Bus Pass |
| Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) |
| Total Submission(s): 82 Accepted Submission(s): 33 |
|
Problem Description
You travel a lot by bus and the costs of all the seperate tickets are starting to add up.
Therefore you want to see if it might be advantageous for you to buy a bus pass. The way the bus system works in your country (and also in the Netherlands) is as follows: when you buy a bus pass, you have to indicate a center zone and a star value. You are allowed to travel freely in any zone which has a distance to your center zone which is less than your star value. For example, if you have a star value of one, you can only travel in your center zone. If you have a star value of two, you can also travel in all adjacent zones, et cetera. You have a list of all bus trips you frequently make, and would like to determine the minimum star value you need to make all these trips using your buss pass. But this is not always an easy task. For example look at the following figure: 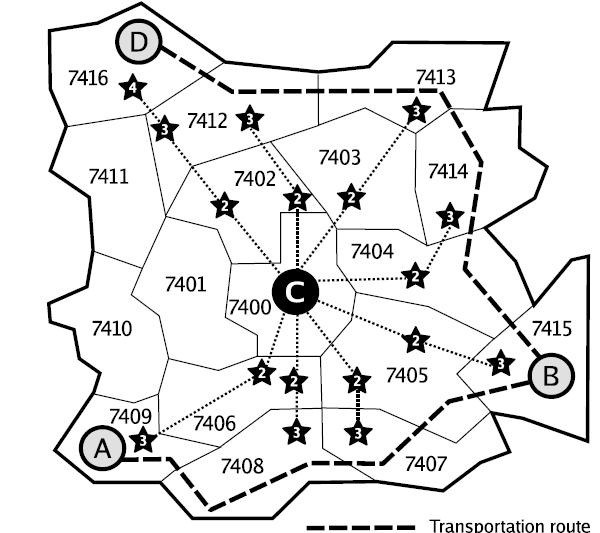 |
|
Input
On the first line an integert(1 <=t<= 100): the number of test cases. Then for each test case:
One line with two integersnz(2 <=nz<= 9 999) andnr(1 <=nr<= 10): the number of zones and the number of bus trips, respectively. nz lines starting with two integers idi (1 <= idi <= 9 999) and mzi (1 <= mzi <= 10), a number identifying the i-th zone and the number of zones adjacent to it, followed by mzi integers: the numbers of the adjacent zones. nr lines starting with one integer mri (1 <= mri <= 20), indicating the number of zones the ith bus trip visits, followed by mri integers: the numbers of the zones through which the bus passes in the order in which they are visited. All zones are connected, either directly or via other zones. |
|
Output
For each test case:
One line with two integers, the minimum star value and the id of a center zone which achieves this minimum star value. If there are multiple possibilities, choose the zone with the lowest number. |
|
Sample Input
1 17 2 7400 6 7401 7402 7403 7404 7405 7406 7401 6 7412 7402 7400 7406 7410 7411 7402 5 7412 7403 7400 7401 7411 7403 6 7413 7414 7404 7400 7402 7412 7404 5 7403 7414 7415 7405 7400 7405 6 7404 7415 7407 7408 7406 7400 7406 7 7400 7405 7407 7408 7409 7410 7401 7407 4 7408 7406 7405 7415 7408 4 7409 7406 7405 7407 7409 3 7410 7406 7408 7410 4 7411 7401 7406 7409 7411 5 7416 7412 7402 7401 7410 7412 6 7416 7411 7401 7402 7403 7413 7413 3 7412 7403 7414 7414 3 7413 7403 7404 7415 3 7404 7405 7407 7416 2 7411 7412 5 7409 7408 7407 7405 7415 6 7415 7404 7414 7413 7412 7416 |
|
Sample Output
4 7400 |
|
Source
bapc2007
|
|
Recommend
lcy
|
分析:计算公交路线上每个点到所有点的最短路,同时记录每个点的星级,最后枚举找到最小星级点。
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> using namespace std; typedef pair<int, int> pii; #define maxn 0xfffffff priority_queue <pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii> > q; int ans[10010], d[10010], vis[10010], ok[10010], have[10010]; int cnt, k; typedef struct S { int v; struct S *next; } EDGE; EDGE *node[10010], edge[100010]; void add(int a, int b) { edge[cnt].v = b; edge[cnt].next = node[a]; node[a] = &edge[cnt++]; } int main() { int T, n, m, a, b, mz, mr, i, j, s, pos; pii U; scanf("%d", &T); while (T--) { scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); memset(ok, 0, sizeof (ok)); memset(ans, 0, sizeof (ans)); for (i = 1; i <= 9999; ++i) { node[i] = NULL; } cnt = 0; k = 0; while (n--) { scanf("%d%d", &a, &mz); have[k++] = a; while (mz--) { scanf("%d", &b); add(a, b); } } while (m--) { scanf("%d", &mr); while (mr--) { scanf("%d", &s); if (ok[s]) continue; ok[s] = 1; memset(vis, 0, sizeof (vis)); for (i = 0; i < k; ++i) d[have[i]] = maxn; d[s] = 0; q.push(make_pair(d[s], s)); while (!q.empty()) { U = q.top(); q.pop(); a = U.second; vis[a] = 1; EDGE *temp; temp = node[a]; for (; temp; temp = temp->next) { b = temp->v; if (!vis[b] && d[a] + 1 < d[b]) { d[b] = d[a] + 1; q.push(make_pair(d[b], b)); } } } for (i = 0; i < k; ++i) { if (d[have[i]] > ans[have[i]]) ans[have[i]] = d[have[i]]; } } } int min = maxn; for (i = 0; i < k; ++i) { if (ans[have[i]] < min || (ans[have[i]]==min && have[i]<have[pos])) { min = ans[have[i]]; pos = i; } } printf("%d %d\n", min + 1, have[pos]); } return 0; }