对于应用服务器来说,性能是非常重要的,基本可以说决定着这款应用服务器的未来。通常从软件角度来说,应用服务器性能包括如下几个方面:
1、请求处理的并发程度,当前主流服务器均采用异步的方式处理客户端的请求;
2、减少网络传输的数据量,提高网络利用率;
3、降低新建网络链接的开销,以实现链接在多个请求之间的复用;
4、选择合适的I/O方式,例如NIO等。
一、阻塞与非阻塞、同步与异步
------同步:发出一个调用时,没有得到结果之前,该调用不返回,由调用者主动等待调用结果。 | 关注的是消息通信机制---------------------| | ------异步:调用发出之后,调用直接返回,此时不会拿到返回结果。被调用者通过状态通知调用者或回调函数处理这个调用。 ------阻塞:调用结果返回之前,当前线程会被挂起。 | 关注的是程序在等待调用结果时的状态---------| | ------非阻塞:调用返回结果之前,当前线程不会被挂起。
二、BIO
概念:bio基于流,是同步阻塞IO模式,数据的读取写入必须阻塞在一个线程内等待其完成。这里使用那个经典的烧开水例子,这里假设一个烧开水的场景,有一排水壶在烧开水,BIO的工作模式就是, 叫一个线程停留在一个水壶那,直到这个水壶烧开,才去处理下一 个水壶。但是实际上线程在等待水壶烧开的时间段什么都没有做。不知道io操作中什么时候有数据可读,所以一直是阻塞的模式。
缺点:当并发数达到一定量时,并且服务端需要一定的时间去处理请求时,例如1-2s,这时需要开启非常多的线程数,并且这些线程啥事不干,都是等着请求返回,大大浪费了系统资源,而且在线程切换上下文的过程中,也会浪费很多的资源
BIO是阻塞式I/O,通过socket在客户端与服务端建立双向链接以实现通信,主要步骤如下:
- a、服务端监听某个端口是否有链接请求;
- b、客户端向服务端发出链接请求;
- c、服务端向客户端返回accept()消息,此时链接成功;
- d、客户端和服务端通过send()、write()等方法与对方通信;
- e、关闭链接
eg:简单的网络通信如下:
服务端:


客户端:


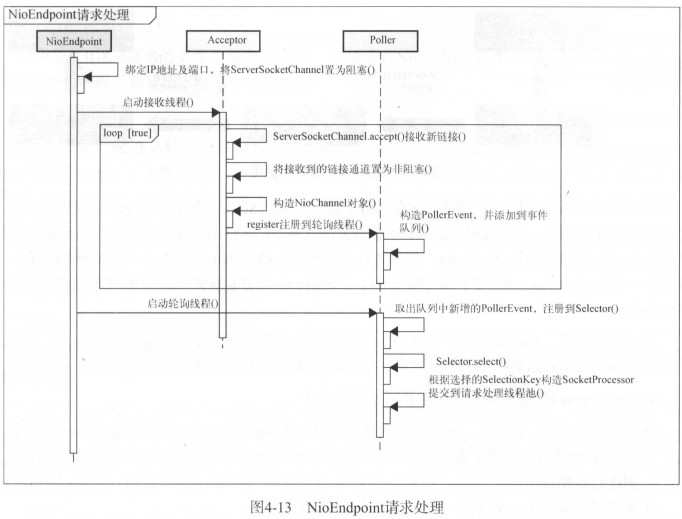
这种简单的示例只支持一个客户端链接到一个服务端,现实情况是N个客户端链接到服务端。Tomcat是这么实现的:

三、NIO
概念:bio的性能是相对较差的,在NIO中,基于块的概念,可以在不编写本地代码的情况下利用底层优化。
NIO结构图:
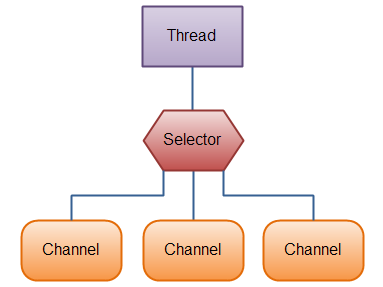
来个复杂点的:

selectionKey则是用来描述相关事件。
1、通道(channel)

2、缓冲区(buffer)

3、选择器(selector)

简单的NIO示例:
服务端:NIOServer
package com.ty.server; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; /** * 服务端 */ public class NIOServer { /** * 定义服务端的selector, * 主要作用: * 1、将各种事件注册到selector中,selector监控各种事件的发生,例如accept、read等 * 2、将不同事件分配到不同的channel */ private Selector selector; //服务端初始化 public void init() throws IOException { //创建一个selector对象 this.selector = Selector.open(); //创建serverSocketChanel对象 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChanel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //设置为非阻塞 serverSocketChanel.configureBlocking(false); //通过serverSocketChannel对象获取serverSocket ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChanel.socket(); //绑定端口 InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(8080); serverSocket.bind(address); //注册accept事件到selector中,accept用于获取客户端请求 serverSocketChanel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); } //服务端启动服务 public void start() throws IOException { //这地方只做一个最简单的示例,不考虑服务端stop while(true) { /** * selector监控客户端是否有对应事件发生,例如accept、read等等。 * 注:此方法是阻塞的,当客户端一直没有事件触发,线程一直挂起,直到至少有一事件触发,走后续流程 */ selector.select(); //获取该selector监控到的所有触发的事件 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //拿到迭代器,循环所有监控到的事件 Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { //事件用SelectionKey描述,主要包括connect、accept、read、write事件 SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next(); //每种事件只处理一次,避免重复处理 iterator.remove(); if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()) { accept(selectionKey); } if(selectionKey.isReadable()) { read(selectionKey); } } } } private void accept(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException { /** * 从selectionkey中获取serverSocketChannel。 * ServerSocketChannel 是一个可以监听新进来的TCP连接的通道, 就像标准IO中的ServerSocket一样 */ ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); //serverSocketChannel监听到新连接后,会创建socketChannel。获取socketChannel SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); //设置为非阻塞 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); } private void read(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException { /** * SocketChannel是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道,就像标准IO中的socket * 创建方式:可以通过以下2种方式创建SocketChannel * 1、打开一个SocketChannel并连接到互联网上的某台服务器。 * 2、一个新连接到达ServerSocketChannel时,会创建一个SocketChannel。 */ SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); //创建读取缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //通过socketChannel.read()获取客户端的请求数据 socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); String request = new String(byteBuffer.array()).trim(); System.out.println("客户端发送的请求为:" + request); //将一个数组包装成ByteBuffer ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("请求收到啦!".getBytes()); //数据发送到客户端 socketChannel.write(outBuffer); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { NIOServer server = new NIOServer(); server.init(); server.start(); } }
客户端:NIOClient
package com.ty.client; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; public class NIOClient { private Selector selector; private BufferedReader clientInput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); public void init() throws IOException { //创建selector this.selector = Selector.open(); //创建SocketChannel SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080)); //注册connect事件 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); } public void start() throws IOException { while(true) { selector.select(); Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); if(selectionKey.isConnectable()) { connect(selectionKey); } if(selectionKey.isReadable()) { read(selectionKey); } } } } public void connect(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException { SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); //如果客户端正在链接 if(socketChannel.isConnectionPending()) { //如果客户端已经链接成功 if(socketChannel.finishConnect()) { socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //链接成功后自然要获取服务端的返回,因此注册read事件 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); String request = clientInput.readLine(); //数据发送到服务端 socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(request.getBytes())); }else { //事件未注册成功,取消掉 selectionKey.cancel(); } } } public void read(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException { //socketChannel与服务端的对应,双方友好建立一个通道 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); System.out.println("服务端响应为:" + new String(byteBuffer.array()).trim()); String request = clientInput.readLine(); socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(request.getBytes())); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { NIOClient client = new NIOClient(); client.init(); client.start(); } }
测试结果:
服务端:
客户端:
这样通过NIO,客户端与服务端即可正常通信。
Tomcat中的NIO实现: