单体架构
单体架构就是一个项目里面包含这个项目中的全部代码,一个应用搞定全部功能,DNS服务器可以是单映射,也可以配置多个映射

软件代码结构
在单体结构项目中,团队都是通过包(package)进行区分每个模块

优缺点
优点,部署简单,维护方便,成本低
缺点,当项目规模大,用户访问频率高,并发量大,数据量大时,会大大降低程序执行效率,甚至出现服务器宕机
使用项目
传统管理项目,小型互联网项目
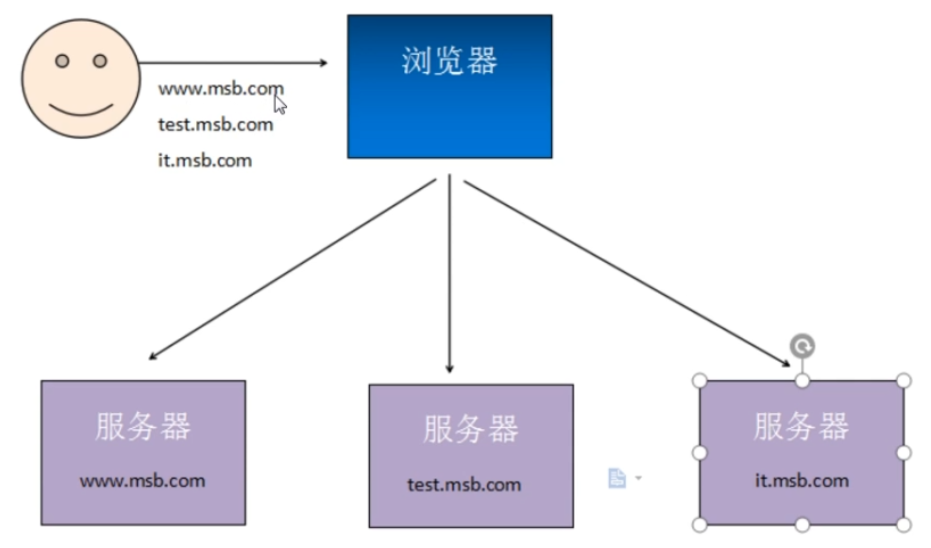
分布式架构
架构图(简易版)
分布式架构会把一个项目按照特定要求(多按照模块或功能)拆分成多个项目,每个项目分别部署到不同的服务器上
软件代码结构

优缺点
优点
- 增大了系统可用性,减少单点故障,导致整个应用不可用
- 增加重用性,因为模块化,所以重用性更高
- 增加可扩展性,有新的模块增加新的项目即可
- 增加每个模块的负载能力,每个模块都是一个项目,每个模块负载能力更强
缺点
- 成本更高
- 架构更加复杂
- 整体响应时间更长,一些业务需要多项目通信后给出结果
- 吞吐量更大,吞吐量=请求数/秒
待解决问题
分布式结构可以使用Http协议,也可以使用RPC协议通信,RPC比Http更适合内部通信
RPC简介
RFC,(Requeest For comments)是由互联网工程任务组发布的文件集
文件集中每个文件都有唯一编号
RPC在rfc远程过程调用协议,RPC协议规定允许互联网中一台主机程序调用另一台主机程序
程序员无需对这个交互过程进行编程,在RPC协议中强调当A程序调用B程序中功能或方法时,A不知道B中方法的具体实现
RPC是上层协议,底层可以基于TCP协议,也可以基于HTTP协议,RPC是基于RPC的具体实现,如:Dubbo框架
满足网络中进行通讯调用的都称为RPC,甚至HTTP都可以称为RPC,具体分析RPC要比HTTP协议更加高效
RPC和HTTP对比
具体实现
RPC:可以基于TCP协议,也可以基于HTTP协议
HTTP:基于HTTP协议
效率
RPC:自定义具体实现可以减少很多无用的报文内容,使得报文体积更小
HTTP:如果是HTTP1.1报文中很多内容都是无用的,如果是HTTP2.0以后和RPC相差不大,比RPC少的可能就是一些服务治理
连接方式
RPC:长连接支持
HTTP:每次连接都是3次握手
性能
RPC可以基于很多序列化方式,如:thrift
HTTP主要通过JSON,序列化和反序列效率更低
注册中心
RPC:一般RPC框架都带有注册中心
HTTP:都是直连
负载均衡:
RPC:绝大多数RPC框架都带有负载均衡测量
HTTP:一般都需要借助第三方工具,如nginx
综合结论
RPC有丰富的服务治理功能,更适合企业内部接口调用,HTTP适合多平台间调用
HttpClient实现RPC
服务端
新建控制器
@Controller public class DemoController{ @RequestMapping("/demo") @ResponseBody public String demo(String param){ return "demo" + param; } }
新建启动器
@SpringBootApplication public class ServerApplication{ public static void main(String[] args){ SpringApplication.run(ServerApplication.class, args); } }
使用GET方法
添加依赖,官方地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.httpcomponents/httpclient
public class HttpClientDemo{ @Test public void testGetDemo() throws { // 发送请求, 解析响应 CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault(); try{ // 确定请求路径 URIBuilder uriBuilder = new URIBuilder("http://localhost:8080/demo"); // 创建httpGet请求对象 HttpGet get = new HttpGet(uriBuilder.build()); // 创建响应对象 CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(get); // 由于响应体是字符串, 因此把HttpEntity类型转换为字符串类型, 并设置字符集编码 String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "utf-8"); // 输出结果 System.out.println(result); // 释放资源 response.close(); httpClient.close(); }catch(URISyntaxException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void testPostDemo(){ try{ // 创建Http工具(理解成: 浏览器) 发送请求, 解析响应 CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault(); // 创建HttpPost请求对象 HttpPost post = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/"); // 创建请求参数 List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<>(NameValuePair); params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("param", "value")); HttpEntity httpEntity = new UrlEncodeFormEntity(params, "utf-8"); post.setEntity(httpEntity); // 创建响应对象 CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(post); // 把HttpEntity类型转换为字符串类型 String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()); // 输出结果, 释放资源 System.out.println(result); response.close(); httpClient.close(); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Jackson用法
添加依赖,官方地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.11.2</version> </dependency>
jackson常用方法
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); User user = objectMapper.readValue(content, User.class); // 使用jackson把对象转换为Json String userJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user); System.out.println(userJson); response.close(); httpClient.close();
流数据,控制器
@Controller public class DemoController{ @RequestMapping("/demo") @ResponseBody public String demo(String param){ return param + "abc"; } @RequestMapping("/demo2") @ResponseBody public User demo2(User user){ return user; } @RequestMapping("/demo3") @ResponseBody public User demo3(User user){ List<User> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new User(1, "aaa")); list.add(new User(2, "bbb")); return list; } @RequestMapping("/demo4") @ResponseBody public String demo4(@RequestBody List<User> list){ System.out.println(list); return list.toString(); } @RequestMapping("/demo5") @ResponseBody @CrossOrigin public List<User> demo5(@RequestBody List<User> list){ System.out.println(list); return list; } @Test public void testListPostDemo(){ try{ CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault(); HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/demo3"); CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()); System.out.println(content); response.close(); httpClient.close(); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void testInputStream(){ CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpCliens.createDefault(); HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/demo4"); List<User> listParam = new ArrayList<User>(); listParam.add(new User(1, "zsf")); listParam.add(new User(2, "zwj")); ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 集合对象转换为json try{ String jsonParam = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(listParam); HttpEntity httpEntity = new StringEntity(jsonParam, ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON); httpPost.setEntity(httpEntity); CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()); response.close(); httpClient.close(); }catch(JsonProcessingException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }