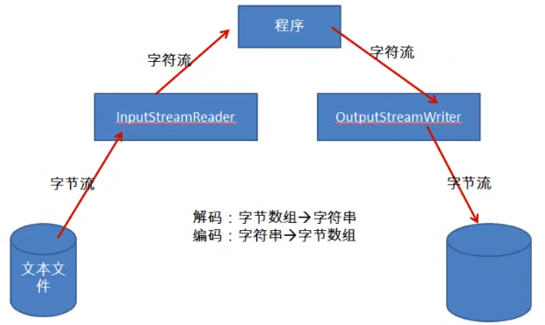
转换流的作用
TestOtherStream
package com.aff.file; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import org.junit.Test; //转换流InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter // 编码:字符串--->字节数组 // 解码:字节数组--->字符串 public class TestOtherStream { @Test public void test1() { BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { // 解码 File file1 = new File("jdbc.properties"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf-8"); br = new BufferedReader(isr); // 编码 File file2 = new File("jdbc6.properties"); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2); OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "utf-8"); bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); String str; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (bw != null) { try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (br != null) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
// 标准的输入输出流 // 练习:从键盘输入字符流,要求将读取到的整字符串转成大写输出, // 然后继续进行输入操作,直至当输入e或者exit时,退出程序 @Test public void test2() { BufferedReader br = null; /* * 标准的输入输出流: 标准的输入流: * System.in 标准的输出流:System.out */ try { InputStream is = System.in;// 字节流 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);// 字节流转换为字符流 br = new BufferedReader(isr);// 在字符流外面包一层缓冲流 String str; while (true) { System.out.println("输入字符串"); str = br.readLine(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("e") || str.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) { break; } String str1 = str.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(str1); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (br != null) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }