场景
Java中ExecutorService线程池的使用(Runnable和Callable多线程实现):
https://blog.csdn.net/BADAO_LIUMANG_QIZHI/article/details/126242904
在上面学习线程池ExecutorService的使用,实现Callable接口,并获取返回结果时
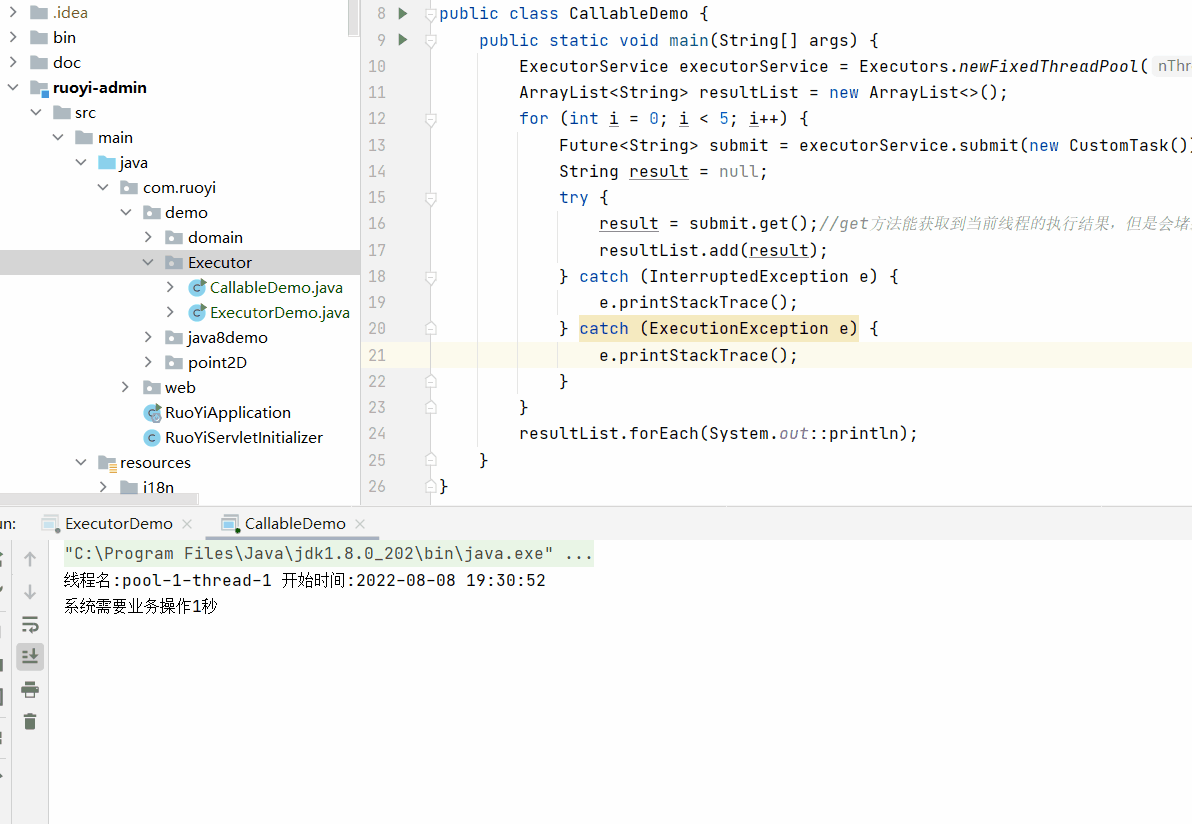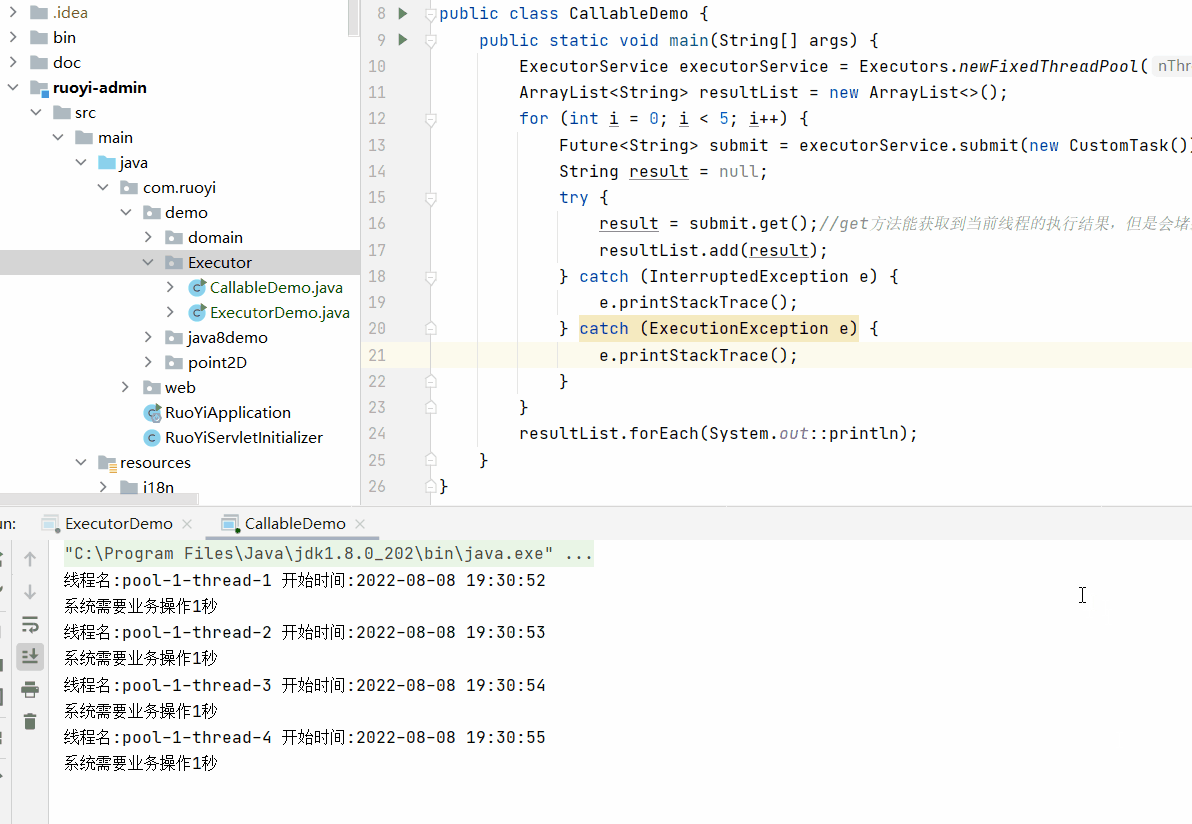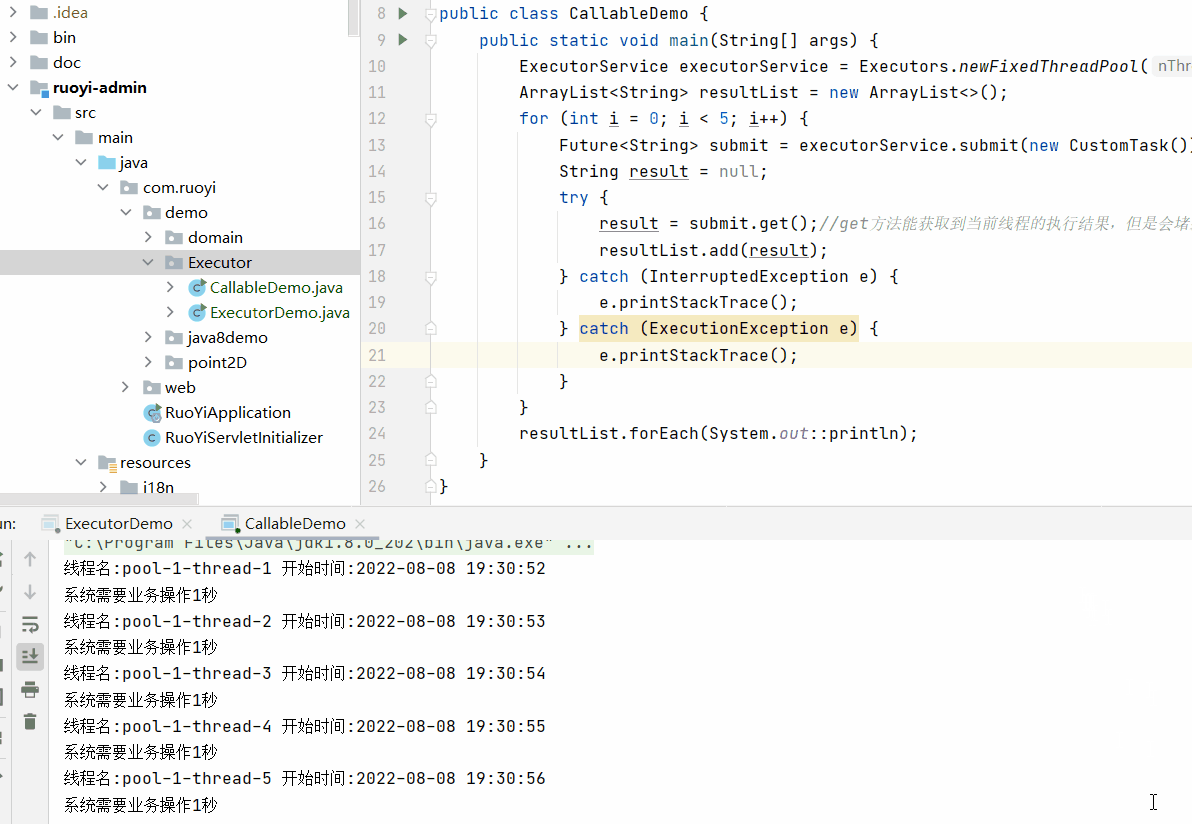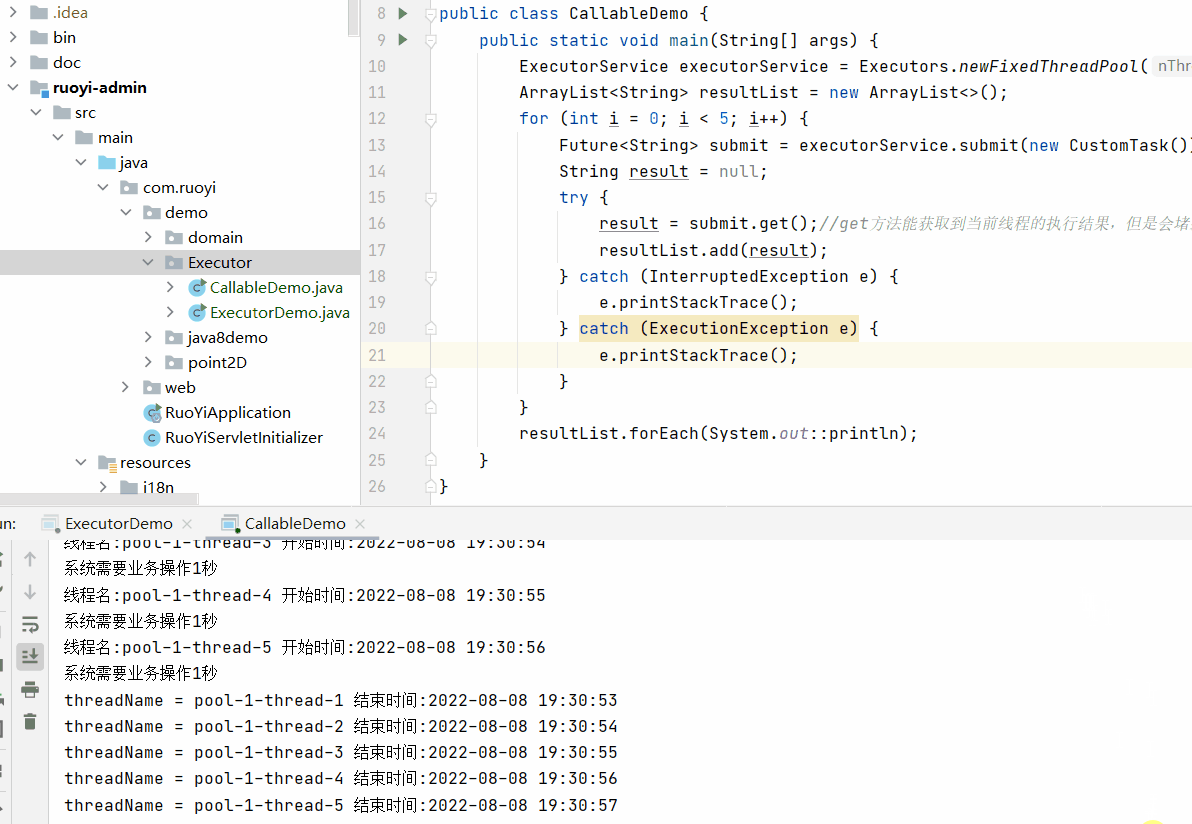
需要注意future的get()方法会堵塞当前线程的执行。
即当前线程执行结束并获取到结果之后才会继续执行下个线程。
这样就无法实现多线程的效果。
比如:
// ArrayList<String> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); // for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // Future<String> submit = executorService.submit(new CustomTask()); // String result = null; // try { // result = submit.get();//get方法能获取到当前线程的执行结果,但是会堵塞当前线程 // resultList.add(result); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } catch (ExecutionException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // }
执行效果为
注:
博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/badao_liumang_qizhi
关注公众号
霸道的程序猿
获取编程相关电子书、教程推送与免费下载。
实现
1、解决方式为创建一个数组存储所有的future,在所有线程循环结束以后再遍历list获取结果。
ArrayList<Future<String>> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Future<String> submit = executorService.submit(new CustomTask()); resultList.add(submit); } resultList.forEach(result -> { try { System.out.println(result.get()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } });
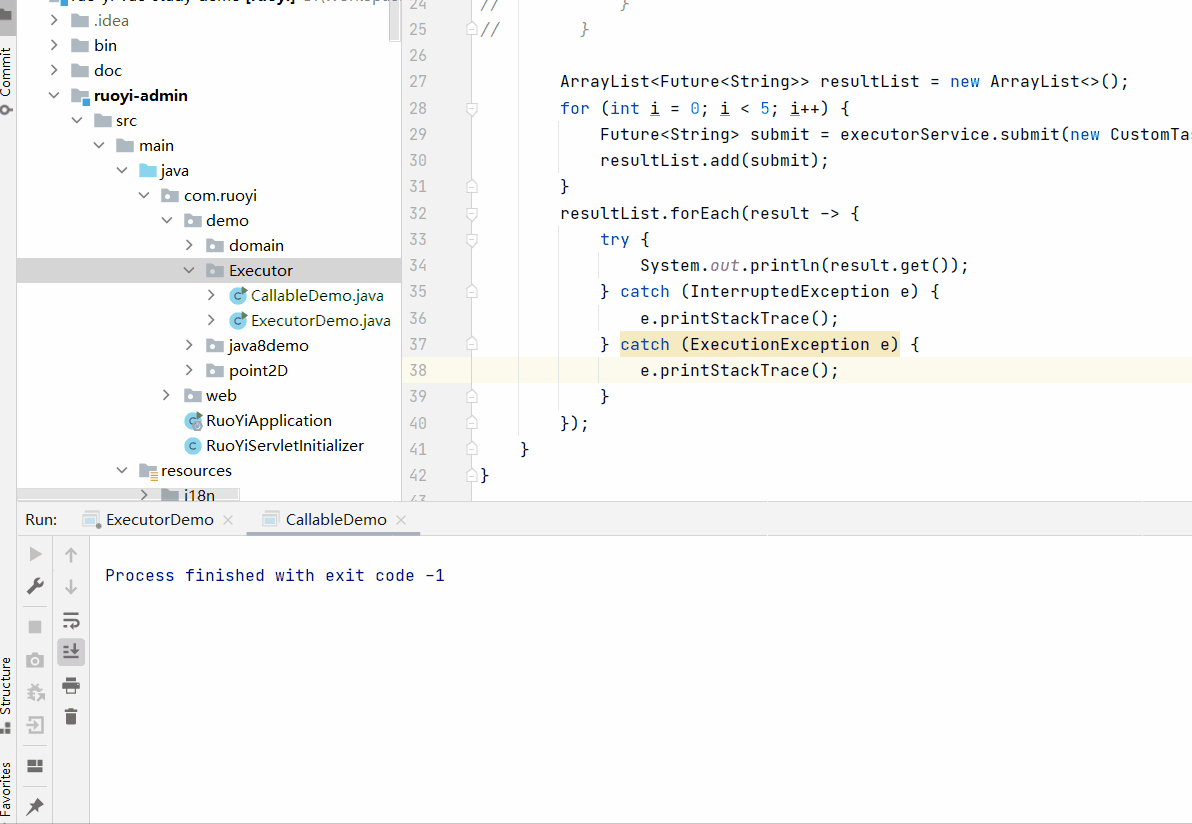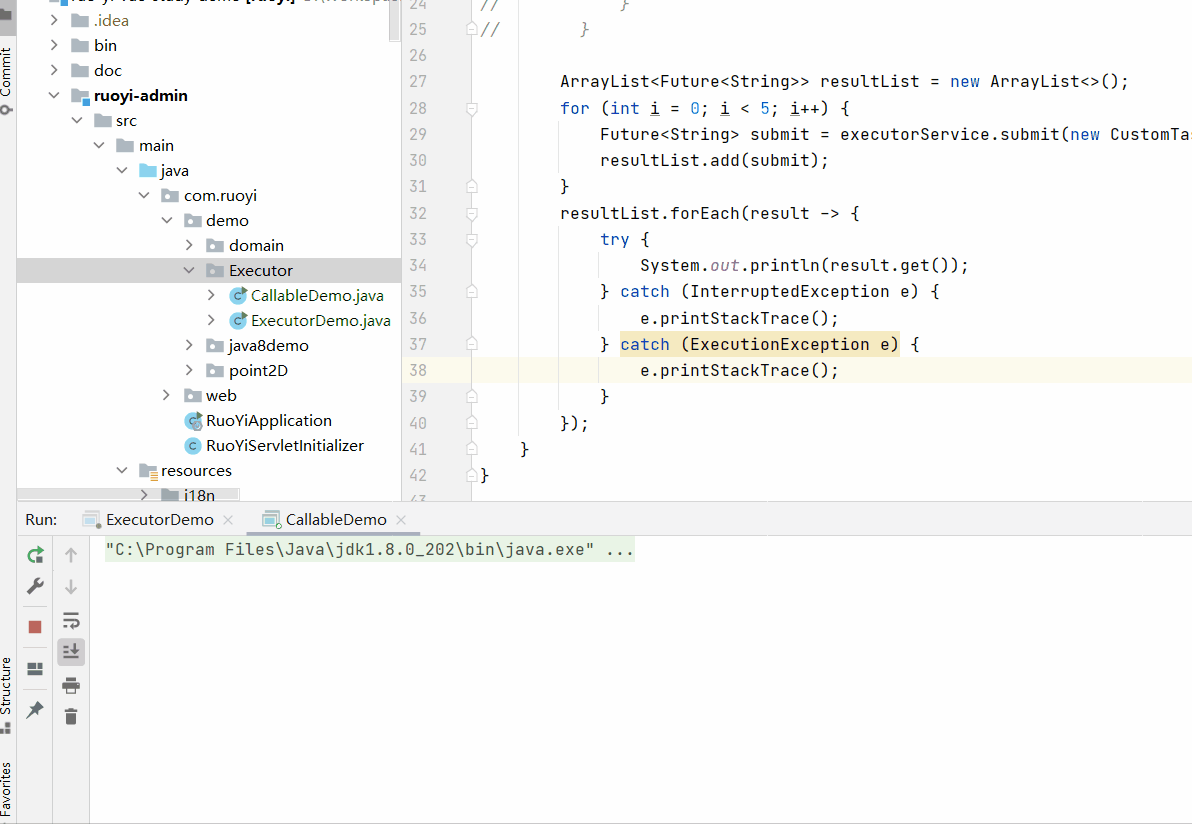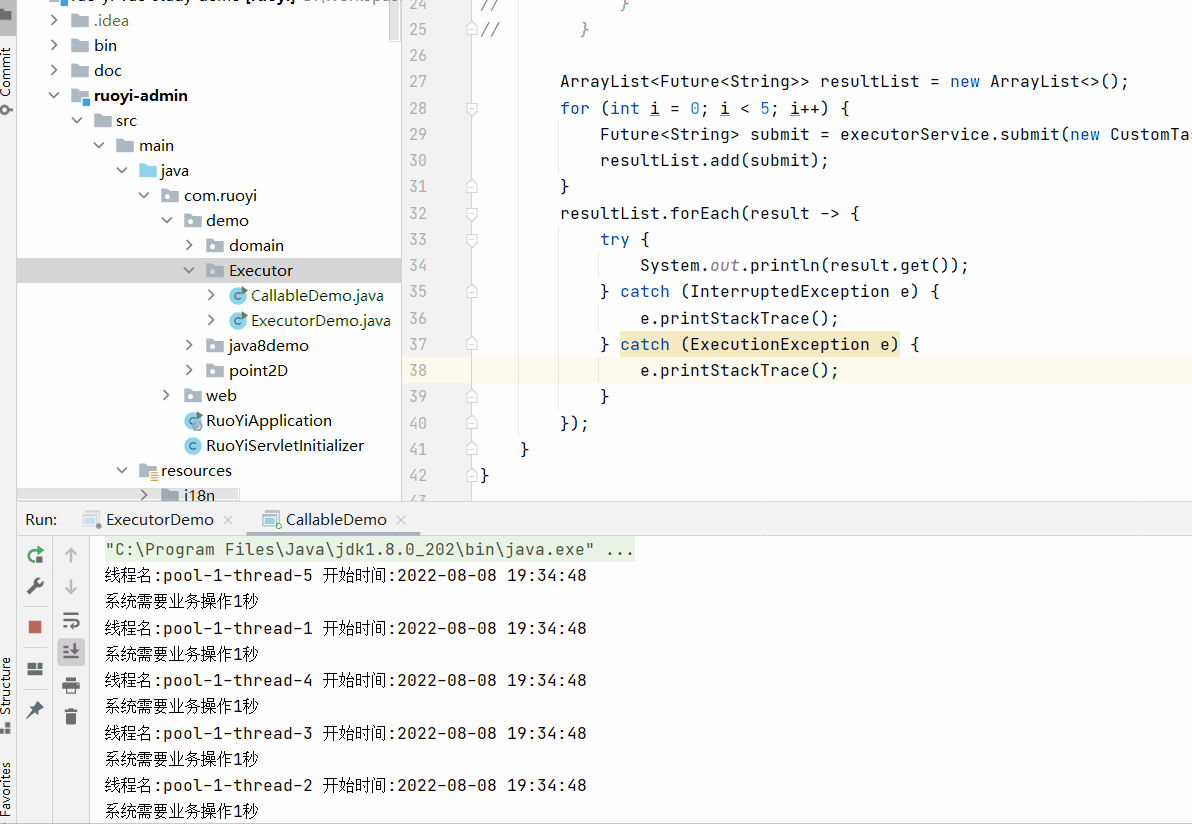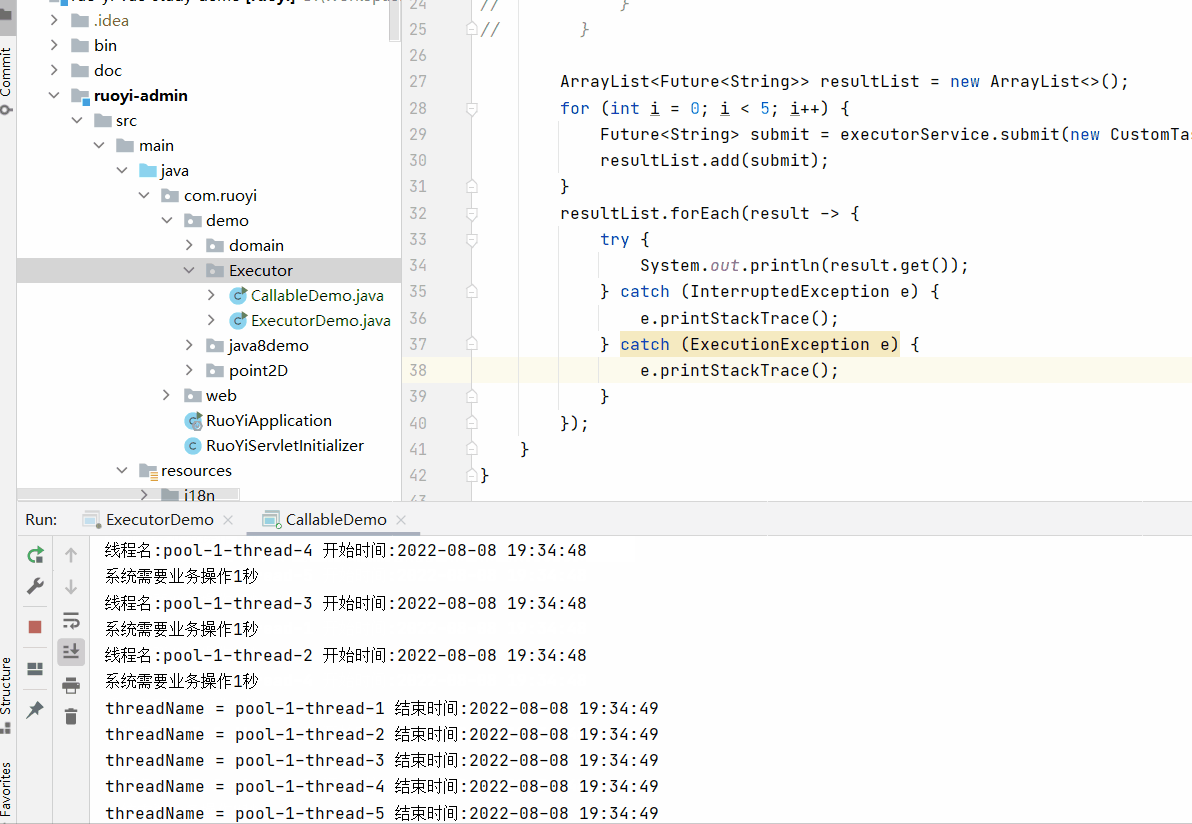
上面这种执行效果
2、完整示例代码
package com.ruoyi.demo.Executor; import com.ruoyi.common.utils.DateUtils; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CallableDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); ArrayList<Future<String>> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Future<String> submit = executorService.submit(new CustomTask()); resultList.add(submit); } resultList.forEach(result -> { try { System.out.println(result.get()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } } class CustomTask implements Callable<String> { @Override public String call() throws Exception { String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println("线程名:" + threadName + " 开始时间:" + DateUtils.getTime()); System.out.println("系统需要业务操作1秒"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "threadName = "+threadName +" 结束时间:"+DateUtils.getTime(); } }