1.1 抽象
抽象是面向对象语言的普遍特性,就是把现实生活中的问题(对象)转化为计算机来处理。
抽象就是抽出像的部分
抽象的步骤:
[1]归类。找出所属的分类。
[2]属性。找出与具体业务相关的特性。
[3]方法。找出与具体业务相关的行为。
案例分析:抽象一个下载资源类。
[1]归类,找出所属分类,并命名Resource,一般而然,类名为名词。
[2]属性。name、url、size、type等。一般为名词。
[3]方法。start(),pause(),stop()。一般为动词。
1.2 UML类图(C)
UML中的类图用于把抽象出来的类通过图形表示出来。
在线UML工具: https://www.processon.com
1.3 构造方法
构造方法专门用于构造对象,是一类特殊的方法。语法
[修饰符] 类名(){ // code }
构造可以根据有无参数分为有无参构造和有参构造。
1.3.1 无参构造
构造方法中没有任何形式参数。形式
[修饰符] 类名(){ // code }
public Dog(){ }
无参构造在new Dog() 时执行,可以把构造对象时的初始值的代码放到无参构造中。
1.3.2 有参构造
当new对象时想传入一些自定义的参数时,可以使用有参构造,形式
[修饰符] 类名(参数1,参数2,…){
}
public Dog(String _name,int _health,int _love){ name = _name; health = _health; love = _love; }
一般而言,我们使用有参构造时,通常需要把参数传递给对象的成员变量。目前而言,需要把形参和成员变量区分开,写法一般建议:xxx = _xxx;
1.3.2.1 局部变量和成员变量的优先级
当局部变量和成员变量同名时,在方法中访问该同名变量,一定是访问的是局部变量。
局部变量的优先级比成员变量的优先级高。
1.3.2.2 有参构造的常见问题
[1]当类中没有定义构造方法(无参和有参都没定义)时,jvm会为类分配一个默认的无参构造。形式如
public Dog(){ }
如果开发者提供了无参构造方法,jvm不在给类分配无参构造。
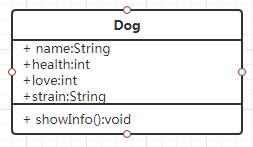
[2]如果类中提供了有参构造,但开发过程中没有使用有参构造,而是用无参构造,编译错误。
总结:
[1]开发者定义了有参构造,一定要写上无参构造。à好的编程习惯。
[2]无参构造和有参构造是方法重载。
1.4 This关键字(上)
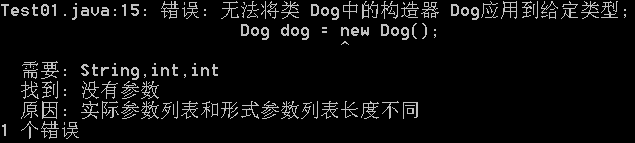
对象内存图分配
总结:
[1] 构造方法在形式上没有返回值。本质上存在一个返回值this,属于该类类型。
[2] this 本质是一个变量,存储一个内存地址,this表示本对象。
[3] 用面向对象的思维,访问属性时可以用this.xxx
[4] this主要用于类的内部,而new出来的对象用于外部。
public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ // System.out.println("name="+name); this.name = name; this.health = health; this.love = love; this.strain = strain; }
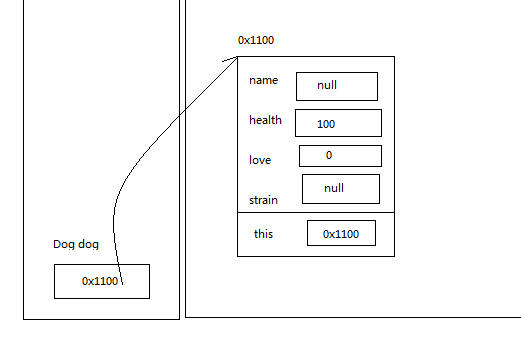
1.5 实例方法调用过程
当我们创建一个对象后,通过对象.属性或者对象.方法() 来调用对象的成员。属性也称为实例变量,方法称为实例方法。
可以认为:
通过对象调用的属性或者方法称为实例变量或者实例方法。
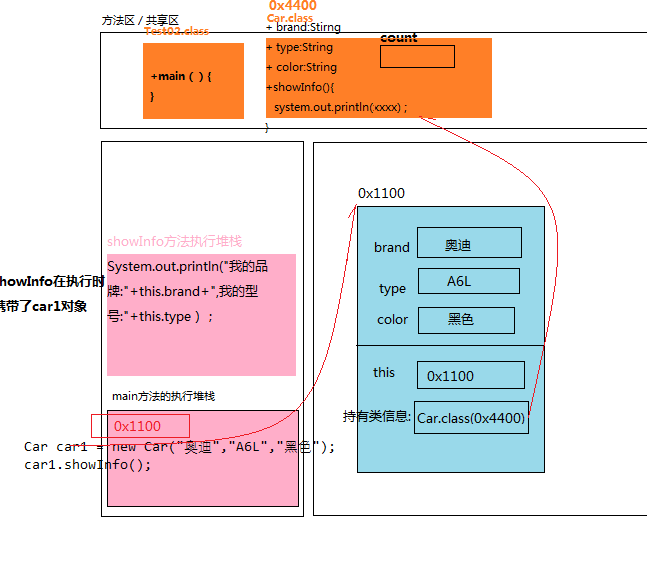
public class Car{ String brand; String type; String color; public Car(){ } public Car(String brand,String type,String color){ this.brand = brand; this.type = type; this.color = color; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("我的品牌:"+this.brand+",我的型号:"+this.type+",我的颜色:"+this.color); System.out.println("我是第"+this.count+"辆车"); } }
public class Test02{ public static void main(String[] args){ Car car1 = new Car("奥迪","A6L","黑色"); car1.showInfo(); } }
总结
方法区:用于加载字节码文件的内存区域。其中,类中定义的方法存储在该区。
需求:统计Car到底创建了多少辆车?
分析:统计Car创建了多少辆车的功能最好归类所有。
ð 把变量count声明在Car.class所在空间。
ð static 关键字
1.6 Static
Static表示静态的意思。可以用于修饰变量,也可以用于修饰方法。
被static修饰的成员称为静态(类)成员,归类所有。类成员包含类属性和类方法。
判断题:类中包含两种成员:一种是静态成员、一种是实例成员。
1.6.1 Static 静态变量
static 修饰变量后,变量变成了静态变量,归类所有,也称为类变量。
static int 变量名 [= 初始值];
静态变量的访问形式
[1]类名.静态变量(推荐写法)
[2]对象.静态变量
总结
[1]静态变量分配在方法区/共享区。静态变量归类所有,被所有实例共享。
[2]静态变量最好声明之后立即初始化。
1.6.2 静态方法
static 修饰方法后,方法变成了静态方法,归类所有,也称为类方法。
[修饰符] static 返回值 方法名(){}
静态变量的访问形式
[1]类名.静态方法(推荐写法)
[2]对象.静态方法
静态方法中可以直接访问静态变量。
public class Car{ String brand; String type; String color; static int count = 0; public Car(){ Car.count++; } public Car(String brand,String type,String color){ this.brand = brand; this.type = type; this.color = color; Car.count++; } public static int getCount(){ return count; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("我的品牌:"+this.brand+",我的型号:"+this.type+",我的颜色:"+this.color); System.out.println("我是第"+Car.count+"辆车"); } }
可以在实例方法中访问静态变量。
读代码以下代码
public static int getCount(){ // 静态方法中不能访问实例变量 //System.out.println(brand); // 静态方法中不能访问实例方法 showInfo(); // 省略this this.showInfo(); return count; }
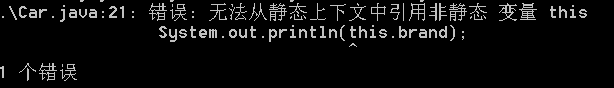
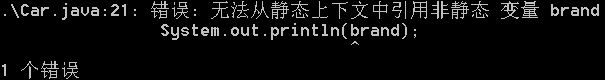

静态方法不能访问实例变量和实例方法。
静态方法不能访问实例成员。
静态方法不能访问非静态成员。
1.6.3 Static 静态特性
jvm在加载.class 文件时,
[1]读取.class中的静态特性,为静态变量和静态方法分配空间.
[2]读取实例变量,计算创建该类对象需要的内存空间。
public class Test03{ public static void main(String[] args){ Car.getCount(); } }
一句话:静态成员一定比实例成员先分配空间。
1.7 代码块
在类中,根据代码块所处的位置和修饰符,可以把代码块分为普通代码块、构造代码块、静态代码块、同步代码块(多线程讲解)。
在java中,用{}表示代码块。
1.7.1 普通代码块
普通代码块位于方法中,形成作用域。
public void showInfo(){ int num = 10; { System.out.println("num="+num); int num2 = 20; } System.out.println("num2="+num2); }
1.7.2 构造代码块
构造代码块位于方法外,类的内部。
public class Person{ String name; int age; // 构造代码块 { System.out.println("我是构造代码块"); } public Person(){ System.out.println("Person()"); } public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("我的名字:"+this.name); } }
总结
[1] 构造代码块执行多次。构造一次对象,执行一次。
[2] 构造代码块比构造方法先执行。
1.7.3 静态代码块
静态代码块位于方法外,类的内部,用static。
public class Person{ String name; int age; // 静态代码块 static{ System.out.println("我是静态代码块"); }
总结
[1]执行一次。在.class加载时执行。
[2]比构造方法先执行。
1.8 封装
1.8.1 封装的概念
将类的某些信息隐藏在类内部,不允许外部程序直接访问,而是通过该类提供的方法来实现对隐藏信息的操作和访问
封装的步骤
[1] 属性私有化。
[2] setter/getter
[3] setter/getter添加业务逻辑或者校验逻辑。
public class Student{ private String name; private int age; // age的设置器(setter) public void setAge(int age){ if(age >= 18){ this.age = age; }else{ System.out.println("年龄值不合法!"); } } // age访问器(getter) public int getAge(){ return this.age; } public void setName(String name){ if(!name.equals("")){ this.name = name; }else{ System.out.println("姓名不能为空!"); } } public String getName(){ return this.name; } }
封装的好处
[1] 隐藏类的实现细节。
[2] 只能通过提供的setter/getter方法访问数据
[3] 方便加入业务逻辑和校验逻辑
[4] 方便后期维护
1.9 This关键字(下)
this 关键字表示本对象/对象本身。
[1]this 访问属性
[2]this 访问方法。
public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字:"+this.getName()); System.out.println(",年龄:"+this.getAge()); }
[3]this 调用构造方法。形式
this(); this(参数1,参数2)
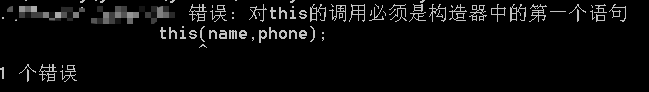
public Student(){ } public Student(String name,String phone){ this.setName(name); this.setPhone(phone); } public Student(String name,String phone,int age){ this(name,phone); this.setAge(age); }
1.10 静态常量
静态变量经常和常量结合使用形成静态常量。
public class Penguin2{ String name; int health = 100; int love = 0; static final String SEX_MAN = "雄"; static final String SEX_FEMAN = "雌"; private String gender; public void setGender(String gender){ if(gender.equals(Penguin2.SEX_MAN) || gender.equals(Penguin2.SEX_FEMAN)){ this.gender = gender; }else{ System.out.println("性别不合法!"); } } public String getGender(){ return this.gender; } public Penguin2(){ } public Penguin2(String name,int health,int love,String gender){ this.name = name; this.health = health; this.love = love; this.setGender(gender); } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("我的自白:"); System.out.print("我的名字是:"+name+",我的健康值:"+health); System.out.print(",我的亲密度:"+love+",我是一只:"+this.getGender()); } }
作业
