机器学习的分类:
有监督学习:
基于连续输出称为回归,如股票预测
基于离散量输出为分类,如数字识别
(常见的有监督学习:回归预测分析,分类;垃圾邮件检测;模式检测;自然语言处理;情绪分析;自动图像分类;自动序列生成等)
无监督的学习:
对象分割,相似性检测,自动标记
强化学习:
(不懂啊,是不是还有一个半监督学习,还是看周志华的机器学习那本吧,现在是意大利的一个人的书)
特征选择与特征工程:
创建训练集和测试集:
训练和测试数据集要满足原始数据分布,并随机混合,避免出现连续元素之间的相关性。
一种将数据分割开为训练和测试的方法如下:0.75:0.25。随机数种子1000,用于再现实验过程等
1 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 2 X_train,X_test,Y_train,Y_test = train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.25,random_state=1000)
管理分类数据,将数据转换为数字量等:
#创建 import numpy as np X = np.random.uniform(0.0,1.0,size=(10,2)) Y = np.random.choice(('Male','Female'),size=(10)) #管理,输出为数字量表示 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder le = LabelEncoder() yt = le.fit_transform(Y) print(yt)
获得反向的数据:
output = [1,0,1,1,0,0] decoded_output = [le.classes_[i] for i in output] decoded_output
其他方法的编码,如独热编码:每个数据标签转化为一个数组,数组为只有一个特征为1其它为0的数组量:
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer lb = LabelBinarizer() Yb = lb.fit_transform(Y) Yb#独热编码
数据量较小时,还可以采用其它编码:
data = [ {'feature_1':10.0,'feature_2':15.0}, {'feature_1':-5.0,'feature_3':33.0}, {'feature_3':-2.0,'feature_4':10.0} ] from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer,FeatureHasher dv = DictVectorizer() Y_dict = dv.fit_transform(data) Y_dict.todense() #可以产生稀疏矩阵

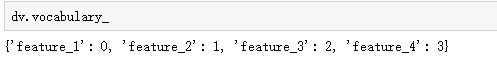
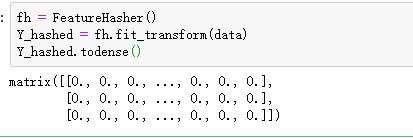
使用oneHotEncoding提供的独热编码:第一个数字进行了编码:
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder data1 = [ [0, 10], [1, 11], [1, 8], [0, 12], [0, 15] ] oh = OneHotEncoder(categorical_features=[0]) Y_oh = oh.fit_transform(data1) Y_oh.todense()

管理缺失特征:对缺失的数据进行平均值,中值,频率的补全
import numpy as np from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer data = np.array([[1, np.nan, 2], [2, 3, np.nan], [-1, 4, 2]]) print(data) # Imputer with mean-strategy print('Mean strategy') imp = Imputer(strategy='mean') print(imp.fit_transform(data)) # Imputer with median-strategy print('Median strategy') imp = Imputer(strategy='median') print(imp.fit_transform(data)) # Imputer with most-frequent-strategy print('Most-frequent strategy') imp = Imputer(strategy='most_frequent') print(imp.fit_transform(data))

数据缩放和归一化:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, RobustScaler 5 # For reproducibility 6 np.random.seed(1000) 7 if __name__ == '__main__': 8 # Create a dummy dataset 9 data = np.ndarray(shape=(100, 2)) 10 for i in range(100): 11 data[i, 0] = 2.0 + np.random.normal(1.5, 3.0) 12 data[i, 1] = 0.5 + np.random.normal(1.5, 3.0) 13 # Show the original and the scaled dataset 14 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5)) 15 16 ax[0].scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1]) 17 ax[0].set_xlim([-10, 10]) 18 ax[0].set_ylim([-10, 10]) 19 ax[0].grid() 20 ax[0].set_xlabel('X') 21 ax[0].set_ylabel('Y') 22 ax[0].set_title('Raw data') 23 24 # Scale data 25 ss = StandardScaler() 26 scaled_data = ss.fit_transform(data) 27 28 ax[1].scatter(scaled_data[:, 0], scaled_data[:, 1]) 29 ax[1].set_xlim([-10, 10]) 30 ax[1].set_ylim([-10, 10]) 31 ax[1].grid() 32 ax[1].set_xlabel('X') 33 ax[1].set_ylabel('Y') 34 ax[1].set_title('Scaled data') 35 36 plt.show() 37 38 # Scale data using a Robust Scaler 39 fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 8)) 40 41 ax[0, 0].scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1]) 42 ax[0, 0].set_xlim([-10, 10]) 43 ax[0, 0].set_ylim([-10, 10]) 44 ax[0, 0].grid() 45 ax[0, 0].set_xlabel('X') 46 ax[0, 0].set_ylabel('Y') 47 ax[0, 0].set_title('Raw data') 48 49 rs = RobustScaler(quantile_range=(15, 85)) 50 scaled_data = rs.fit_transform(data) 51 52 ax[0, 1].scatter(scaled_data[:, 0], scaled_data[:, 1]) 53 ax[0, 1].set_xlim([-10, 10]) 54 ax[0, 1].set_ylim([-10, 10]) 55 ax[0, 1].grid() 56 ax[0, 1].set_xlabel('X') 57 ax[0, 1].set_ylabel('Y') 58 ax[0, 1].set_title('Scaled data (15% - 85%)') 59 60 rs1 = RobustScaler(quantile_range=(25, 75)) 61 scaled_data1 = rs1.fit_transform(data) 62 63 ax[1, 0].scatter(scaled_data1[:, 0], scaled_data1[:, 1]) 64 ax[1, 0].set_xlim([-10, 10]) 65 ax[1, 0].set_ylim([-10, 10]) 66 ax[1, 0].grid() 67 ax[1, 0].set_xlabel('X') 68 ax[1, 0].set_ylabel('Y') 69 ax[1, 0].set_title('Scaled data (25% - 75%)') 70 71 rs2 = RobustScaler(quantile_range=(30, 65)) 72 scaled_data2 = rs2.fit_transform(data) 73 74 ax[1, 1].scatter(scaled_data2[:, 0], scaled_data2[:, 1]) 75 ax[1, 1].set_xlim([-10, 10]) 76 ax[1, 1].set_ylim([-10, 10]) 77 ax[1, 1].grid() 78 ax[1, 1].set_xlabel('X') 79 ax[1, 1].set_ylabel('Y') 80 ax[1, 1].set_title('Scaled data (30% - 60%)') 81 82 plt.show()
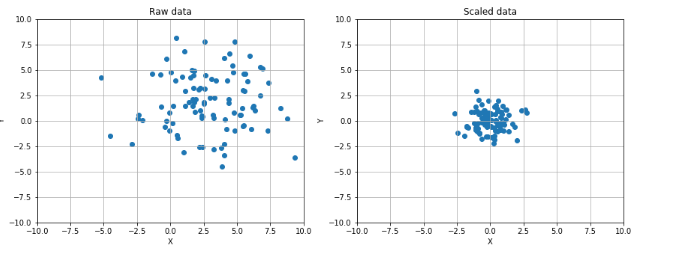
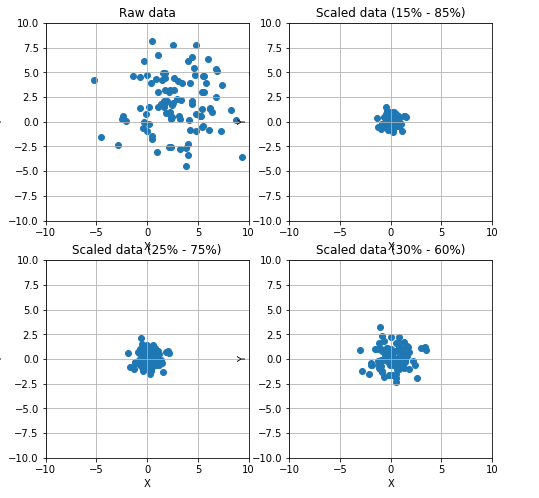
其中的Max L1 L2的缩放定义如下:
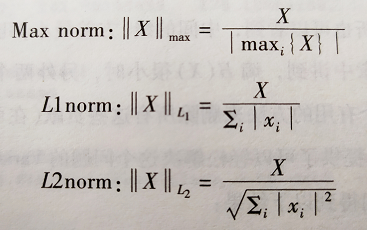
特征选择和过滤:过滤掉信息量比较少的变量:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold 7 8 # For reproducibility 9 np.random.seed(1000) 10 11 if __name__ == '__main__': 12 # Create a dummy dataset 13 X = np.ndarray(shape=(100, 3)) 14 15 X[:, 0] = np.random.normal(0.0, 5.0, size=100) 16 X[:, 1] = np.random.normal(0.5, 5.0, size=100) 17 X[:, 2] = np.random.normal(1.0, 0.5, size=100) 18 19 # Show the dataset 20 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 8)) 21 ax.grid() 22 ax.set_xlabel('X') 23 ax.set_ylabel('Y') 24 25 ax.plot(X[:, 0], label='STD = 5.0') 26 ax.plot(X[:, 1], label='STD = 5.0') 27 ax.plot(X[:, 2], label='STD = 0.5') 28 29 plt.legend() 30 plt.show() 31 32 # Impose a variance threshold 33 print('Samples before variance thresholding') 34 print(X[0:10, :]) 35 36 vt = VarianceThreshold(threshold=1.5) 37 X_t = vt.fit_transform(X) 38 39 # After the filter has removed the componenents 40 print('Samples after variance thresholding') 41 print(X_t[0:10, :])
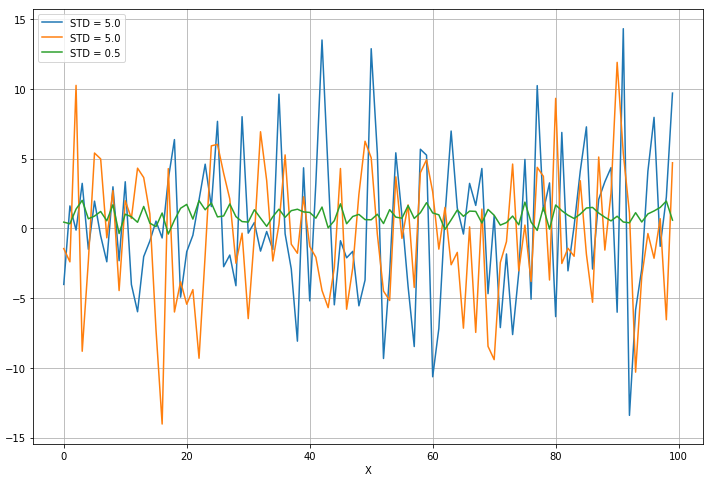
第三列是方差小的那一列,所以第三列被去掉了:

对MNIST做主成分分析!:

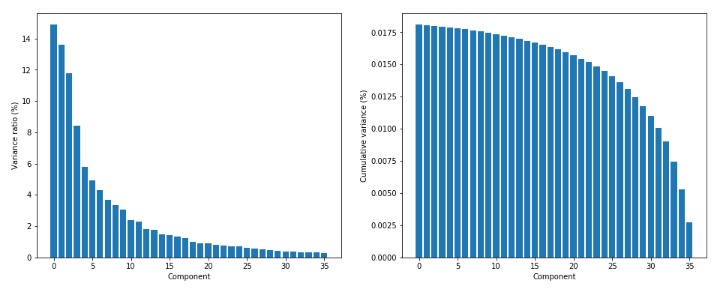
1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 7 from sklearn.decomposition import PCA 8 9 # For reproducibility 10 np.random.seed(1000) 11 12 if __name__ == '__main__': 13 # Load MNIST digits 14 digits = load_digits() 15 16 # Show some random digits 17 selection = np.random.randint(0, 1797, size=100) 18 19 fig, ax = plt.subplots(10, 10, figsize=(10, 10)) 20 21 samples = [digits.data[x].reshape((8, 8)) for x in selection] 22 23 for i in range(10): 24 for j in range(10): 25 ax[i, j].set_axis_off() 26 ax[i, j].imshow(samples[(i * 8) + j], cmap='gray') 27 28 plt.show() 29 30 # Perform a PCA on the digits dataset 31 pca = PCA(n_components=36, whiten=True) 32 X_pca = pca.fit_transform(digits.data / 255) 33 34 print('Explained variance ratio') 35 print(pca.explained_variance_ratio_) 36 37 # Plot the explained variance ratio 38 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 6)) 39 40 ax[0].set_xlabel('Component') 41 ax[0].set_ylabel('Variance ratio (%)') 42 ax[0].bar(np.arange(36), pca.explained_variance_ratio_ * 100.0) 43 44 ax[1].set_xlabel('Component') 45 ax[1].set_ylabel('Cumulative variance (%)') 46 ax[1].bar(np.arange(36), np.cumsum(pca.explained_variance_)[::-1]) 47 48 plt.show() 49 50 # Rebuild from PCA and show the result 51 fig, ax = plt.subplots(10, 10, figsize=(10, 10)) 52 53 samples = [pca.inverse_transform(X_pca[x]).reshape((8, 8)) for x in selection] 54 55 for i in range(10): 56 for j in range(10): 57 ax[i, j].set_axis_off() 58 ax[i, j].imshow(samples[(i * 8) + j], cmap='gray') 59 60 plt.show()
原图:64维,8X8点图,

方差比和累计方差:
pca = PCA(n_components=36, whiten=True)
X_pca = pca.fit_transform(digits.data / 255)
samples = [pca.inverse_transform(X_pca[x]).reshape((8, 8)) for x in selection]
做逆变换投射到原始空间后的图:

非负矩阵分解:当数据集由非负元素组成时:例子如下:
1 from sklearn.datasets import load_iris 2 from sklearn.decomposition import NMF 3 iris = load_iris() 4 iris.data.shape 5 6 iris.data[0:5] 7 Xt[0:5] 8 nmf.inverse_transform(Xt[0:5])

核PCA:可以对非线性的数据集分类,包含比较复杂的数学公式:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs 7 from sklearn.decomposition import KernelPCA 8 9 # For reproducibility 10 np.random.seed(1000) 11 12 if __name__ == '__main__': 13 # Create a dummy dataset 14 Xb, Yb = make_blobs(n_samples=500, centers=3, n_features=3) 15 16 # Show the dataset 17 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 8)) 18 ax.scatter(Xb[:, 0], Xb[:, 1]) 19 ax.set_xlabel('X') 20 ax.set_ylabel('Y') 21 ax.grid() 22 23 plt.show() 24 25 # Perform a kernel PCA (with radial basis function) 26 kpca = KernelPCA(n_components=2, kernel='rbf', fit_inverse_transform=True) 27 X_kpca = kpca.fit_transform(Xb) 28 29 # Plot the dataset after PCA 30 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 8)) 31 ax.scatter(kpca.X_transformed_fit_[:, 0], kpca.X_transformed_fit_[:, 1]) 32 ax.set_xlabel('First component: Variance') 33 ax.set_ylabel('Second component: Mean') 34 ax.grid() 35 36 plt.show()

原子提取和字典学习:类似主成分,从原子的稀疏字典重建样本。

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 5 from sklearn.decomposition import DictionaryLearning 6 7 # For reproducibility 8 np.random.seed(1000) 9 10 if __name__ == '__main__': 11 # Load MNIST digits 12 digits = load_digits() 13 14 # Perform a dictionary learning (and atom extraction) from the MNIST dataset 15 dl = DictionaryLearning(n_components=36, fit_algorithm='lars', transform_algorithm='lasso_lars') 16 X_dict = dl.fit_transform(digits.data[0:35]) 17 18 # Show the atoms that have been extracted 19 fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 6, figsize=(8, 8)) 20 21 samples = [dl.components_[x].reshape((8, 8)) for x in range(34)] 22 23 for i in range(6): 24 for j in range(6): 25 ax[i, j].set_axis_off() 26 ax[i, j].imshow(samples[(i * 5) + j], cmap='gray') 27 28 plt.show()
结果:

