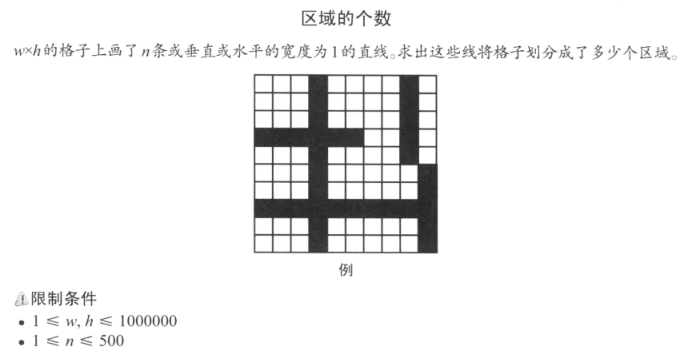

准备好 w * h 的数组,并记录是否有直线通过,然后利用深度优先搜索可以求出被分割出的区域的个数。但是这个问题中 w 和 h 最大为10000000,所以没办法创建 w * h 的数组。因此我们可以使用坐标离散化这一技巧。
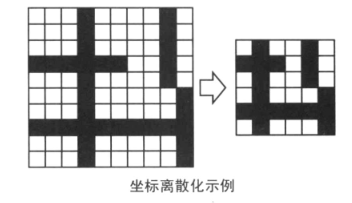
如上图所示,将前后没有变化的行列消除后并不会影响区域的个数。
数组里只需要存储有直线的行列以及前后的行列就足够了,这样的话最多 6n * 6n 就足够了。
int W, H, N; int X1[MAX_N], X2[MAX_N], Y1[MAX_N], Y2[MAX_N]; bool fld[MAX_N * 6][MAX_N * 6]; //对X1和X2进行坐标离散化,并返回离散化后的宽度 int compress(int *x1, int x2, int w) { vector<int> xs; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) for (int d = -1; d <= 1; d++) { int tx1 = x1[i] + d, tx2 = x2[i] + d; if (1 <= tx1 && tx1 <= W) xs.push_back(tx1); if (1 <= tx2 && tx2 <= W) xs.push_back(tx2); } sort(xs.begin(), xs.end()); xs.erase(unique(xs.begin(), xs.end()), xs.end()); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { x1[i] = find(xs.begin(), xs.end(), x1[i]) - xs.begin(); x1[2] = find(xs.begin(), xs.end(), x2[i]) - xs.begin(); } return xs.size(); } void solve() { // 坐标离散化 W = compress(X1, X2, W); H = compress(Y1, Y2, H); // 填充有直线的部分 memset(fld, 0, sizeof(fld)); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) for (int y = Y1[i]; y <= Y2[i]; y++) for (int x = X1[i]; x <= X2[i]; x++) fld[y][x] = true; //求区域的个数 int ans = 0; for (int y = 0; y < H; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < W; x++) { if (fld[y][x]) continue; ans++; //宽度优先搜索 queue<pair<int, int> > q; q.push(make_pair(x, y)); while (!q.empty()) { int sx = q.front().first(); int sy = q.front().second(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int tx = sx + dx[i], ty = sy + dy[i]; if (tx < 0 || W <= tx || ty < 0 || H <= ty) continue; q.push(make_pair(tx, ty)); fld[tx][ty] = true; } } } } printf("%d ", ans); }