1.简介
线性表是最基本、最简单、也是最常用的一种数据结构。一个线性表是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 
前驱元素:
若A元素在B元素的前面,则称A为B的前驱元素
后继元素:
若B元素在A元素的后面,则称B为A的后继元素
线性表的特征:数据元素之间具有一种“一对一”的逻辑关系。
1. 第一个数据元素没有前驱,这个数据元素被称为头结点;
2. 最后一个数据元素没有后继,这个数据元素被称为尾结点;
3. 除了第一个和最后一个数据元素外,其他数据元素有且仅有一个前驱和一个后继。
如果把线性表用数学语言来定义,则可以表示为(a1,...ai-1,ai,ai+1,...an),ai-1领先于ai,ai领先于ai+1,称ai-1是ai的前驱元素,ai+1是ai的后继元素
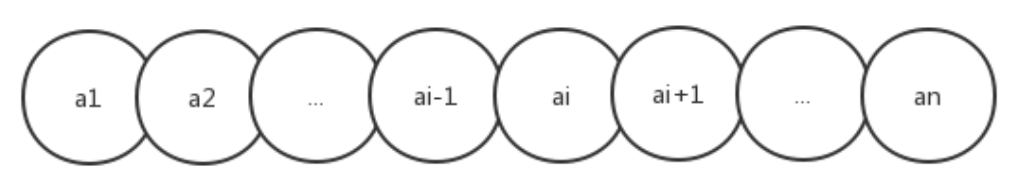
线性表的分类:
线性表中数据存储的方式可以是顺序存储,也可以是链式存储,按照数据的存储方式不同,可以把线性表分为顺序表和链表。
2.顺序表
顺序表是在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表,线性表的顺序存储是指用一组地址连续的存储单元,依次存储线性表中的各个元素、使得线性表中再逻辑结构上响铃的数据元素存储在相邻的物理存储单元中,即通过数据元素物理存储的相邻关系来反映数据元素之间逻辑上的相邻关系。 
2.1 顺序表的实现
顺序表API设计:
| 类名 | SequenceList |
| 构造方 法 |
SequenceList(int capacity):创建容量为capacity的SequenceList对象 |
| 成员方 法 |
1.public void clear():空置线性表 2.publicboolean isEmpty():判断线性表是否为空,是返回true,否返回false 3.public int length():获取线性表中元素的个数 4.public T get(int i):读取并返回线性表中的第i个元素的值 5.public void insert(int i,T t):在线性表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素。 6.public void insert(T t):向线性表中添加一个元素t 7.public T remove(int i):删除并返回线性表中第i个数据元素。 8.public int indexOf(T t):返回线性表中首次出现的指定的数据元素的位序号,若不存在,则返 回-1。 |
| 成员变 量 |
1.private T[] eles:存储元素的数组 2.private int N:当前线性表的长度 |
顺序表的代码实现:

1 package cn.itcast.algorithm.Demo.linear; 2 3 4 import cn.itcast.algorithm.linear.SequenceList; 5 6 import java.util.Iterator; 7 import java.util.Spliterator; 8 import java.util.function.Consumer; 9 10 public class SequenceListDemo<T> implements Iterable<T> { 11 //成员变量 12 /* 13 1.private T[] eles:存储元素的数组 14 2.private int N:当前线性表的长度 15 */ 16 private T[] eles; 17 private int N; 18 19 20 //构造方法 21 /* 22 SequenceList(int capacity):创建容量为capacity的SequenceList对象 23 */ 24 public SequenceListDemo(int capacity) { 25 //初始化数组 26 this.eles = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; 27 //初始化长度 28 this.N = 0; 29 } 30 31 //成员方法 32 /* 33 1.public void clear():空置线性表 34 2.public boolean isEmpty():判断线性表是否为空,是返回true,否返回false 35 3.public int length():获取线性表中元素的个数 36 4.public T get(int i):读取并返回线性表中的第i个元素的值 37 5.public void insert(int i,T t):在线性表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素。 38 6.public void insert(T t):向线性表中添加一个元素t 39 7.public T remove(int i):删除并返回线性表中第i个数据元素。 40 8.public int indexOf(T t):返回线性表中首次出现的指定的数据元素的位序号,若不存在,则返回-1。 41 */ 42 43 //1.public void clear():空置线性表 44 public void clear() { 45 this.N = 0; 46 } 47 48 //2.public boolean isEmpty():判断线性表是否为空,是返回true,否返回false 49 public boolean isEmpty() { 50 return N == 0; 51 } 52 53 //3.public int length():获取线性表中元素的个数 54 public int length() { 55 return N; 56 } 57 58 //4.public T get(int i):读取并返回线性表中的第i个元素的值 59 public T get(int i) { 60 return eles[i]; 61 } 62 63 //5.public void insert(int i,T t):在线性表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素。 64 public void insert(int i, T t) { 65 //扩容 66 if (N == eles.length) { 67 resize(2 * eles.length); 68 } 69 70 //先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向后移动一位 71 for (int index = N; index > i; index--) { 72 eles[index] = eles[index - 1]; 73 } 74 //再把t元素放到i索引处即可 75 eles[i] = t; 76 77 //元素个数+1 78 N++; 79 } 80 81 //6.public void insert(T t):向线性表中添加一个元素t.添加在尾部 82 public void insert(T t) { 83 84 if (N == eles.length) { 85 resize(2 * eles.length); 86 } 87 88 eles[N++] = t; 89 } 90 91 //根据参数newSize,重置eles的大小 92 public void resize(int newSize) { 93 94 //定义一个临时数组,指向原数组 95 T[] temp = eles; 96 //创建新数组 97 eles = (T[]) new Object[newSize]; 98 //把原数组的数据拷贝到新数组即可 99 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 100 eles[i] = temp[i]; 101 } 102 } 103 104 //7.public T remove(int i):删除并返回线性表中第i个数据元素。 105 public T remove(int i) { 106 T current = eles[i]; 107 //先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向前移动一位 108 for (int index = N; index > i; index--) { 109 eles[index - 1] = eles[index]; 110 } 111 //元素个数-1 112 N--; 113 //缩容 114 if (N < eles.length / 4) { 115 resize(eles.length / 2); 116 } 117 return current; 118 } 119 120 //8.public int indexOf(T t):返回线性表中首次出现的指定的数据元素的位序号,若不存在,则返回-1。 121 public int indexOf(T t) { 122 for (int i = 0; i < eles.length; i++) { 123 if (eles[i].equals(t)) { 124 return i; 125 } 126 } 127 return -1; 128 } 129 130 131 @Override 132 public Iterator<T> iterator() { 133 return new SIterator(); 134 } 135 136 private class SIterator implements Iterator{ 137 private int cusor; 138 public SIterator(){ 139 this.cusor=0; 140 } 141 @Override 142 public boolean hasNext() { 143 return cusor<N; 144 } 145 146 @Override 147 public Object next() { 148 return eles[cusor++]; 149 } 150 } 151 }
测试类:

1 package cn.itcast.algorithm.DemoTest.sortTest.linearTest; 2 3 import cn.itcast.algorithm.Demo.linear.SequenceListDemo; 4 5 public class SequenceListDemoTest { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //创建对象 8 SequenceListDemo<String> s = new SequenceListDemo<>(10); 9 //插入元素 10 s.insert("中秋节"); 11 s.insert("国庆节"); 12 s.insert("元宵节"); 13 s.insert("清明节"); 14 15 16 System.out.println("------------------------------"); 17 //遍历元素 18 System.out.println("遍历元素"); 19 for (String s1 :s){ 20 System.out.println(s1); 21 } 22 23 System.out.println("------------------------------"); 24 boolean sEmpty = s.isEmpty(); 25 System.out.println(sEmpty); 26 27 System.out.println("------------------------------"); 28 //移除元素 29 System.out.println("移除元素"); 30 s.remove(3); 31 for (String s1 :s){ 32 System.out.println(s1); 33 } 34 35 System.out.println("------------------------------"); 36 //在线性表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素 37 System.out.println("在线性表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素"); 38 s.insert(0,"劳动节"); 39 s.insert(1,"儿童节"); 40 for (String s1 :s){ 41 System.out.println(s1); 42 } 43 44 45 } 46 47 }
2.2. 顺序表的遍历
一般作为容器存储数据,都需要向外部提供遍历的方式,因此我们需要给顺序表提供遍历方式。
在java中,遍历集合的方式一般都是用的是foreach循环,如果想让我们的SequenceList也能支持foreach循环,则
需要做如下操作:
1.让SequenceList实现Iterable接口,重写iterator方法;
2.在SequenceList内部提供一个内部类
