BIO
BIO:blocking IO,分别写一个服务端和客户端交互的C/S实例。
服务器端:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* Created by atai on 2019/3/19.
*/
public class BIOServer {
private String host;
private int port;
private static Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 9010;
try (ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(port)) {
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream(), charset));
String mess = null;
while ((mess = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(mess);
}
s.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Created by atai on 2019/3/19.
*/
public class BIOClient implements Runnable {
private String host;
private int port;
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public BIOClient(String host, int port) {
super();
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (Socket s = new Socket(host, port); OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String mess = scanner.nextLine();
out.write(mess.getBytes(charset));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BIOClient client = new BIOClient("localhost", 9010);
client.run();
}
}
启动时,记得先启动服务器代码,才能正常启动客户端代码,不然客户端会报连接异常(不存在可用端口号)。
上面的服务器端代码每次只能同时受理一个客户端请求,其他客户端此时只能等待,为了让服务端支持处理多个客户端请求,可以改造成多线程形式:
public class BIOServerV2 {
private static Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 9010;
try (ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(port)) {
while (true) {
new Thread(new SocketProcess(ss.accept())).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class SocketProcess implements Runnable {
Socket s;
public SocketProcess(Socket s) {
super();
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream(), charset))) {
String mess = null;
while ((mess = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(mess);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1、理解什么是阻塞
2、思考:阻塞对服务端有什么影响?
3、阻塞时,服务端什么也干不了,不能处理其他客户端的连接,如何改进?
4、多线程
5、如果并发请求量很大,比如一万、十万,会有什么问题?
6、32位系统1个线程对象默认最大需要320KB内存,64位系统默认最大需要1M内存,业务对象也需要内存,内存会不足。过多的线程需要OS频繁切换,也会大大影响性能。
7、怎么办?
8、线程池
既然使用线程池可以避免频繁创建、销毁、切换线程,那就写一个使用线程池的服务端实现:
public class BIOServerV3 {
private static Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 9010;
int threads = 100;
ExecutorService tpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threads);
try (ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(port)) {
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
// 丢到线程池中执行
tpool.execute(new SocketProcess(s));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
tpool.shutdown();
}
static class SocketProcess implements Runnable {
Socket s;
public SocketProcess(Socket s) {
super();
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream(), charset))) {
String mess = null;
while ((mess = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(mess);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
9、阻塞对线程池的方式有什么影响?
10、阻塞等待接收客户端的数据时,这段时间占着线程,而池中线程数是有限的,并发量大时,将导致没有线程处理请求,请求的响应时间长,甚至拒绝服务。
11、如果能不阻塞,在没有数据时,就去干点别的事情,有数据了才处理数据那该多好。
这个时候,终于等到NIO闪亮登场。
NIO
NIO:new IO,java1.4开始推出的可非阻塞IO,在java.io包中。特点如下:
1、可解决BIO阻塞的不足;
2、但比BIO学习、使用复杂;
3、可以以阻塞、非阻塞两种方式工作;
4、在非阻塞模式下,可以用少量(甚至一个)线程处理大量的IO连接;
5、Java7推出了NIO.2(又称AIO,即异步IO)
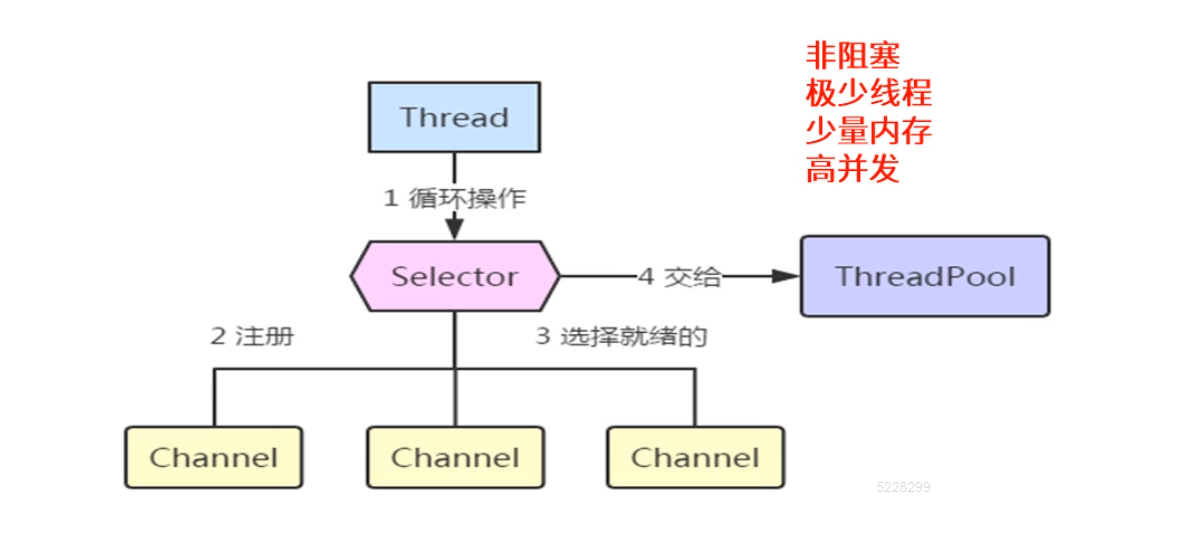
Select选择器:非阻塞模式下,一个选择器可检测多个SelectableChannel,获得为读写等操作准备好的通道,就不需要我们用循环去判断了。
Selector的用法:
1、创建Selector
Selector selector = new Selector.open();
2、将要交给Selector检测的SelectableChannel注册进来
channel.configureBlocking(false); // 注意:一定要设为非阻塞模式 SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
channel.register方法的第二个参数指定要selector帮忙监听的就绪操作:
SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT SelectionKey.OP_READ SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
3、通过Selector来选择就绪的Channel,有三个select方法
int select() // 阻塞直到有就绪的Channel int select(long timeout) // 阻塞最长多久 int selectNow() // 不阻塞这
这三个方法返回值:就绪的Channel数量
int n = selector.select();
注意:select()方法返回当前的就绪数量。
4、获得就绪的SelectionKey集合(当有就绪的Channel时)
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKey = selector.selectedKeys();
5、处理selectedKeys set(详见后面的服务端代码)
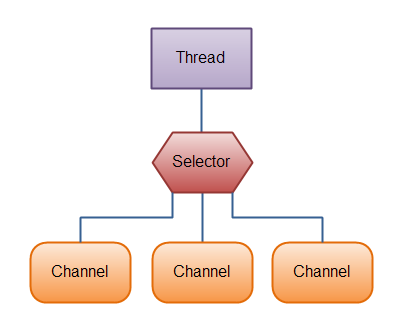
Channel通道:数据的来源或去向目标
1、Channel的实现
FileChannel(只能用于BIO)
DatagramChannel
SocketChannel
SocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel
2、各Channel的API方法
open():创建通道
read(Buffer):从通道中读取数据放入到buffer
write(Buffer):将buffer中的数据写给通道
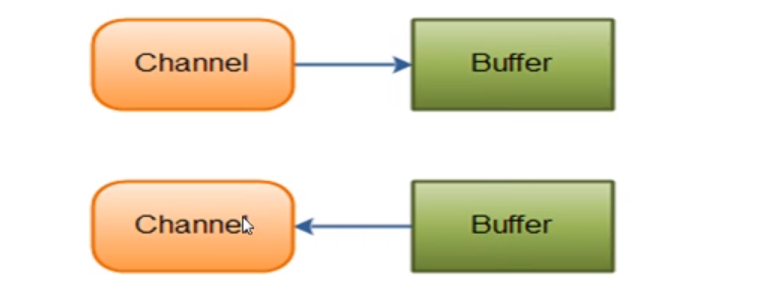
Buffer缓冲区,数据的临时存放区
ByteBuffer、MappedByteBuffer、CharBuffer、DoubleBuffer等
Buffer的基本使用步骤:
1、调用xxxBuffer.allocate(int)创建Buffer
2、调用put方法往Buffer中写数据
3、调用buffer.flip()将buffer转为读模式
4、读取buffer中的数据
5、清理数据buffer.clear(),整理数据buffer.compact()
Buffer的三个重要属性capacity、position、limit
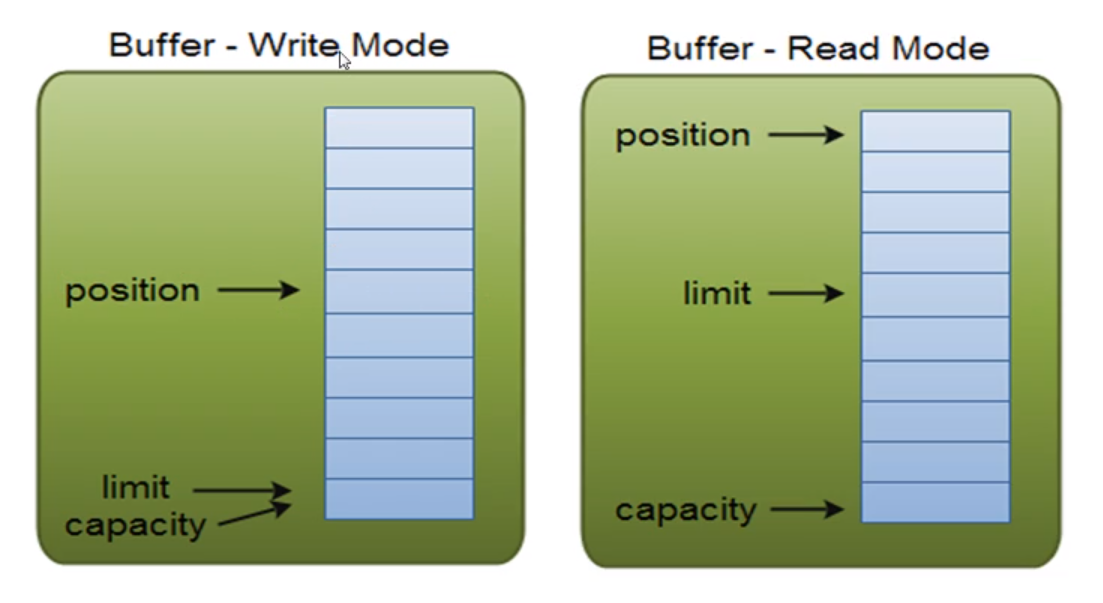
以下是NIO代码的具体实例。
服务器端:
public class NioServer {
private static Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private static CharsetDecoder decoder = charset.newDecoder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建一个selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
int port = 9200;
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
// 2注册到selector
// 设置非阻塞
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
// ssc向selector注册,监听连接到来
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 连接的计数
int connectionCount = 0;
// 极少量线程
int threads = 3;
ExecutorService tpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threads);
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待就绪的事件
int readyChannelCount = selector.select();
if (readyChannelCount == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// a connection was accepted by a ServerSocketChannel.
ServerSocketChannel ssssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 接收连接
SocketChannel cc = ssssc.accept();
// 请selectoror帮忙监测数据到了没
cc.configureBlocking(false);
// 向selector注册
cc.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_READ, ++connectionCount);
} else if (key.isConnectable()) {
// a connection was established with a remote server.
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// a channel is ready for reading
// 交给线程池去处理数据读
tpool.execute(new SocketProcess(key));
// 取消Selector注册,防止线程池处理不及时,重复选择
key.cancel();
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
// a channel is ready for writing
}
// 处理后,一定要从selectedKey集合中移除
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
static class SocketProcess implements Runnable {
SelectionKey key;
public SocketProcess(SelectionKey key) {
super();
this.key = key;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("连接" + key.attachment() + " 发来了:" + readFromChannel());
key.channel().close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private String readFromChannel() throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int bfsize = 1024;
ByteBuffer rbf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(bfsize);
// 定义一个更大的buffer
ByteBuffer bigBf = null;
// 读的次数
int count = 0;
while ((sc.read(rbf) != -1)) {
count++;
ByteBuffer temp = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(bfsize * (count + 1));
if (bigBf != null) {
// 将buffer由写转为读模式
bigBf.flip();
temp.put(bigBf);
}
bigBf = temp;
// 将这次读到的数据放入大buffer
rbf.flip();
bigBf.put(rbf);
// 为了下次读,清理Buffer
rbf.clear();
}
if (bigBf != null) {
bigBf.flip();
try {
// 将字节转为字符,返回接收到的字符串
return decoder.decode(bigBf).toString();
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
客户端:
public class NioClient {
private static Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open()) {
boolean connected = sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9200));
System.out.println("connected=" + connected);
// 写
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String mess = scanner.nextLine();
ByteBuffer bf = ByteBuffer.wrap(mess.getBytes(charset));
while (bf.hasRemaining()) {
int writedCount = sc.write(bf);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}