Socket一般用于网络之间的通信,在这里,实现的是服务端与客户端的简单消息通信。
首先是客户端的搭建,一般步骤是先建立Socket绑定本地的IP和端口,并对远端连接进行连接进行监听,这里的监听一般开启后台线程进行循环处理;如果远端有连接到本机的Socket的端口,则获取一个新的Socket对象并重新添加一个线程用于对远端地址进行消息通信(消息的收发),这样,服务端的Socket就简单实现,下面是winForm的具体实现。
一、先建立Socket的服务类SocketServerManager,用于对Socket各种操作的统一管理:
public class SocketManager
{
Socket _socket = null;
EndPoint _endPoint = null;
bool _isListening = false;
int BACKLOG = 10;
public SocketManager(string ip, int port)
{
_socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
IPAddress _ip = IPAddress.Parse(ip);
_endPoint = new IPEndPoint(_ip, port);
}
public void Start()
{
_socket.Bind(_endPoint); //绑定端口
_socket.Listen(BACKLOG); //开启监听
Thread acceptServer = new Thread(AcceptWork); //开启新线程处理监听
acceptServer.IsBackground = true;
_isListening = true;
acceptServer.Start();
}
public void AcceptWork()
{
while (_isListening)
{
Socket acceptSocket = _socket.Accept();
if (acceptSocket != null)
{
Thread socketConnectedThread = new Thread(newSocketReceive);
socketConnectedThread.IsBackground = true;
socketConnectedThread.Start(acceptSocket);
}
Thread.Sleep(200);
}
}
public void newSocketReceive(object obj)
{
Socket socket = obj as Socket;
while (true)
{
try
{
if (socket == null) return;
//这里向系统投递一个接收信息的请求,并为其指定ReceiveCallBack做为回调函数
socket.BeginReceive(buffer, 0, buffer.Length, SocketFlags.None, ReceiveCallBack, buffer);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return;
}
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
private void ReceiveCallBack(IAsyncResult ar)
{
}
}
public class SockeServertManager
上面是Socket管理类的模型,具体的方法是初始化和开启监听,接下来就是在Form的界面调用建立类和Start方法。
客户端同样是初始化socket,然后就不是监听socket,而是调用Connect连接指定的Socket地址,最后是开启新的线程接收和发送消息。
public class SocketClientManager
{
public Socket _socket = null;
public EndPoint endPoint = null;
public bool _isConnected = false;
public SocketClientManager(string ip, int port)
{
IPAddress _ip = IPAddress.Parse(ip);
endPoint = new IPEndPoint(_ip, port);
_socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
}
public void Start()
{
_socket.BeginConnect(endPoint, ConnectedCallback, _socket);
_isConnected = true;
Thread socketClient = new Thread(SocketClientReceive);
socketClient.IsBackground = true;
socketClient.Start();
}
public void SocketClientReceive()
{
while (_isConnected)
{
try {
_socket.BeginReceive(buffer, 0, buffer.Length, SocketFlags.None, ReceiveCallback, buffer);
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
_isConnected = false;
}
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
public void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
}
}
public class SocketClientManager
主要记住的是,客户端是监听Socket是固定的,是监听绑定地址的,每当有新的连接访问,则开启新的线程与之进行交互,而客户端只简单实现与服务端交互,服务端则只有一个。
Socket的进行发送与接收,一般是通过异步方法BeginReceive和BeginSend进行处理,方法一般带有回调函数,用于执行操作之后的处理。
还有就是连接的关闭,每关闭一个连接,先要结束在Socket所在的线程方法,我这里的处理是停止掉死循环的函数调用,每当线程所在函数执行完毕,则线程自动销毁。之后就是关闭所连接的socket。
下面是我程序的完整实现,为了方便socket的管理,我把服务器的所有与客户端对话的Socket统一用字典管理,并封装在SocketInfo的内部类中,消息的发送与接收必须先找到该连接socket。
最后就是界面的调用,完成Socket的网络消息交互。
下面是具体的实现及源码:
public class SocketManager
{
public Dictionary<string,SocketInfo> _listSocketInfo = null;
Socket _socket = null;
public SocketInfo socketInfo = null;
EndPoint _endPoint = null;
bool _isListening = false;
int BACKLOG = 10;
public delegate void OnConnectedHandler(string clientIP);
public event OnConnectedHandler OnConnected;
public delegate void OnReceiveMsgHandler(string ip);
public event OnReceiveMsgHandler OnReceiveMsg;
public event OnReceiveMsgHandler OnDisConnected;
public SocketManager(string ip, int port)
{
_socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
IPAddress _ip = IPAddress.Parse(ip);
_endPoint = new IPEndPoint(_ip, port);
_listSocketInfo = new Dictionary<string, SocketInfo>();
}
public void Start()
{
_socket.Bind(_endPoint); //绑定端口
_socket.Listen(BACKLOG); //开启监听
Thread acceptServer = new Thread(AcceptWork); //开启新线程处理监听
acceptServer.IsBackground = true;
_isListening = true;
acceptServer.Start();
}
public void AcceptWork()
{
while (_isListening)
{
Socket acceptSocket = _socket.Accept();
if (acceptSocket != null && this.OnConnected != null)
{
SocketInfo sInfo = new SocketInfo();
sInfo.socket = acceptSocket;
_listSocketInfo.Add(acceptSocket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), sInfo);
OnConnected(acceptSocket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
Thread socketConnectedThread = new Thread(newSocketReceive);
socketConnectedThread.IsBackground = true;
socketConnectedThread.Start(acceptSocket);
}
Thread.Sleep(200);
}
}
public void newSocketReceive(object obj)
{
Socket socket = obj as Socket;
SocketInfo sInfo = _listSocketInfo[socket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()];
sInfo.isConnected = true;
while (sInfo.isConnected)
{
try
{
if (sInfo.socket == null) return;
//这里向系统投递一个接收信息的请求,并为其指定ReceiveCallBack做为回调函数
sInfo.socket.BeginReceive(sInfo.buffer, 0, sInfo.buffer.Length, SocketFlags.None, ReceiveCallBack, sInfo.socket.RemoteEndPoint);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return;
}
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
private void ReceiveCallBack(IAsyncResult ar)
{
EndPoint ep = ar.AsyncState as IPEndPoint;
SocketInfo info = _listSocketInfo[ep.ToString()];
int readCount = 0;
try
{
if (info.socket == null) return;
readCount = info.socket.EndReceive(ar);
}catch(Exception ex){
return;
}
if (readCount > 0)
{
//byte[] buffer = new byte[readCount];
//Buffer.BlockCopy(info.buffer, 0, buffer, 0, readCount);
if (readCount < info.buffer.Length)
{
byte[] newBuffer = new byte[readCount];
Buffer.BlockCopy(info.buffer, 0, newBuffer, 0, readCount);
info.msgBuffer = newBuffer;
}
else
{
info.msgBuffer = info.buffer;
}
string msgTip = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(info.msgBuffer);
if (msgTip == "���faild")
{
info.isConnected = false;
if (this.OnDisConnected != null) OnDisConnected(info.socket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
_listSocketInfo.Remove(info.socket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
info.socket.Close();
return;
}
if (OnReceiveMsg != null) OnReceiveMsg(info.socket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
}
}
public void SendMsg(string text, string endPoint)
{
if (_listSocketInfo.Keys.Contains(endPoint) && _listSocketInfo[endPoint] != null)
{
_listSocketInfo[endPoint].socket.Send(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text));
}
}
public void Stop()
{
_isListening = false;
foreach (SocketInfo s in _listSocketInfo.Values)
{
s.socket.Close();
}
}
public class SocketInfo
{
public Socket socket = null;
public byte[] buffer = null;
public byte[] msgBuffer = null;
public bool isConnected = false;
public SocketInfo()
{
buffer = new byte[1024 * 4];
}
}
}
public class SocketServerManager
public class SocketClientManager
{
public Socket _socket = null;
public EndPoint endPoint = null;
public SocketInfo socketInfo = null;
public bool _isConnected = false;
public delegate void OnConnectedHandler();
public event OnConnectedHandler OnConnected;
public event OnConnectedHandler OnFaildConnect;
public delegate void OnReceiveMsgHandler();
public event OnReceiveMsgHandler OnReceiveMsg;
public SocketClientManager(string ip, int port)
{
IPAddress _ip = IPAddress.Parse(ip);
endPoint = new IPEndPoint(_ip, port);
_socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
}
public void Start()
{
_socket.BeginConnect(endPoint, ConnectedCallback, _socket);
_isConnected = true;
Thread socketClient = new Thread(SocketClientReceive);
socketClient.IsBackground = true;
socketClient.Start();
}
public void SocketClientReceive()
{
while (_isConnected)
{
SocketInfo info = new SocketInfo();
try {
_socket.BeginReceive(info.buffer, 0, info.buffer.Length, SocketFlags.None, ReceiveCallback, info);
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
_isConnected = false;
}
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
public void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
socketInfo = ar.AsyncState as SocketInfo;
if (this.OnReceiveMsg != null) OnReceiveMsg();
}
public void ConnectedCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
Socket socket = ar.AsyncState as Socket;
if (socket.Connected)
{
if (this.OnConnected != null) OnConnected();
}
else
{
if (this.OnFaildConnect != null) OnFaildConnect();
}
}
public void SendMsg(string msg)
{
byte[] buffer = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(msg);
_socket.Send(buffer);
}
public class SocketInfo
{
public Socket socket = null;
public byte[] buffer = null;
public SocketInfo()
{
buffer = new byte[1024 * 4];
}
}
}
public class SocketClientManager
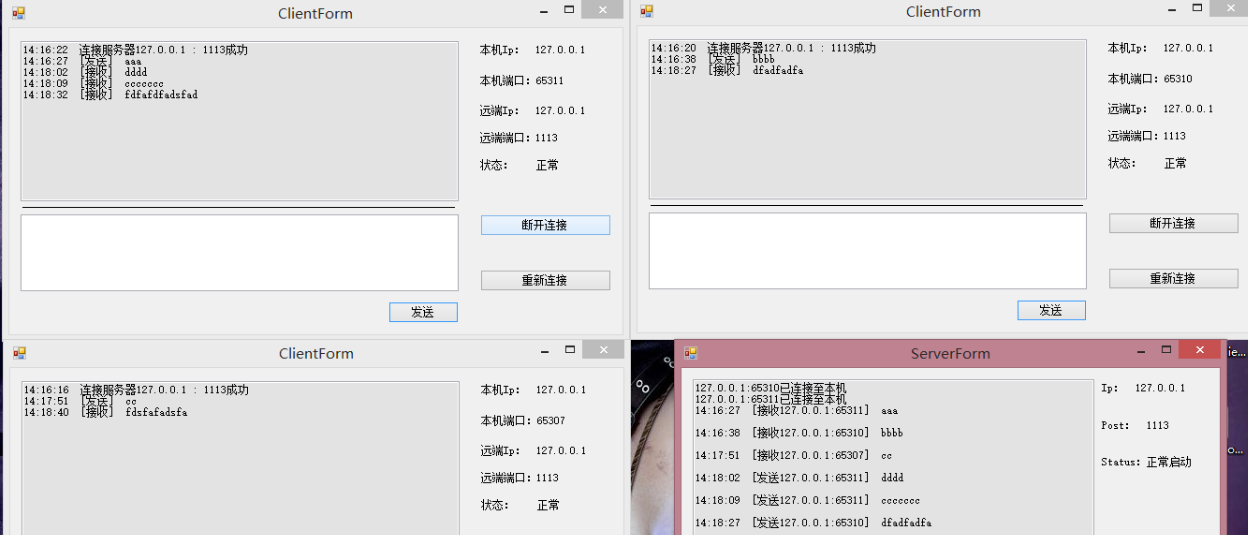
具体源码(.net4.5,vs2013)下载:
------------------------------------------分割线------------------------------------------
免费下载地址在 http://linux.linuxidc.com/
用户名与密码都是www.linuxidc.com
具体下载目录在 /2015年资料/1月/29日/C#的Socket简单实现消息发送/
下载方法见 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-07/87684.htm
------------------------------------------分割线------------------------------------------