散列表类似于数组,可以把散列表的散列值看成数组的索引值。访问散列表和访问数组元素一样快速,它可以在常数时间内实现查找和插入操作。
由于无法通过散列值知道键的大小关系,因此散列表无法实现有序性操作。
查找
- 用散列函数将被查找的键转化程数组的一个索引(理想状态下,不同的键都能转化为不同的索引值。当然这只是理想情况,所以我们需要面对两个或者多个键都会散列到相同的索引值也就是碰撞
- 处理碰撞(拉链法和线性探索法
散列函数
散列函数应该满足以下三个条件:
- 一致性:相等的键应当有相等的 hash 值,两个键相等表示调用 equals() 返回的值相等。
- 高效性:计算应当简便,有必要的话可以把 hash 值缓存起来,在调用 hash 函数时直接返回。
- 均匀性:所有键的 hash 值应当均匀地分布到 [0, M-1] 之间,如果不能满足这个条件,有可能产生很多冲突,从而导致散列表的性能下降。
软缓存
如果散列值的计算很耗时,那么我们或许可以将每个键的散列值缓存起来
碰撞处理
-
基于拉链法的散列表
拉链法使用链表来存储 hash 值相同的键,从而解决冲突。
查找需要分两步,首先查找 Key 所在的链表,然后在链表中顺序查找。

-
基于线性探测法的散列表
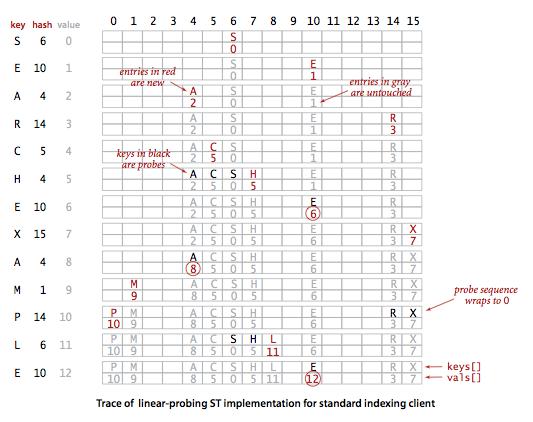
线性探测法使用空位来解决冲突,当冲突发生时,向前探测一个空位来存储冲突的键。
使用线性探测法,数组的大小 M 应当大于键的个数 N(M>N)。
实现
- 基于拉链法的散列表
public class SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 4;
private int n;//键值对总数
private int m;//散列表大小
private SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>[] st;//这里使用了之前实现的[无序链表](https://www.cnblogs.com/aiguozou/p/11420339.html)
public SeparateChainingHashST() {
this(INIT_CAPACITY);
}
public SeparateChainingHashST(int m) {
this.m = m;
st = (SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>[]) new SequentialSearchST[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
st[i] = new SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>();
}
private void resize(int chains) {
SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value> temp = new SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value>(chains);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (Key key : st[i].keys()) {
temp.put(key, st[i].get(key));
}
}
this.m = temp.m;
this.n = temp.n;
this.st = temp.st;
}
private int hash(Key key) {
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % m;
}
public int size() {
return n;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
public Value get(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");
int i = hash(key);
return st[i].get(key);
}
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null");
//如果值为Null删除
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
if (n >= 10 * m) resize(2 * m);
int i = hash(key);
if (!st[i].contains(key)) n++;
st[i].put(key, val);
}
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null");
int i = hash(key);
if (st[i].contains(key)) n--;
st[i].delete(key);
if (m > INIT_CAPACITY && n <= 2 * m) resize(m / 2);
}
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
LinkedList<Key> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (Key key : st[i].keys())
queue.add(key);
}
return queue;
}
}
- 基于线性探测法的散列表
to be continue