模式匹配:只要等号两边的模式相同,左边的变量就会被赋予对应的值。
let [a, b, c] = [1, 2, 3];
嵌套数组进行解构:
let [foo, [[bar], baz]] = [1, [[2], 3]];
foo // 1
bar // 2
baz // 3
let [ , , third] = ["foo", "bar", "baz"];
third // "baz"
let [x, , y] = [1, 2, 3];
x // 1
y // 3
let [head, ...tail] = [1, 2, 3, 4];
head // 1
tail // [2, 3, 4]
let [x, y, ...z] = ['a'];
x // "a"
y // undefined
z // []
不完全解构:等号左边的模式,只匹配一部分的等号右边的数组。
let [x, y] = [1, 2, 3];
x // 1
y // 2
let [a, [b], d] = [1, [2, 3], 4];
a // 1
b // 2
d // 4
只要某种数据结构具有 Iterator 接口,都可以采用数组形式的解构赋值:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> function* fibs() { let a = 0; let b = 1; while (true) { yield a; [a, b] = [b, a + b]; } } let [first, second, third, fourth, fifth, sixth] = fibs(); alert(sixth); </script> </body> </html>
对象的解构赋值
解构不仅可以用于数组,还可以用于对象。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> let { foo, bar } = {foo: "aaa", bar: "bbb"}; console.log(foo); console.log(bar); </script> </body> </html>
结果:aaa,bbb
简写:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> let obj = { first: 'hello', last: 'world' }; let { first: f, last: l } = obj; console.log(f); console.log(l); </script> </body> </html>
结果:
hello
world
数组本质是特殊的对象,因此可以对数组进行对象属性的解构。
如下
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> let arr = [1, 2, 3]; let {0 : first, [arr.length - 1] : last} = arr; console.log(first); // 1 console.log(last); // 3 </script> </body> </html>
结果为:
1
3
字符串的解构赋值
字符串也可以解构赋值。这是因为此时,字符串被转换成了一个类似数组的对象。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> const [a, b, c, d, e] = 'hello'; a // "h" b // "e" c // "l" d // "l" e // "o" console.log(a); console.log(b); console.log(c); console.log(d); console.log(e); </script> </body> </html>
数值和布尔值的解构赋值
解构赋值时,如果等号右边是数值和布尔值,则会先转为对象。
let {toString: s} = 123;
s === Number.prototype.toString // true
let {toString: s} = true;
s === Boolean.prototype.toString // true
函数参数的解构赋值
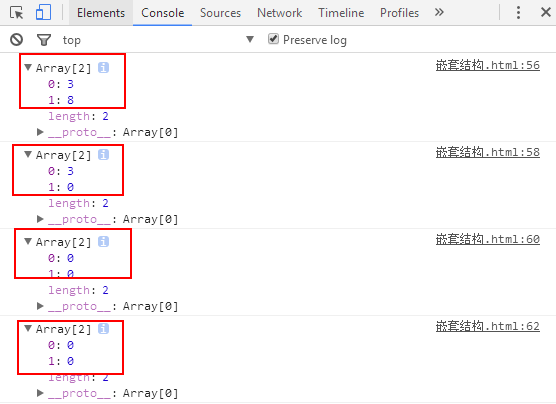
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> function move({x = 0, y = 0} = {}) { return [x, y]; } console.log(move({x: 3, y: 8})); console.log(move({x: 3})); console.log(move({})); console.log(move()); </script> </body> </html>
结果: