给定一个整数数列,找出其中和为特定值的那两个数。
你可以假设每个输入都只会有一种答案,同样的元素不能被重用。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9 因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9 所以返回 [0, 1]
解法一:.刚开始看到的的时候,第一个想到的就是用一个嵌套循环把nums列表遍历两次,虽然测试通过了但是耗时实在太长了,然后就考虑了其他时间复杂度低的方法
class Solution: def twoSum(self,nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: List[int] """ #用len()方法取得nums列表的长度 n = len(nums) #x取值从0一直到n(不包括n) for x in range(n): #y取值从x+1一直到n(不包括n) #用x+1是减少不必要的循环,y的取值肯定是比x大 for y in range(x+1,n): #假如 target-nums[x]的某个值存在于nums中 if nums[y] == target - nums[x]: #返回x和y return x,y break else: continue
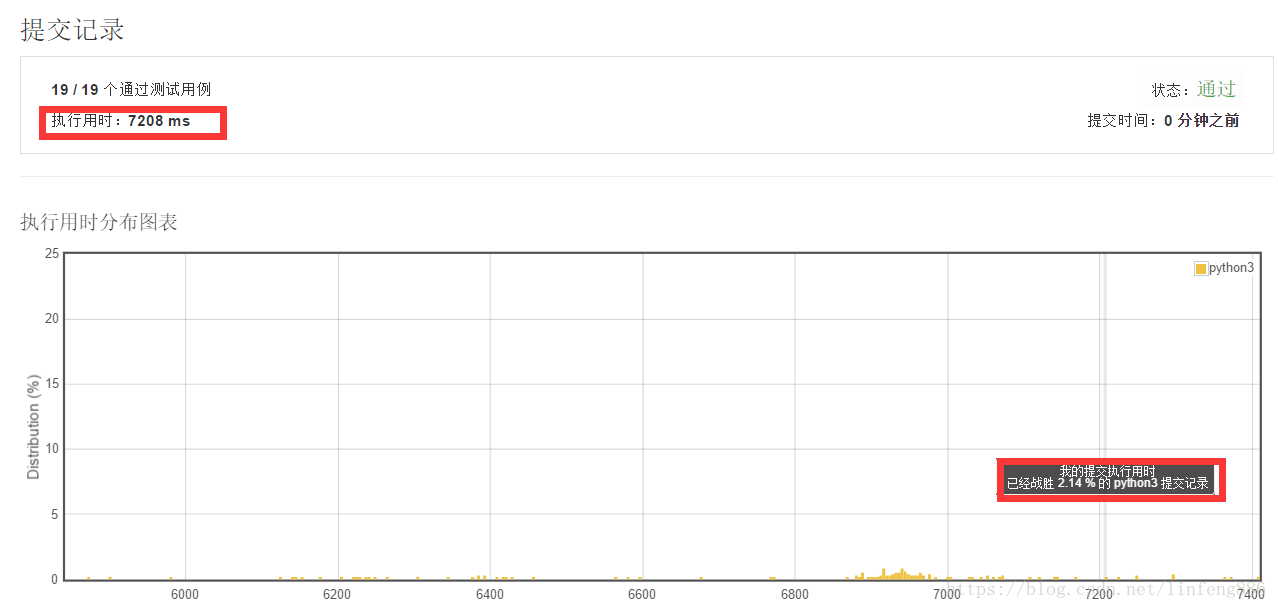
解法二:用一个for循环,直接在里面查询target-nums[x]是否存在于nums列表中,速度比解法一快了许多,但还是不够
class Solution: def twoSum(self,nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: List[int] """ #用len()方法取得nums列表长度 n = len(nums) #x从0到n取值(不包括n) for x in range(n): a = target - nums[x] #用in关键字查询nums列表中是否有a if a in nums: #用index函数取得a的值在nums列表中的索引 y = nums.index(a) #假如x=y,那么就跳过,否则返回x,y if x == y: continue else: return x,y break else : continue
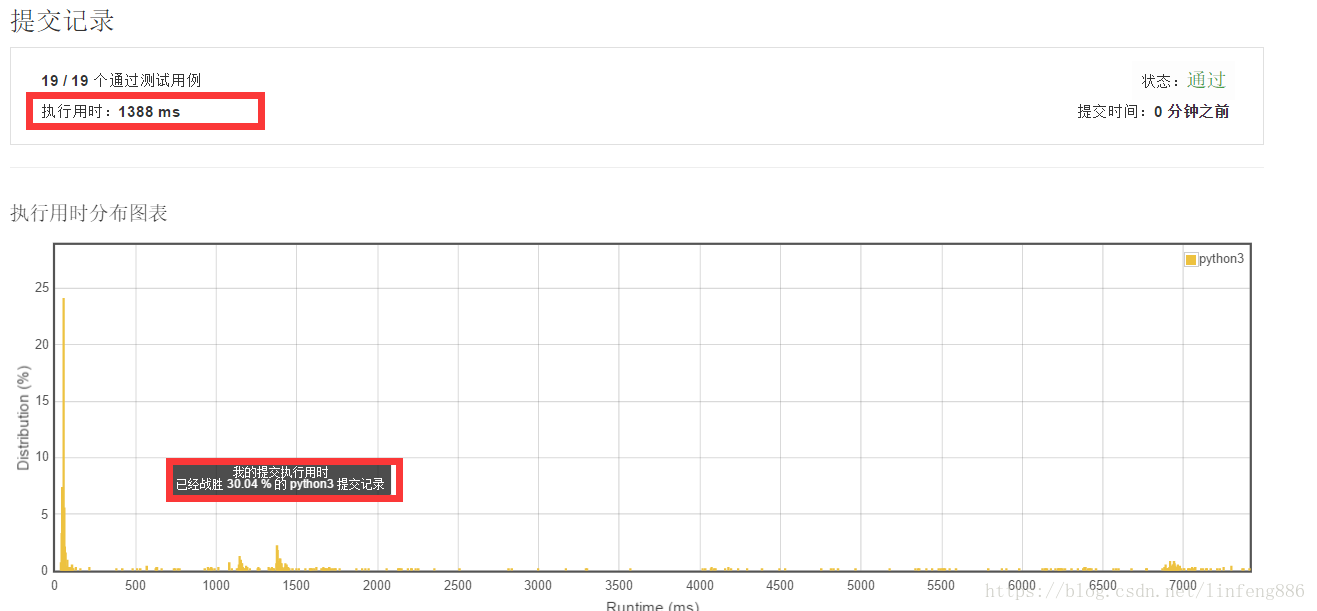
解法三:这个解法是我看了排名前几个的答案后才知道的, 先创建一个空字典,然后依次把target-nums[x]的值存入字典,存入一个就跟nums[x+1]去比较, 字典中的key为target-nums[x],value为x,也就是nums[x]在nums列表中的索引位置。当字典d中有nums[x+1]时,也就是target - nums[y] = nums[x+1] , y肯定是小于x+1的(因为y是x+1之前循环过的数字)
所以是 return y,x+1
class Solution: def twoSum(self,nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: List[int] """ #用len()方法取得nums列表长度 n = len(nums) #创建一个空字典 d = {} for x in range(n): a = target - nums[x] #字典d中存在nums[x]时 if nums[x] in d: return d[nums[x]],x #否则往字典增加键/值对 else: d[a] = x #边往字典增加键/值对,边与nums[x]进行对比
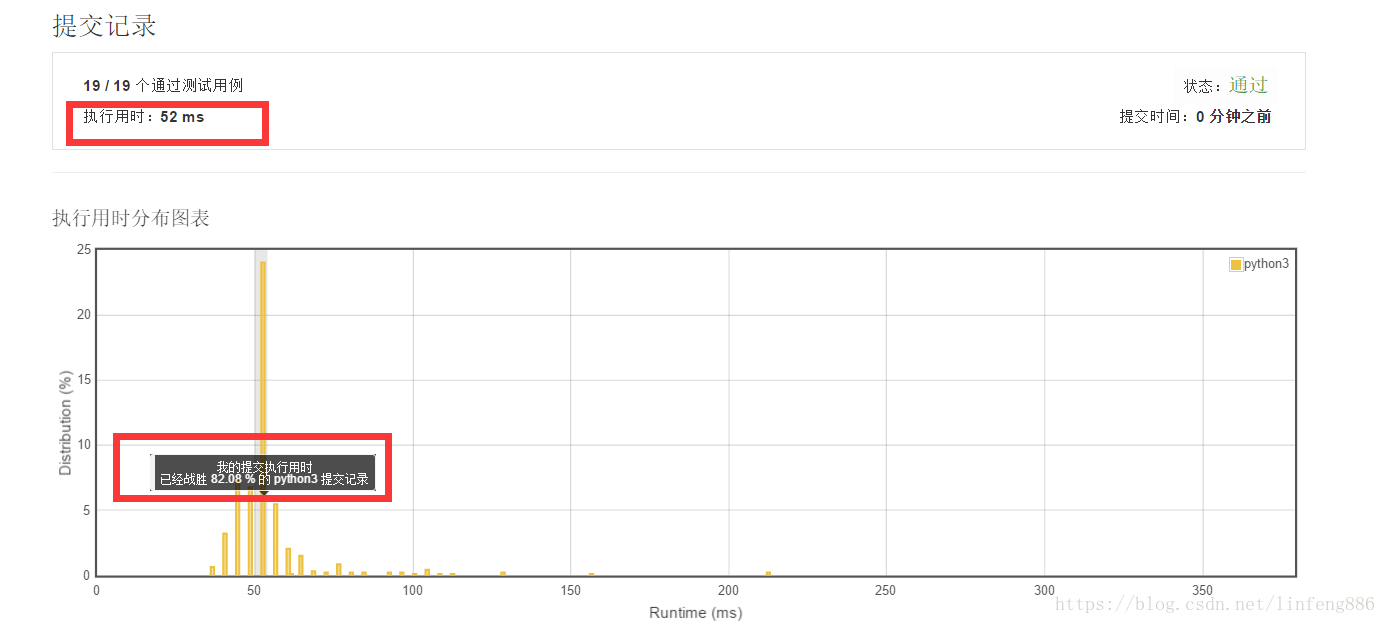
转载自: