一、简介
在Java程序执行过程中, 总是会发生不被期望的事件, 阻止程序按照程序员预期正常运行, 这就是Java程序出现的异常。在企业级开发中, 容易导致各种各样的小bug, 严重影响产品的运行和用户体验。所以大多数开发团队都有自己的异常处理的规则和方法。如果你是一个团队的新手,你可能会惊讶于这些方法与你之前使用过的那些方法有多么不同。
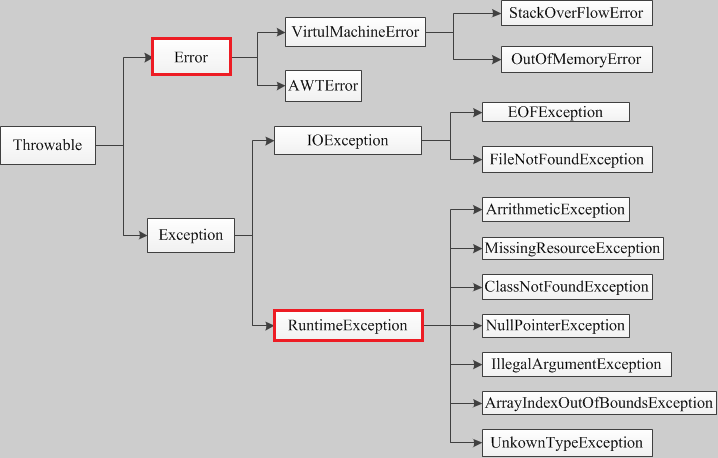
二、Java异常体系
Java所有异常的父类都是java.lang.Throwable、无论是内部的异常还是自定义异常。只有直接或者间接集成java.lang.Throwable类,JVM才会认为这是异常对象并且处理。
Java异常体系中Error为错误,较Exception严重。Error不是由我们程序自身导致的,是JVM运行错误导致的,所以暂时不是我们讨论的范围。Exception则是异常的基类,又可以分为"运行时异常"与"编译时异常"(又称为"非检查异常和检查异常")。
非检查异常RuntimeException; 在编译阶段无法检查,如ArithmeticException(除0引发)、InputMismatchException(输入的数据不能被转换为int类型引发)。引发非检查异常大多数原因是编码错误,应该检查程序。
检查异常(IOException),在编译时可以检查, 需要异常处理。处理方式有二种、(1)函数签名中throws抛出异常 (2)tryCatch语句捕获。
三 、异常现象
下面的代码会演示2个异常类型:ArithmeticException 和 InputMismatchException。前者由于整数除0引发,后者是输入的数据不能被转换为int类型引发。
1 package it.check.exception; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 /* 4 * 初步测试Java的“非检查异常”、如ArithmeticException(除0引发)、InputMismatchException(输入的数据不能被转换为int类型引发) 5 * “非检查异常”在编译时不会提示信息、在运行是则会抛出异常。通常不需要try{} catch(){} finally{}处理 6 * 7 * **/ 8 public class ArithmeticExceptionRun { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 System . out. println( "----欢迎使用命令行除法计算器----" ) ; 12 CMDCalculate (); 13 14 } 15 public static void CMDCalculate () 16 { 17 Scanner scan = new Scanner ( System. in ); 18 int num1 = scan .nextInt () ; //阻塞、等待输入 19 int num2 = scan .nextInt () ; 20 int result = devide (num1 , num2 ) ; 21 System . out. println( "result:" + result) ; 22 scan .close () ; 23 } 24 public static int devide (int num1, int num2 ){ 25 return num1 / num2 ; 26 } 27 28 }
/** * ----欢迎使用命令行除法计算器---- 2 0 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at it.check.exception.ArithmeticExceptionRun.devide(ArithmeticExceptionRun.java:25) at it.check.exception.ArithmeticExceptionRun.CMDCalculate(ArithmeticExceptionRun.java:20) at it.check.exception.ArithmeticExceptionRun.main(ArithmeticExceptionRun.java:12) * * */ /** * ----欢迎使用命令行除法计算器---- a Exception in thread "main" java.util.InputMismatchException at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Scanner.java:864) at java.util.Scanner.next(Scanner.java:1485) at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Scanner.java:2117) at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Scanner.java:2076) at it.check.exception.ArithmeticExceptionRun.CMDCalculate(ArithmeticExceptionRun.java:18) at it.check.exception.ArithmeticExceptionRun.main(ArithmeticExceptionRun.java:12) * */
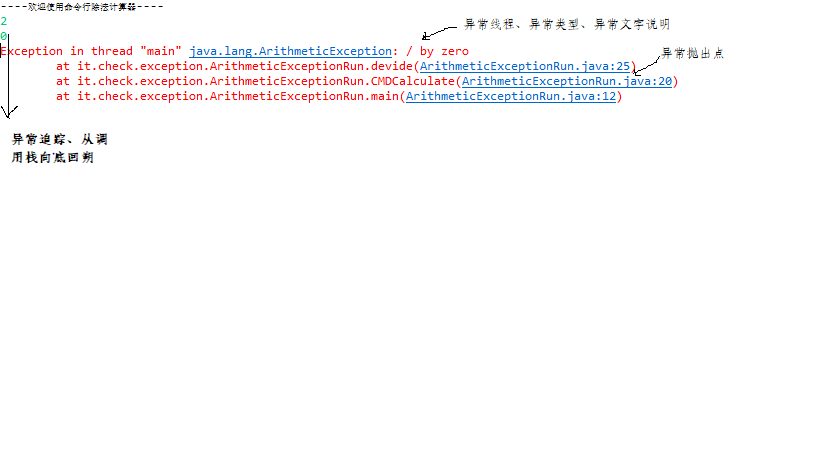
异常追踪栈; 异常在函数中产生,函数存在调用栈,main 调用CMDCalculate方法、CMDCalculate方法在调用device。当发生/0 异常时, 当这些被影响的函数以异常信息输出时、形成异常追踪栈、由device->CMDCalculate->main 栈顶向栈底回朔。
以上例子为非检查异常、接着是检查异常, 有二种处理方式。
方式一: 使用tryCatchFinally语句捕获
public class BufferDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { bufferRead("E:"+File.separatorChar+"a.txt"); } /** 使用缓冲技术读取数据 * * */ public static void bufferRead(String path) { BufferedInputStream bi=null; byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; int length=0; try { bi=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(path)); while((length=bi.read(buf))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if(bi!=null){ bi.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
方式二:throws抛出,由调用者处理。函数使用throws抛出异常可能是(1)函数本身不知道怎么处理异常 (2)把异常交给调用者处理(捕获等)更加合适。
public class BufferDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { try { bufferRead("E:"+File.separatorChar+"a.txt"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** 使用缓冲技术读取数据 * @throws IOException * * * */ public static void bufferRead(String path) throws IOException{ BufferedInputStream bi=null; byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; int length=0; bi=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(path)); while((length=bi.read(buf))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length)); bi.close(); } } }
四、异常链化
在一些大型的,模块化的软件开发中,一旦一个地方发生异常,则如骨牌效应一样,将导致一连串的异常。假设B模块完成自己的逻辑需要调用A模块的方法,如果A模块发生异常,则B也将不能完成而发生异常,但是B在抛出异常时,会将A的异常信息掩盖掉,这将使得异常的根源信息丢失。异常的链化可以将多个模块的异常串联起来,使得异常信息不会丢失。
异常链化:以一个异常对象为参数构造新的异常对象。新的异对象将包含先前异常的信息。这项技术主要是异常类的一个带Throwable参数的函数来实现的。这个当做参数的异常,我们叫他根源异常(cause)。
查看Throwable类源码,可以发现里面有一个Throwable字段cause,就是它保存了构造时传递的根源异常参数。这种设计和链表的结点类设计如出一辙,因此形成链也是自然的了。
public class Throwable implements Serializable { private Throwable cause = this; public Throwable(String message, Throwable cause) { fillInStackTrace(); detailMessage = message; this.cause = cause; } public Throwable(Throwable cause) { fillInStackTrace(); detailMessage = (cause==null ? null : cause.toString()); this.cause = cause; } //........ }
下面是一个例子,演示了异常的链化:从命令行输入2个int,将他们相加,输出。输入的数不是int,则导致getInputNumbers异常,从而导致add函数异常,则可以在add函数中抛出一个链化的异常。给出链化例子。
1 public static void main(String[] args) 2 { 3 4 System.out.println("请输入2个加数"); 5 int result; 6 try 7 { 8 result = add(); 9 System.out.println("结果:"+result); 10 } catch (Exception e){ 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 //获取输入的2个整数返回 15 private static List<Integer> getInputNumbers() 16 { 17 List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); 18 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 19 try { 20 int num1 = scan.nextInt(); 21 int num2 = scan.nextInt(); 22 nums.add(new Integer(num1)); 23 nums.add(new Integer(num2)); 24 }catch(InputMismatchException immExp){ 25 throw immExp; 26 }finally { 27 scan.close(); 28 } 29 return nums; 30 } 31 32 //执行加法计算 33 private static int add() throws Exception 34 { 35 int result; 36 try { 37 List<Integer> nums =getInputNumbers(); 38 result = nums.get(0) + nums.get(1); 39 }catch(InputMismatchException immExp){ 40 throw new Exception("计算失败",immExp); /////////////////////////////链化:以一个异常对象为参数构造新的异常对象。 41 } 42 return result; 43 } 44 45 /* 46 请输入2个加数 47 r 1 48 java.lang.Exception: 计算失败 49 at practise.ExceptionTest.add(ExceptionTest.java:53) 50 at practise.ExceptionTest.main(ExceptionTest.java:18) 51 Caused by: java.util.InputMismatchException 52 at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Scanner.java:864) 53 at java.util.Scanner.next(Scanner.java:1485) 54 at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Scanner.java:2117) 55 at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Scanner.java:2076) 56 at practise.ExceptionTest.getInputNumbers(ExceptionTest.java:30) 57 at practise.ExceptionTest.add(ExceptionTest.java:48) 58 ... 1 more 59 60 */