- 27.34%
Ryuji is not a good student, and he doesn't want to study. But there are n books he should learn, each book has its knowledge a[i]a[i].
Unfortunately, the longer he learns, the fewer he gets.
That means, if he reads books from ll to rr, he will get a[l] imes L + a[l+1] imes (L-1) + cdots + a[r-1] imes 2 + a[r]a[l]×L+a[l+1]×(L−1)+⋯+a[r−1]×2+a[r] (LL is the length of [ ll, rr ] that equals to r - l + 1r−l+1).
Now Ryuji has qq questions, you should answer him:
11. If the question type is 11, you should answer how much knowledge he will get after he reads books [ ll, rr ].
22. If the question type is 22, Ryuji will change the ith book's knowledge to a new value.
Input
First line contains two integers nn and qq (nn, q le 100000q≤100000).
The next line contains n integers represent a[i]( a[i] le 1e9)a[i](a[i]≤1e9) .
Then in next qq line each line contains three integers aa, bb, cc, if a = 1a=1, it means question type is 11, and bb, ccrepresents [ ll , rr ]. if a = 2a=2 , it means question type is 22 , and bb, cc means Ryuji changes the bth book' knowledge to cc
Output
For each question, output one line with one integer represent the answer.
样例输入
5 3 1 2 3 4 5 1 1 3 2 5 0 1 4 5
样例输出
10 8
题目来源
题意很好理解,我有两种方法来写这道题目。
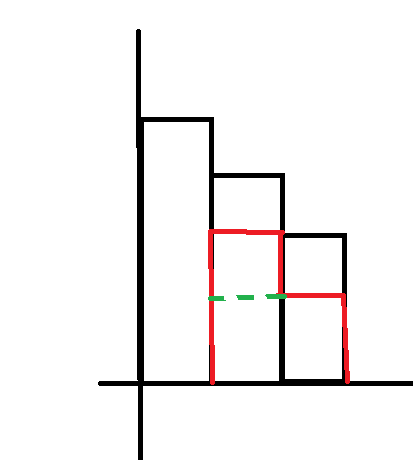
第一种就是树状数组,倒的梯形面积。其实并不是严格意义上的三角形,应该是梯形的面积,但是抽象一下,就是三角形,好理解。

因为下标是从1开始的,所以r+1。横坐标上面的是a数组,下面的是b数组。
代码:
1 //H-树状数组 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cassert> 8 #include<cctype> 9 #include<cmath> 10 #include<cstdlib> 11 #include<ctime> 12 #include<deque> 13 #include<iomanip> 14 #include<list> 15 #include<map> 16 #include<queue> 17 #include<set> 18 #include<stack> 19 #include<vector> 20 using namespace std; 21 typedef long long ll; 22 23 const double PI=acos(-1.0); 24 const double eps=1e-6; 25 const ll mod=1e9+7; 26 const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f; 27 const int maxn=1e5+10; 28 const int maxm=1e3+10; 29 #define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 30 31 ll a[maxn],b[maxn],n,q; 32 33 int lowbit(int x) 34 { 35 return x&(-x); 36 } 37 38 void add(ll a[],int x,ll val) 39 { 40 for(int i=x;i<=n;i+=lowbit(i)) 41 a[i]+=val; 42 } 43 44 ll query(ll a[],int x) 45 { 46 ll ans=0; 47 for(int i=x;i>0;i-=lowbit(i)) 48 ans+=a[i]; 49 return ans; 50 } 51 52 int main() 53 { 54 cin>>n>>q; 55 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 56 ll val; 57 cin>>val; 58 add(a,i,val);//单纯的保存,类似前缀和 59 add(b,i,i*val);//这样保存,减去的时候正好满足条件,*L,*(L-1)。。。 60 } 61 while(q--){ 62 ll op,l,r; 63 cin>>op>>l>>r; 64 if(op==2){ 65 ll cnt=query(a,l)-query(a,l-1);//单点更新 66 add(a,l,r-cnt); 67 ll ret=query(b,l)-query(b,l-1);//同上 68 add(b,l,l*r-ret); 69 } 70 else{ 71 ll cnt=(r+1)*(query(a,r)-query(a,l-1));//先算出横坐标的和,然后*(r+1)就是一个大矩形的面积 72 ll ret=query(b,r)-query(b,l-1);//倒着的梯形面积,(因为从1开始的,所以是梯形不是三角形) 73 cout<<cnt-ret<<endl; 74 } 75 } 76 }
还有一种线段树的方法,线段树的就是左儿子+右儿子+两者包围的矩形的面积。
为了好理解,画成三角形,其实严格意义上是梯形,因为最后一个数是×1,但是为了好理解,画成三角形。

某种意义上是一个个小矩形。
首先我求每一个小的三角形(矩形)就是ans[rt]+sum[rt]*(tmp-len[rt]);
举个例子,只有一个长度的。
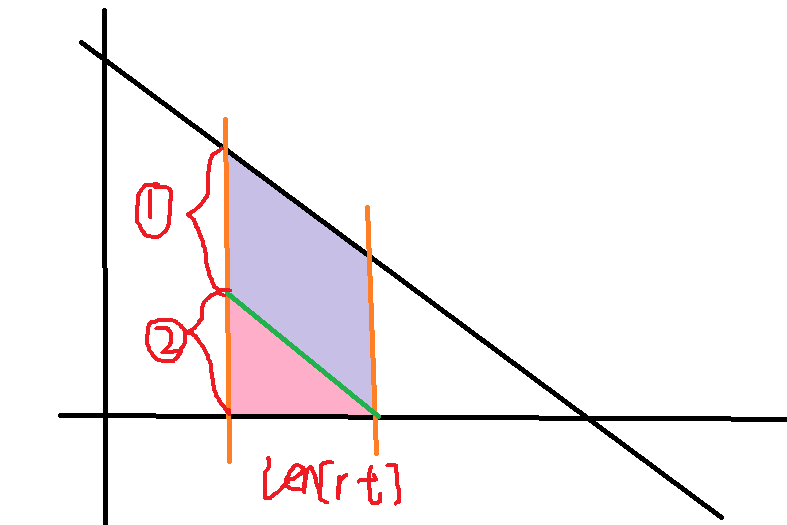
sum为单点的值,tmp为总的区间查询长度,len[rt]为当前的区间长度。
怎么求粉色三角形的面积呢?就是我一开始线段树存的大的梯形的面积-紫色平行四边形的面积。
tmp就是总长度为小圈1+小圈2的长度,小圈1的长度就是tmp-len[rt],OK了。
ll query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) { if(L<=l&&r<=R){ int tmp=Len; Len-=len[rt]; return ans[rt]+sum[rt]*(tmp-len[rt]); } int m=(l+r)>>1; ll ret=0; if(L<=m) ret+=query(L,R,lson); if(R >m) ret+=query(L,R,rson); return ret; }
然后就是总的面积,就是左儿子+右儿子+左儿子的区间和*右儿子的区间长。
代码睡醒上完课再贴,想睡觉了,头发要紧,哈哈哈哈哈。
直接代码了。
1 //H-线段树 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cassert> 8 #include<cctype> 9 #include<cmath> 10 #include<cstdlib> 11 #include<ctime> 12 #include<deque> 13 #include<iomanip> 14 #include<list> 15 #include<map> 16 #include<queue> 17 #include<set> 18 #include<stack> 19 #include<vector> 20 using namespace std; 21 typedef long long ll; 22 23 const double PI=acos(-1.0); 24 const double eps=1e-6; 25 const ll mod=1e9+7; 26 const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f; 27 const int maxn=1e5+10; 28 const int maxm=1e3+10; 29 #define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 30 #define lson l,m,rt<<1 31 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 32 33 ll sum[maxn<<2],ans[maxn<<2],len[maxn<<2]; 34 //sum为单点的价值(横坐标),ans为总价值,len为区间长度 35 int Len; 36 37 void pushup(int rt) 38 { 39 ans[rt]= ans[rt<<1]+ans[rt<<1|1]+sum[rt<<1]*len[rt<<1|1];//总价值为左儿子+右儿子+左儿子区间和*右儿子区间长 40 len[rt]=len[rt<<1]+len[rt<<1|1]; 41 sum[rt]=sum[rt<<1]+sum[rt<<1|1]; 42 } 43 44 void build(int l,int r,int rt) 45 { 46 if(l==r){ 47 scanf("%lld",&sum[rt]); 48 len[rt]=1; 49 ans[rt]=sum[rt]; 50 return; 51 } 52 53 int m=(l+r)>>1; 54 build(lson); 55 build(rson); 56 pushup(rt); 57 } 58 59 ll query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) 60 { 61 if(L<=l&&r<=R){ 62 int tmp=Len; 63 Len-=len[rt]; 64 return ans[rt]+sum[rt]*(tmp-len[rt]);//求小三角形的面积就是大的梯形-平行四边形 65 } 66 67 int m=(l+r)>>1; 68 ll ret=0; 69 if(L<=m) ret+=query(L,R,lson); 70 if(R >m) ret+=query(L,R,rson); 71 return ret; 72 } 73 74 void update(int p,ll val,int l,int r,int rt)//单点更新 75 { 76 if(l==r){ 77 sum[rt]=val; 78 ans[rt]=val; 79 return; 80 } 81 82 int m=(l+r)>>1; 83 if(p<=m) update(p,val,lson); 84 else update(p,val,rson); 85 pushup(rt); 86 } 87 88 int main() 89 { 90 int n, m; 91 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){ 92 build(1,n,1); 93 while(m--){ 94 int op; 95 scanf("%d",&op); 96 if(op==1){ 97 int l,r; 98 scanf("%d%d",&l,&r); 99 Len=r-l+1; 100 printf("%lld ",query(l,r,1,n,1)); 101 } 102 else{ 103 int pos; 104 ll val; 105 scanf("%d%lld",&pos,&val); 106 update(pos,val,1,n,1); 107 } 108 } 109 } 110 return 0; 111 }
还有一份学长过的(啊啊啊啊,好厉害,羞涩,哈哈哈)

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <math.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <sstream> 7 #include <algorithm> 8 #include <string> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <map> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <set> 13 #include <utility> 14 #include <stack> 15 #include <list> 16 using namespace std; 17 typedef long long LL; 18 const int N = 1e5+50,M = 1e3+10,inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 19 const LL mod = 1e9+7; 20 const double epx = 1e-6; 21 const double PI = acos(-1.0); 22 23 #define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 24 25 LL a[N],sum[M],block[M],pos[N]; 26 int k; 27 void init(int n) 28 { 29 k=sqrt(n); 30 memset(sum,0,sizeof(sum)); 31 memset(block,0,sizeof(block)); 32 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 33 pos[i]=(i-1)/k+1; 34 for(int i=1;i<=n/k;i++) 35 { 36 int L=(i-1)*k+1; 37 int R=i*k; 38 for(int j=L,t=k;j<=R;j++,t--) 39 { 40 sum[i]+=a[j]; 41 block[i]+=a[j]*(1LL*t); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 void change(int b,int c) 46 { 47 int i=pos[b]; 48 a[b]=c; 49 int L=(i-1)*k+1; 50 int R=i*k; 51 sum[i]=0; 52 block[i]=0; 53 for(int j=L,t=k;j<=R;j++,t--) 54 { 55 sum[i]+=a[j]; 56 block[i]+=a[j]*(1LL*t); 57 } 58 } 59 LL query(int L,int R) 60 { 61 LL ans=0; 62 if(pos[L]==pos[R]) 63 { 64 for(int i=L,len=(R-L+1);i<=R;i++,len--) 65 { 66 ans+=1LL*a[i]*len; 67 } 68 return ans; 69 } 70 int len=(R-L+1); 71 for(int i=L;i<=pos[L]*k;i++) 72 { 73 ans+=1LL*a[i]*len;len--; 74 } 75 for(int i=pos[L]+1;i<pos[R];i++) 76 { 77 ans+=block[i]; 78 ans+=1LL*sum[i]*(len-k); 79 len-=k; 80 } 81 for(int i=(pos[R]-1)*k+1;i<=R;i++) 82 { 83 ans+=1LL*a[i]*len;len--; 84 } 85 return ans; 86 } 87 int main() 88 { 89 int n,q; 90 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)) 91 { 92 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 93 scanf("%lld",&a[i]); 94 init(n); 95 while(q--) 96 { 97 int a,b,c; 98 scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); 99 if(a==1) 100 { 101 printf("%lld ",query(b,c)); 102 } 103 else if(a==2) 104 { 105 change(b,c); 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 return 0; 110 }
就先这样,溜了。
