1、模块化概述


2、模块的基本使用
模块的基本使用步骤
- 创建模块(按照以前随笔中的方式创建模块,创建包,创建类,定义方法)
创建2个模块:myOne,myTwo
- 在模块的src目录下新建一个名为module-info.java的描述性文件,该文件专门定义模块名,访问权限,模块依赖等信息
描述性文件中使用模块导出和模块依赖来进行配置并使用
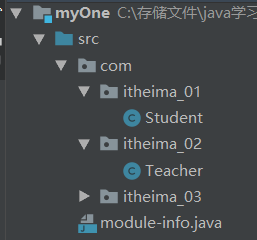
package com.itheima_01; public class Student { public void study(){ System.out.println("好好学习"); } }
package com.itheima_02; public class Teacher { public void teach(){ System.out.println("好好教育"); } }
- 模块中所有未导出的包都是模块私有的,他们是不能在模块之外被访问的
在myOne这个模块下的module-info.java中配置模块导出
模块导出格式:exports 包名;
module myOne {
exports com.itheima_01;
}
- 一个模块要访问其他的模块,必须明确指定依赖哪些模块,未明确指定依赖的模块不能访问
在myTwo这个模块下的module-info.java中配置模块依赖
模块依赖格式:requires 模块名;
注意:写模块名报错,需要按下Alt+Enter提示,然后选择模块依赖
module myTwo {
requires myOne;
}
- 在myTwo这个模块的类中使用依赖模块下的内容
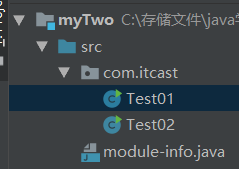
package com.itcast; import com.itheima_01.Student; public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.study(); } }
3、模块服务的使用

模块服务的使用步骤:
- 在myOne模块下创建一个包com.itheima_03,在该包下提供一个接口,接口中定义一个抽象方法
package com.itheima_03;
public interface MyService {
public void service();
}
- 在com.itheima_03包下创建一个包impl,在该包下提供接口的两个实现类Itheima和Czxy
package com.itheima_03.impl; import com.itheima_03.MyService; public class Czxy implements MyService { @Override public void service(){ System.out.println("haohao"); } }
package com.itheima_03.impl; import com.itheima_03.MyService; public class Itheima implements MyService { @Override public void service(){ System.out.println("shide"); } }
- 在myOne这个模块下的module-info.java中添加如下配置
模块导出:exports com.itheima_03;
服务提供:provides MyService with Itheima; //指定MySerive的服务实现类是Itheima
import com.itheima_03.MyService; import com.itheima_03.impl.Itheima; module myOne { exports com.itheima_03; provides MyService with Itheima; }
- 在myTwo这个模块下的module-info.java中添加如下配置
声明服务接口:uses MyService;
import com.itheima_03.MyService; module myTwo { uses MyService; }
- 在myTwo这个模块的类中使用MyService接口提供的服务
ServiceLoader:一种加载服务实现的工具
package com.itcast; import com.itheima_03.MyService; import java.util.ServiceLoader; public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) { ServiceLoader<MyService> sl = ServiceLoader.load(MyService.class); for(MyService my: sl){ my.service(); } } }