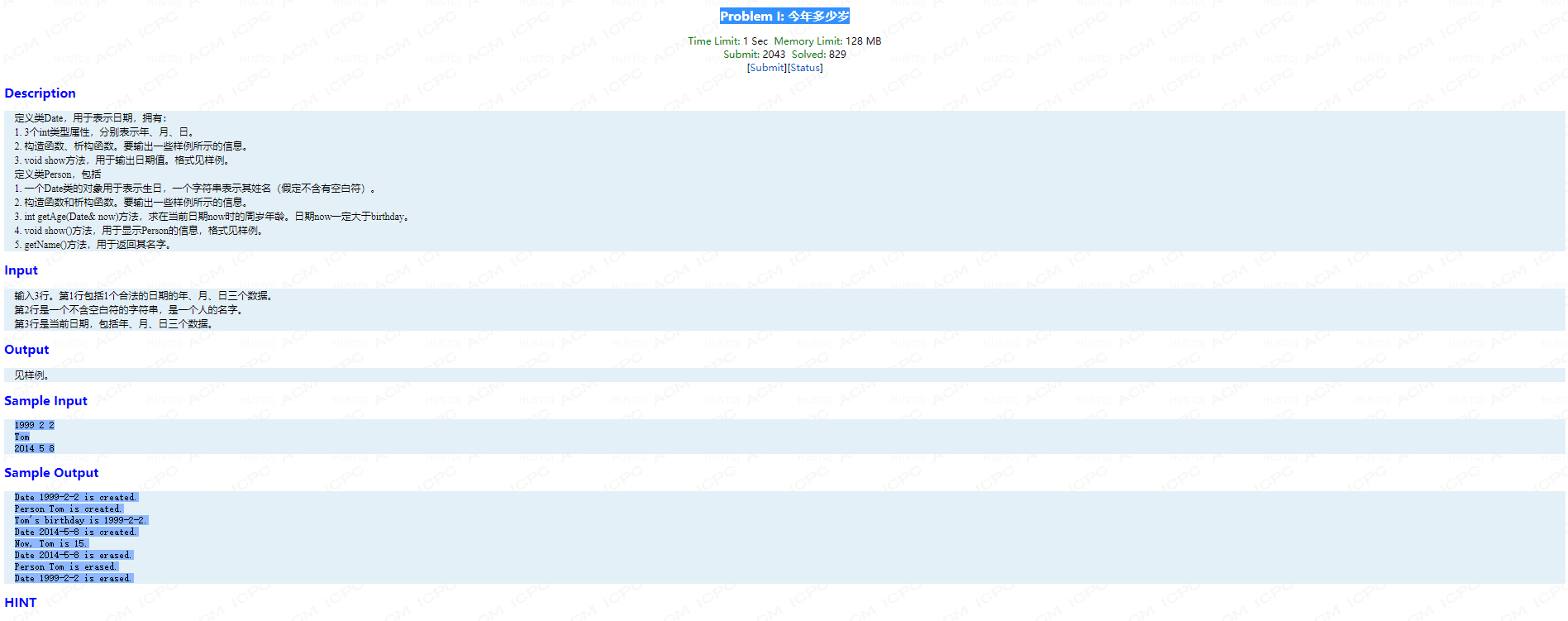
Problem I: 今年多少岁
main函数:
int main() { int y, m, d; string name; cin>>y>>m>>d>>name; Person person(y, m, d, name); person.show(); cin>>y>>m>>d; Date now(y,m,d); cout<<"Now, "<<person.getName()<<" is "<<person.getAge(now)<<"."<<endl; return 0; }
考点:类的使用(注意周岁的计算 ,只用算年的差)
AC代码:
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class Date { public: int y,m,d; Date(int _y,int _m,int _d):y(_y),m(_m),d(_d) { printf("Date %d-%d-%d is created. ",y,m,d); } ~Date() { printf("Date %d-%d-%d is erased. ",y,m,d); } }; class Person { public: Date bir; string name; Person(int y,int m,int d,string _s):bir(y,m,d),name(_s) { cout << "Person " <<name << " is created." << endl; } ~Person() { cout << "Person " <<name << " is erased." << endl; } int getAge(Date &b) { int d = b.y-bir.y; return d; } void show() { cout << name << "'s birthday is " ; printf("%d-%d-%d. ",bir.y,bir.m,bir.d); } string getName() { return name; } };
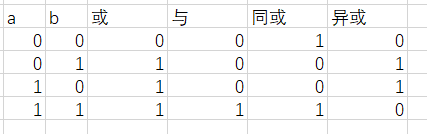
Problem J: 逻辑表达式

main函数:
int main() { int a, b; char ch; while (cin>>a>>ch>>b) { Logical log(a, b, ch); log.show(); } return 0; }
考点:逻辑运算符
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; class Logical { public: int a,b; char op; Logical(int _a, int _b, char _op):a(_a),b(_b),op(_op){} void show() { int d ; printf("%d %c %d = ",a,op,b); if(op=='+') { if(a!=b) d = 1; else d = 0; } else if(op=='-') { if(a==b) d = 1; else d = 0; } else if(op=='*') d = (a&&b); else if(op=='/') d = (a||b); printf("%d ",d); } };