1、参数绑定注解
1》@RequestParam:
用于将指定的请求参数赋值给方法中的指定参数。支持的属性:

2》@PathVariable:可以方便的获得URL中的动态参数,只支持一个属性value,类型为String,表示绑定的名称。
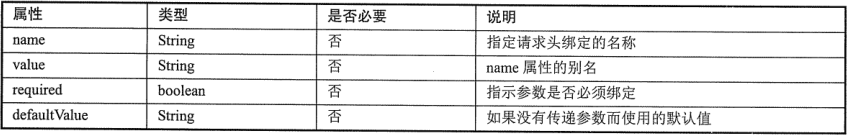
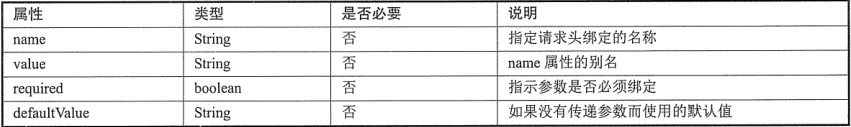
3》@RequestHeader:用于将请求的头信息区数据映射到处理方法的参数上。支持的属性:

4》@CookieValue:将请求的Cookie数据映射到处理方法的参数上。支持的属性有:
举个例子:
@Controller public class CookieValueController{ // 测试@CookieValue注解 // 该方法映射的请求为 /cookieValueTest @GetMapping(value="/cookieValueTest") public void cookieValueTest( @CookieValue(value="JSESSIONID", defaultValue="") String sessionId) { System.out.println("通过@CookieValue获得JSESSIONID: " + sessionId); } }
以上配置自动将JSESSIONID值设置到sessionid参数上,defaultValue表示Cookie中没有JSESSIONID时默认为空。
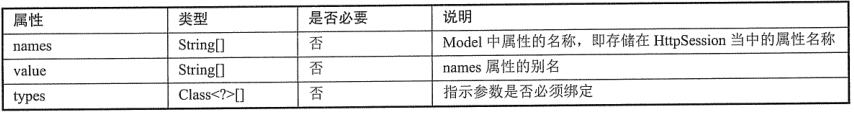
5》@SessionAttributes:只能声明在类上。允许我们有选择的指定Model中的哪些属性需要转存到HttpSession对象中。支持的属性:
6》@ModelAttribute:将请求参数绑定到Model对象。只支持一个属性value,类型为String,表示绑定的属性名称。被@ModelAttribute注释的方法会在Controller每个处理方法执行前被执行。绑定的属性可以在request域被访问到!@ModelAttribute的使用方法:
1>@ModelAttribute(value="attributeName")注释有返回值的方法:将命名为attributeName的属性设置到Model中,而attributeName的属性的值就是该被@ModelAttribute修饰的方法的返回值。被注释方法的参数可以不包含Model类型
2>@ModelAttribute注释void返回值类型的方法:使用model.addAttribute()方法给Model绑定请求参数,前提是被注释方法参数包含Model类型。
3>@ModelAttribute注释返回具体Java Bean类型的方法:没有指定value,即属性名,则具体Java Bean的小写将作为属性名,如被注释方法返回User,则属性名为user。其值即为被注释方法的返回值,在request域可以像访问Java Bean的属性一样访问其内部属性,如request.uesr.username。
4>@ModelAttribute、@RequestMapping同时注释处理方法:@ModelAttribute指定的value的值,则Model的属性名就为该value指定的值,属性的值为被注释方法返回的值;该方法@RequestMapping的value指定的值,作为最后的视图索引,如@RequestMapping("/login"),则被注释方法返回的视图是“/login”。
5>@ModelAttribute注释一个方法的参数:主要实现的是将前端的数据绑定到一个Java Bean,然后将该Java Bean作为处理方法的入参传递参数,现在高版本的spring MVC已经很智能的直接将前端的请求参数对象(如:json对象)对应设置绑定到处理方法的入参中。
@Controller public class ModelAttribute5Controller{
@ModelAttribute("user")
public User userModel(
@RequestParam("loginname") String loginname,
@RequestParam("password") String password
){
User user=new User();
user.setLoginname(loginname);
user.setPassword(password);
return user;
} /* * @ModelAttribute注释方法参数,会自动入参(高版本的spring MVC已经
* 不需要这个参数注解也能自动将参数绑定到参数Java Bean中了) * loginname控件的值会自动入参到User的loginname属性 * password控件的值会自动入参到User的password属性 */ @RequestMapping(value="/login5") public String login5(@ModelAttribute("user") User user) { user.setUsername("管理员"); return "result5"; } }
2、信息转换
1》HttpMessageConverter<T>接口
该接口主要负责将请求信息转换为一个对象(类型为T),并将对象(类型为T)绑定到请求方法的参数中或输出为响应信息。
DispatcherServlet默认已经装配了RequestMappingHandlerAdapter(注解的适配器)作为HandlerAdapter组件的实现类,即HttpMessageConverter由RequestMappingHandlerAdapter使用,将请求信息转换为对象,或将对象转换为响应信息。




如果需要装配其他类型的HttpMessageConverter,则可在spring的web容器的上下文中自定义一个RequestMappingHandlerAdapter:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <property name="messageConverters"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.xml.SourceHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.BufferedImageHttpMessageConverter"/> <!-- 配置fastjson中实现HttpMessageConverter接口的转换器 --> <bean id="fastJsonHttpMessageConverter" class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter"> <!-- 加入支持的媒体类型:返回contentType --> <property name="supportedMediaTypes"> <list> <!-- 这里顺序不能反,一定先写text/html,不然ie下会出现下载提示 --> <value>text/html;charset=UTF-8</value> <value>application/json;charset=UTF-8</value> </list> </property> </bean> </list> </property> </bean>
如果在spring web容器中显式定义了一个RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,spring MVC的RequestMappingHandlerAdapter默认装配的HttpMessageConverter将不再起作用。
Spring MVC默认使用MappingJeckson2HttpMessageConverter转换Json数据,Jackson开源类包可以非常轻松地将Java对象转换json对象或xml文档,同样也可以将json对象、xml文档转换成Java对象。
2》转换数据。
使用org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody注解参数,将request中body的数据转换成json,使用org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody返回json数据。
当前台页面使用GET或POST方式提交数据时,数据编码格式由请求头的ContentType指定,大体的情况分为:

1>使用默认的转换器MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter。该转换器需要使用Jackson包。
举个例子:
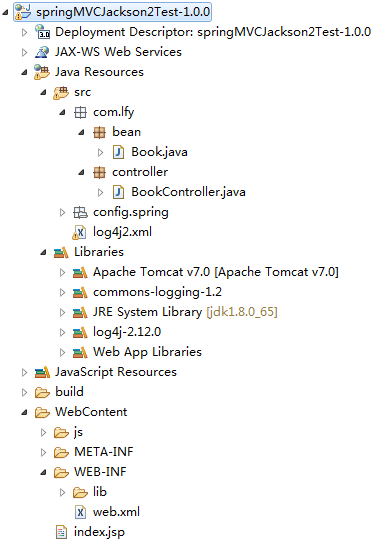
引入的jar包主要是spring框架jar包,jackson-databind-2.9.2.jar、jackson-core-2.9.2.jar、jackson-annotations-2.9.2.jar。
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>测试接收JSON格式的数据</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.11.0.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/json2.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ testRequestBody(); }); function testRequestBody(){ $.ajax("${pageContext.request.contextPath}/json/testRequestBody",// 发送请求的URL字符串。 { dataType : "json", // 预期服务器返回的数据类型。 type : "post", // 请求方式 POST或GET contentType:"application/json", // 发送信息至服务器时的内容编码类型 // 发送到服务器的数据。 data:JSON.stringify({id : 1, name : "Spring+MyBatis企业应用实战"}), async: true , // 默认设置下,所有请求均为异步请求。如果设置为false,则发送同步请求 // 请求成功后的回调函数。 success :function(data){ console.log(data); $("#id").html(data.id); $("#name").html(data.name); $("#author").html(data.author); }, // 请求出错时调用的函数 error:function(){ alert("数据发送失败"); } }); } </script> </head> <body> 编号:<span id="id"></span><br> 书名:<span id="name"></span><br> 作者:<span id="author"></span><br> </body> </html>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>springMVCJackson2Test-1.0.0</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <!-- 定义Spring MVC的前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:config/spring/springmvc-config.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- 让Spring MVC的前端控制器拦截所有请求 --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- 编码过滤器 --> <filter> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <!-- <init-param> <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> --> </filter> <filter-mapping> <!-- 或者 <filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name> --> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app>
springmvc-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!-- 扫描controller --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.lfy.controller"/> <!-- 映射器、适配器策略 --> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <!-- 视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" p:prefix="/WEB-INF/content/" p:suffix=".jsp" /> </beans>
BookController.java
package com.lfy.controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.lfy.bean.Book; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; @Controller @RequestMapping("/json") public class BookController { private static final Log log=LogFactory.getLog(BookController.class); //@RequestBody根据json数据,转换成对应的Object @RequestMapping(value="/testRequestBody") public void setJson(@RequestBody Book book, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception{ //ObjectMapper类是Jackson库的主要类,它提供一些功能将Java Bean转换成json ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); log.info(mapper.writeValueAsString(book)); book.setAuthor("lfy"); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); //将book对象转换成json写出到客户端 response.getWriter().println(mapper.writeValueAsString(book)); } }
Book.java
package com.lfy.bean; import java.io.Serializable; /** * * @author lfy * */ public class Book implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Integer id; private String name; private String author; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", author=" + author + "]"; } }
运行结果:

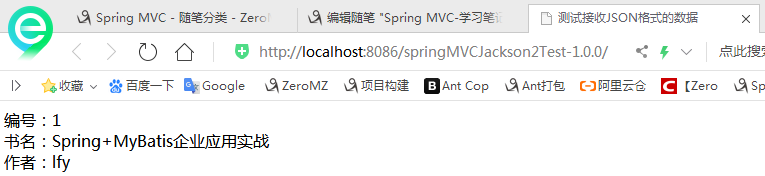
总结:由于RequestMappingHandlerAdapter默认装配MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter,所以使用Jackson在配置方面比较简单,使用的时候只需要在代码中使用ObjectMapper处理数据转换即可。
2>使用fastjson。
引入fastjson的jar包。
springmvc-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd"> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <context:component-scan base-package="org.lfy.controller"/> <!-- 设置配置方案mvc:annotation-driven会自动注册ResquestMappingHandlerMaping 与MappingHandlerAdapter,这是spring为@Controller分发请求必须的,并提供数据绑定 支持 --> <mvc:annotation-driven> <!-- 设置不使用默认的消息转换器 --> <mvc:message-converters register-defaults="false"> <!-- 配置Spring的转换器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.xml.SourceHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.BufferedImageHttpMessageConverter"/> <!-- 配置fastjson中实现HttpMessageConverter接口的转换器 --> <bean id="fastJsonHttpMessageConverter" class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter"> <!-- 加入支持的媒体类型:返回contentType --> <property name="supportedMediaTypes"> <list> <!-- 这里顺序不能反,一定先写text/html,不然ie下会出现下载提示 --> <value>text/html;charset=UTF-8</value> <value>application/json;charset=UTF-8</value> </list> </property> </bean> </mvc:message-converters> </mvc:annotation-driven> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" p:prefix="/WEB-INF/content/" p:suffix=".jsp"/> </beans>
BookController.java
package org.lfy.controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.lfy.bean.Book; @Controller @RequestMapping("/json") public class BookController { /** * RequestBody根据JSON数据转换为对应的Object * @param book * @param response * @throws Exception */ @RequestMapping(value="/testRequestBody") public void setJson(@RequestBody Book book, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception{ System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(book)); book.setAuthor("lfy"); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); response.getWriter().println(JSONObject.toJSONString(book)); } }
运行结果:与使用Jackson的结果一致。

总结:使用fastjson,需要引入fastjson的jar包,同时需要配置HttpMessageConverter将其指向fastjson的转换器。在使用的时候使用JSONObject的方法进行数据转换。(注:如果引入fastjson的jar包,但是没有在适配器中配置转换器为fastjson,发送接收json数据会抛一些问题。)
对比jackson和fastjson,可知只是让适配器使用不同的转换器HttpMessageConverter而已。
==>返回json数据例子:使用@ResponseBody注解方法即可
BookController.java
package org.lfy.controller; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.lfy.domain.Book; @Controller @RequestMapping("/json") public class BookController { /** * * @param book * @param response * @throws Exception */ @RequestMapping(value="/testRequestBody") @ResponseBody public Object getJson(){ List<Book> list=new ArrayList<Book>(); list.add(new Book(1,"mmmmmm","lfy")); list.add(new Book(2,"nnnnnn","lfy")); return list; } @RequestMapping(value="/DataAndView") public ModelAndView setJson(){ List<Book> list=new ArrayList<Book>(); list.add(new Book(1,"kkkkkk","lfy")); list.add(new Book(2,"llllll","lfy")); ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndView(); mv.addObject("data",JSONObject.toJSONString(list)); mv.setViewName("welcome"); return mv; } }
index.jsp读出返回的json数据
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>测试接收JSON格式的数据-jsp</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.11.0.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/json2.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ testRequestBody(); }); function testRequestBody(){ $.post("${pageContext.request.contextPath}/json/testRequestBody",null, function(data){ $.each(data,function(){ var tr=$("<tr align='center'/>"); $("<td/>").html(this.id).appendTo(tr); $("<td/>").html(this.name).appendTo(tr); $("<td/>").html(this.author).appendTo(tr); $("#booktable").append(tr); }) },"json"); } </script> </head> <body> <table id="booktable" border="1" style="border-collapse:collapse;"> <tr align="center"> <th>编号</th> <th>书名</th> <th>作者</th> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
3》转换XML。
Spring MVC提供了处理XML格式请求/响应的HttpMessageConverter,如Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter通过JAXB2读写XML消息,并将请求消息转换到注解XMLRootElement、XmlType作用的类中。
因此只需要在Spring Web容器中为RequestMappingHandlerAdapter装配处理XML的HttpMessageConverter,并在交互中通过请求的Accept指定MIME类型。
Spring MVC默认使用的装换器时Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter转换XML格式的数据,JAXB(Java Architecture for XML Binding)可以很方便地生成XML,也能很方便的生成JSON,所以交换数据比较方便。
JAXB是一个业界的标准,是一项可以根据XML Schema产生Java类的技术。该过程JAXB提供了将XML实例文档反向生成Java对象的方法,并能将Java对象的内容重新写到XML实例文档中,从而使得Java开发者在Java应用程序中能够很方便的处理XML数据。
JAXB常用的注解包括:@XmlRootElement、@XmlElement等。
举个例子:

引入的jar包为spring、commons-logging。
web.xml比较常规,主要是配置前端控制器,引入springmvc-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!-- 扫描controller --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.lfy.controller"/> <!-- 映射器、适配器策略 --> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <!-- 视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" p:prefix="/WEB-INF/content/" p:suffix=".jsp" /> </beans>
sendXml.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>测试接收XML格式的数据</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.11.0.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/json2.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ sendxml(); }); function sendxml(){ var xmlData = "<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?><book><id>1</id><name>疯狂Java讲义</name><author>李刚</author></book>"; $.ajax("${pageContext.request.contextPath}/sendxml",// 发送请求的URL字符串。 { type : "POST", // 请求方式 POST或GET contentType:"application/xml", // 发送信息至服务器时的内容编码类型 // 发送到服务器的数据。 data: xmlData, async: true , // 默认设置下,所有请求均为异步请求。如果设置为false,则发送同步请求 }); } </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
Book.java
package com.lfy.bean; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement; @XmlRootElement public class Book implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Integer id; private String name; private String author; public Book() { super(); } public Book(Integer id, String name, String author) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.author = author; } public Integer getId() { return id; } // 该属性作为xml的element @XmlElement public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } @XmlElement public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } @XmlElement public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", author=" + author + "]"; } }
BookController.java
package com.lfy.controller; import java.io.InputStream; import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext; import javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import com.lfy.bean.Book; @Controller public class BookController { // @RequestBody Book book会将传递的xml数据自动绑定到Book对象 @RequestMapping(value="/sendxml",method=RequestMethod.POST) public void sendxml(@RequestBody Book book) { System.out.println(book); System.out.println("接收XML数据成功"); } // @ResponseBody 会将Book自动转成XML数据返回 @RequestMapping(value="/readxml",method=RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public Book readXml()throws Exception { // 通过JAXBContext的newInstance方法,传递一个class就可以获得一个上下文 JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Book.class); // 创建一个Unmarshall对象 Unmarshaller unmar = context.createUnmarshaller(); InputStream is = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("/book.xml"); // Unmarshall对象的unmarshal方法可以进行xml到Java对象的转换 Book book = (Book) unmar.unmarshal(is); System.out.println(book); return book; } }
运行结果:

==>返回xml数据例子:
book.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <book> <id>1</id> <name>Spring+MyBatis学习笔记</name> <author>lfy</author> </book>
readXml.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>测试返回XML格式的数据</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.11.0.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/json2.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ readxml(); }); function readxml(){ $.ajax("${pageContext.request.contextPath}/readxml",// 发送请求的URL字符串。 { dataType : "text", // 预期服务器返回的数据类型。 type : "POST", // 请求方式 POST或GET async: true , // 默认设置下,所有请求均为异步请求。如果设置为false,则发送同步请求 // 请求成功后的回调函数。 success :function(xml){ // 获得xml数据的id,name,author var id = $("id", xml).text(); var name = $("name", xml).text(); var author = $("author", xml).text(); var tr = $("<tr align='center'/>"); $("<td/>").html(id).appendTo(tr); $("<td/>").html(name).appendTo(tr); $("<td/>").html(author).appendTo(tr); $("#booktable").append(tr); }, // 请求出错时调用的函数 error:function(){ alert("数据接收失败"); } }); } </script> </head> <body> <table id="booktable" border="1" style="border-collapse: collapse;"> <tr align="center"> <th>编号</th> <th>书名</th> <th>作者</th> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
运行结果:
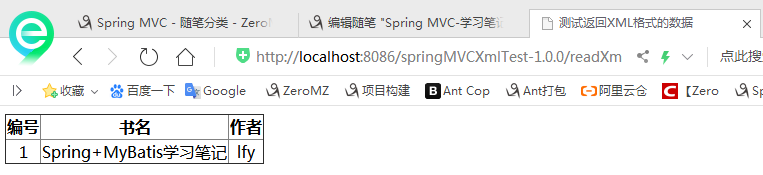
总结:使用@XmlRootElement、@XmlElement注解Java Bean,使用JAXBContext解析XML文件。