I/O:
I/O是什么?
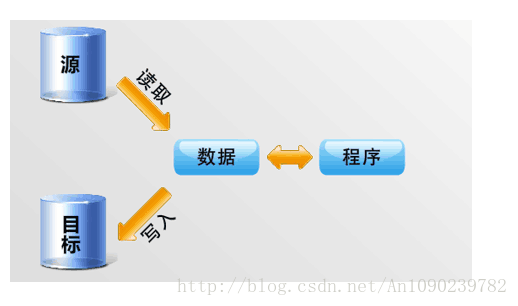
在程序中,所有的数据都是以流的形式进行传输或者保存。
程序需要数据的时候,就要使用输入流读取数据。
程序需要保存数据的时候,就要使用输出流来完成。
程序的输入以及输出都是以流的方式进行的,流中保存的为字节文件。
Java流:
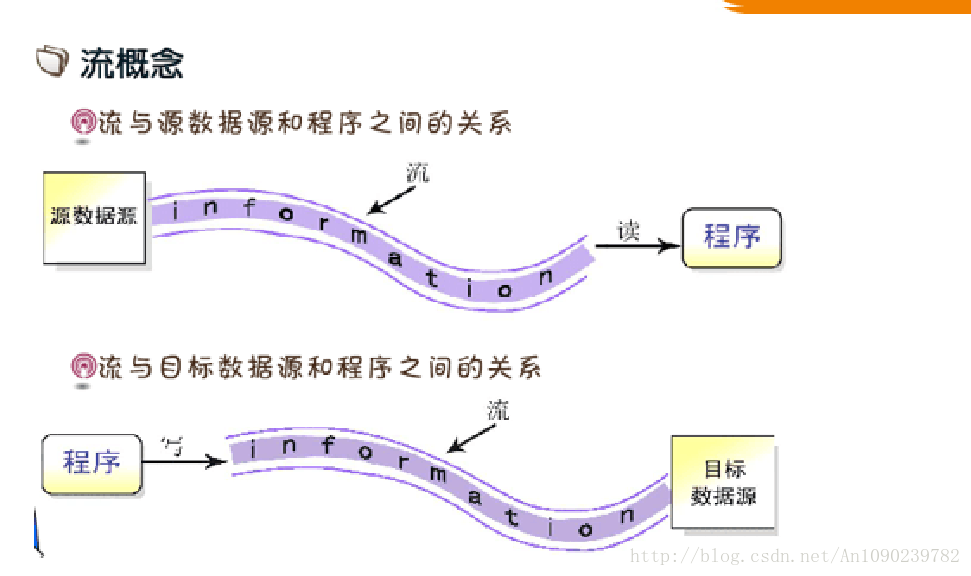
流概念:
流与源数据和程序之间的关系:
源数据与程序时间是以流的形式传输的。
流与目标数据源和程序之间的关系:
程序与目标数据源之间以流的形式传输。
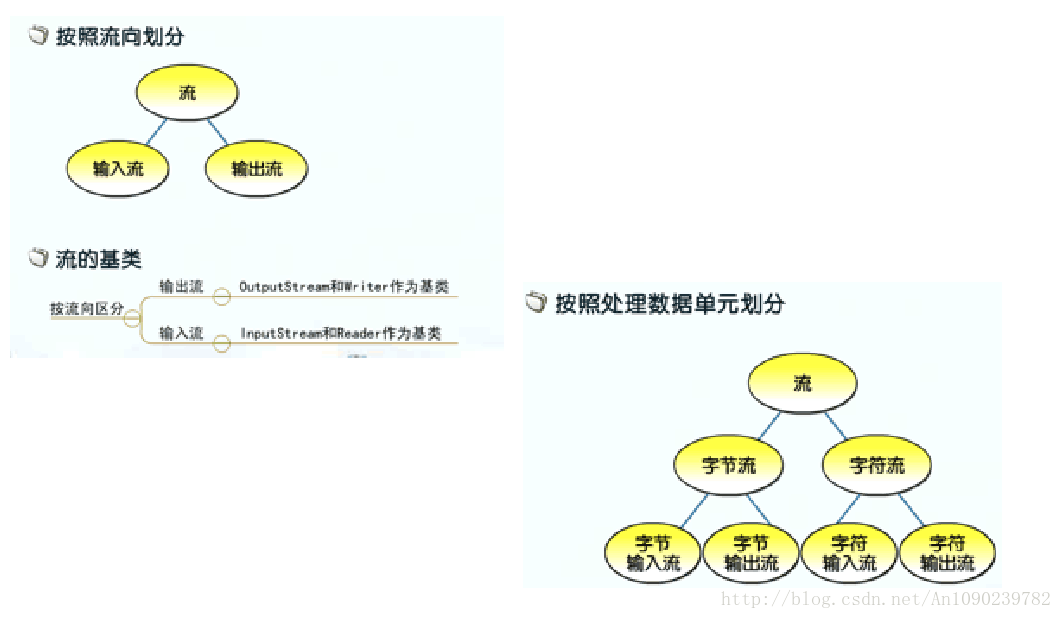
流的分类
按照流向划分:(相对程序而言)
输出流:OutputStream和Writer作为基类 (写入)
输入流:InputStream和Reader作为基类 (读取)
按照处理数据单元划分:
字节流:
字节输入流
字节输出流
字符流:(文本一般以字符为单位)
字符输入流
字符输出流
—-先看流向(入/出),在看处理单元(字符/字节)。
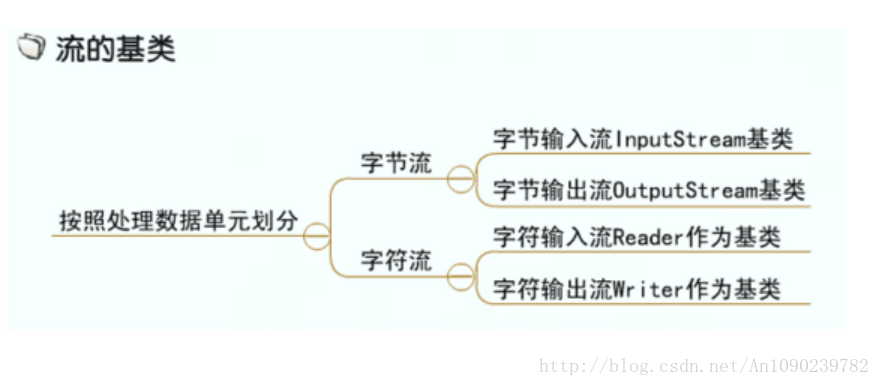
流的基类
流的基类:
输入流:InputStream(字节输入流)和Reader(字符输入流)为基类
输出流:OutputStream(字节输出流)和Writer(字符输出流)为基类
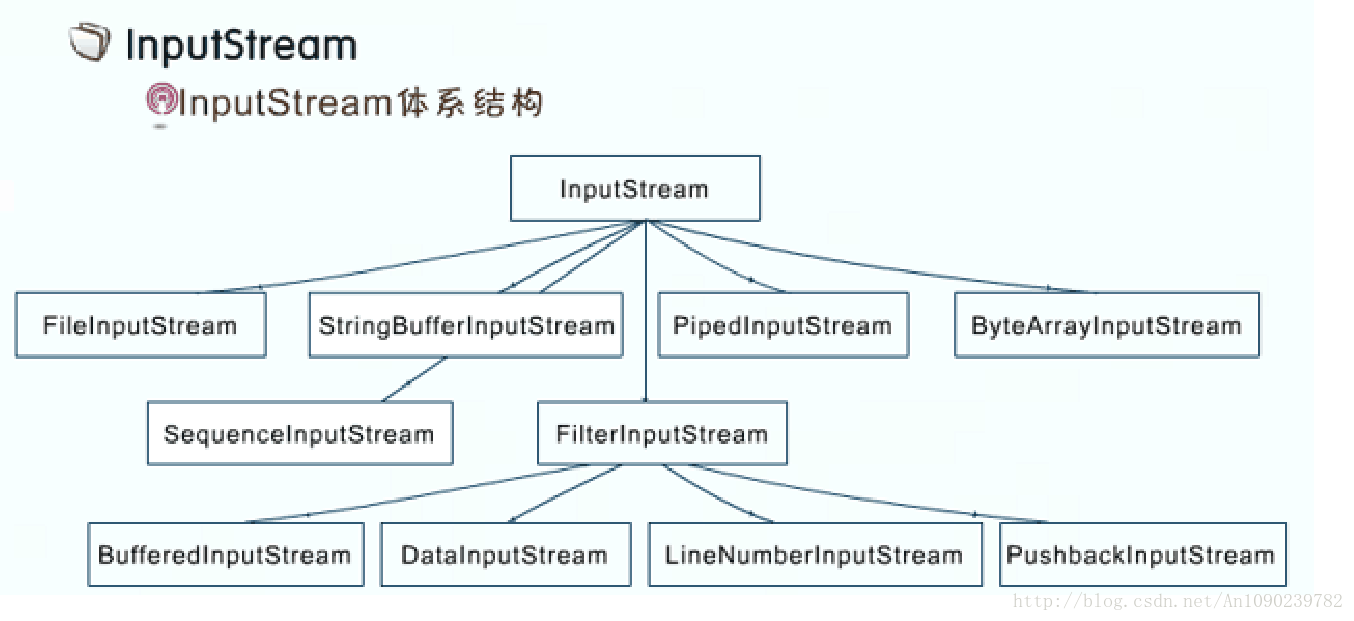
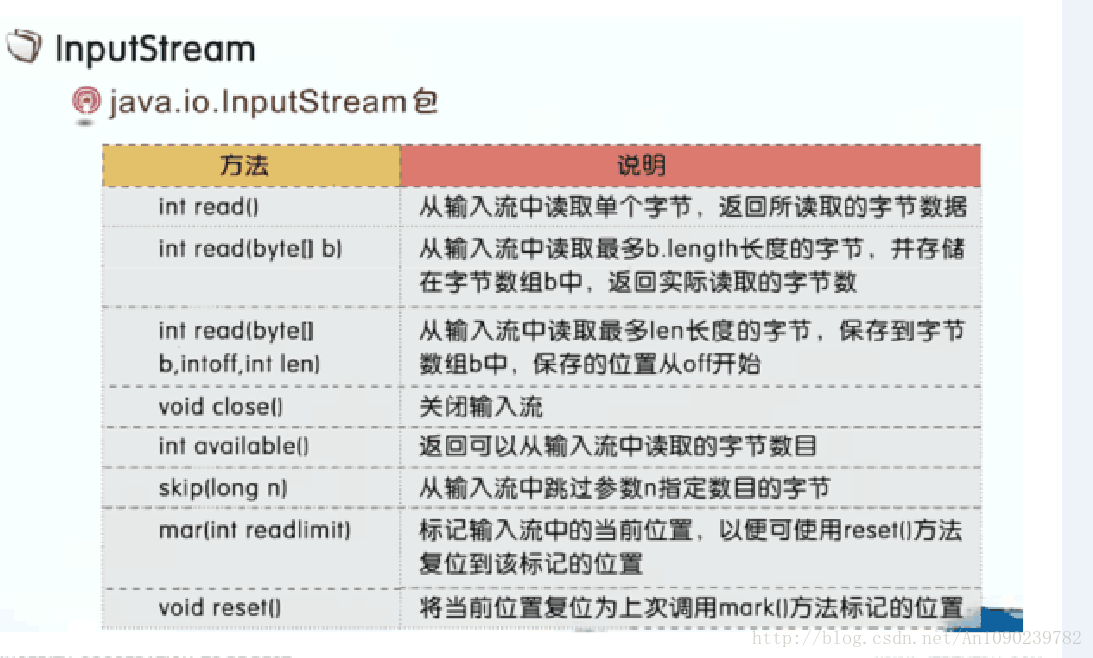
InputStream
读取文件
public static void main(String[] args){
//磁盘路径两种表示方式:
// 1: \ 2: /
try {
//从文件地址中读取内容到程序中
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:/IOFile/Ch02.txt");
//开始读取信息
//先定义一个字节数组存放数据
byte[] b = new byte[8];
//完整的读取一个文件
int off=0;
byte [] c=new byte[is.available()]; //返回文件的大小
while(is.read(b,off,2)!=-1){
off+=2;
// System.out.println(off);
}
// is.read(b,0,2);
// is.read(b,off,len);
//read返回读取的文件大小
//最大不超过b.length,实际读取以文件大小为准
//打印的字节
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
//如何把字节数组转成字符串
System.out.println(new String(b));
// while(is.read(b)!=-1){
//
// }
//关闭流
is.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
//文件没有找到异常
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
//文件读写异常
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}返回文件的大小
byte [] b=new byte[is.available()];读取文件:
BufferInputSream适用于大文件。
读取至一半时还可暂停。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:/IOFile/Ch05.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
//读取文件内容
byte [] b= new byte[bis.available()];
bis.read(b);
System.out.println(new String(b));
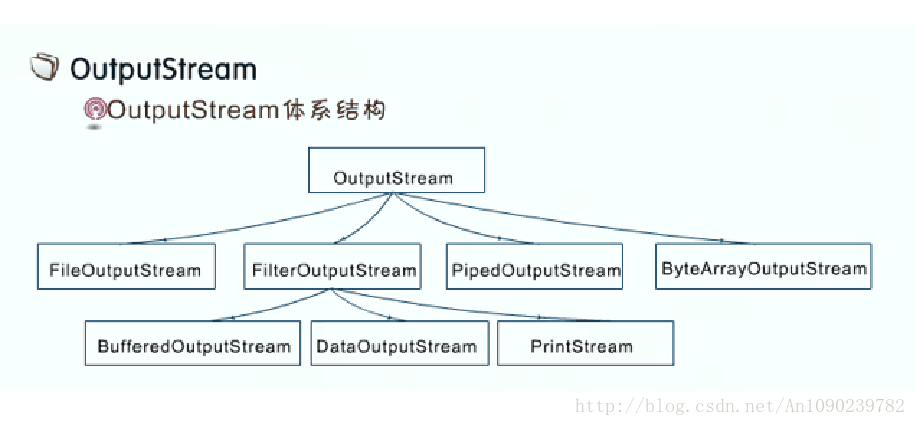
// String(byte[])把字节数组转成字符串OutputStream
写入文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//把程序和目标源建立连接
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/IoFile/out.txt");
//把字符串转成字节数组
String str = "求知若愚,虚心若饥";
fos.write(str.getBytes());
//flush 把数据完全冲刷到目标源中
fos.flush();
fos.close();
System.out.println("文件写入成功!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}BufferedOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//把程序和目标源建立连接
//Buffer更加安全
//直接传文件名,默认覆盖原有内容
//文件名+true;在原有内容后追加新内容
// BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/IoFile/buffer.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/IoFile/buffer.txt",true));
//把字符串转成字节数组
String str = "求知若愚,虚心若饥";
bos.write(str.getBytes());
//flush 把数据完全冲刷到目标源中
bos.flush();
bos.close();
System.out.println("文件写入成功!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}PrintStream
public static void main(String[] args) {
//构造参数传System,out,就是在控制台打印信息
// PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(System.out);
// ps.print("132546u");
try {
PrintStream ps1=
new PrintStream
(new FileOutputStream("D:/IoFile/print.txt"));
ps1.println("虚心若愚");
ps1.println("求知若饥");
ps1.println("求知若饥");
ps1.println("虚心若愚");
ps1.flush();
ps1.close();
System.out.println("写入成功!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}DataInputStream
try {
//写入
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/IoFile/data.txt"));
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeInt(110);
dos.writeUTF("求知若饥");
dos.flush();
dos.close();
System.out.println("写入成功!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//读取
try {
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:/IoFile/data.txt"));
//读的顺序必须与写的顺序相同
dis.readBoolean();
dis.readInt();
dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
dis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}