添加权限
(1)API/utils文件夹下新建premission.py文件,代码如下:
- message是当没有权限时,提示的信息
# utils/permission.py
class SVIPPremission(object):
message = "必须是SVIP才能访问"
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user.user_type != 3:
return False
return True
class MyPremission(object):
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user.user_type == 3:
return False
return True
(2)settings.py全局配置权限
#全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['API.utils.auth.Authentication',],
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":['API.utils.permission.SVIPPremission'],
}
(3)views.py添加权限
- 默认所有的业务都需要SVIP权限才能访问
- OrderView类里面没写表示使用全局配置的SVIPPremission
- UserInfoView类,因为是普通用户和VIP用户可以访问,不使用全局的,要想局部使用的话,里面就写上自己的权限类
- permission_classes = [MyPremission,] #局部使用权限方法
from django.shortcuts import render from django.http import JsonResponse, HttpResponse from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework import exceptions from API import models from API.utils.permission import SVIPPremission, MyPremission ORDER_DICT = { 1: { 'shop': "apple", "price": 12, }, 2: { 'shop': "pear", "price": 15, } } def md5(user): import hashlib import time # 当前时间,相当于生成一个随机字符串 ctime = str(time.time()) m = hashlib.md5(user.encode('utf-8')) m.update(ctime.encode('utf-8')) return m.hexdigest() class AuthView(APIView): '''用于用户登录验证''' authentication_classes = [] # 里面为空,代表不需要认证 permission_classes = [] # 不里面为空,代表不需要权限 def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None} try: user = request._request.POST.get('username') pwd = request._request.POST.get('password') obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user, password=pwd).first() if not obj: ret['code'] = 1001 ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误' else: # 为用户创建token token = md5(user) # 存在就更新,不存在就创建 models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj, defaults={'token': token}) ret['code'] = 2000 ret['msg'] = "成功" ret['token'] = token except Exception as e: ret['code'] = 1002 ret['msg'] = '请求异常' return JsonResponse(ret) class OrderView(APIView): ''' 订单相关业务(只有SVIP用户才能看) ''' def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # request.user # request.auth ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None, 'data': None} try: ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT except Exception as e: pass return JsonResponse(ret) class UserInfoView(APIView): ''' 订单相关业务(普通用户和VIP用户可以看) ''' permission_classes = [MyPremission, ] # 不用全局的权限配置的话,这里就要写自己的局部权限 def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): print(request.user,request.user.username) return HttpResponse('用户信息')
from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from API import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^api/v1/auth/', views.AuthView.as_view()), url(r'^api/v1/order/', views.OrderView.as_view()), url(r'^api/v1/info/', views.UserInfoView.as_view()), ]
from rest_framework import exceptions from API import models from rest_framework.authentication import BasicAuthentication class Authentication(BasicAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): token = request._request.GET.get("token") print(token) token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first() print(token_obj) if not token_obj: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed("认证失败") # 在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用 return (token_obj.user, token_obj) def authenticate_header(self, request): pass
(4)测试
普通用户访问OrderView,提示没有权限
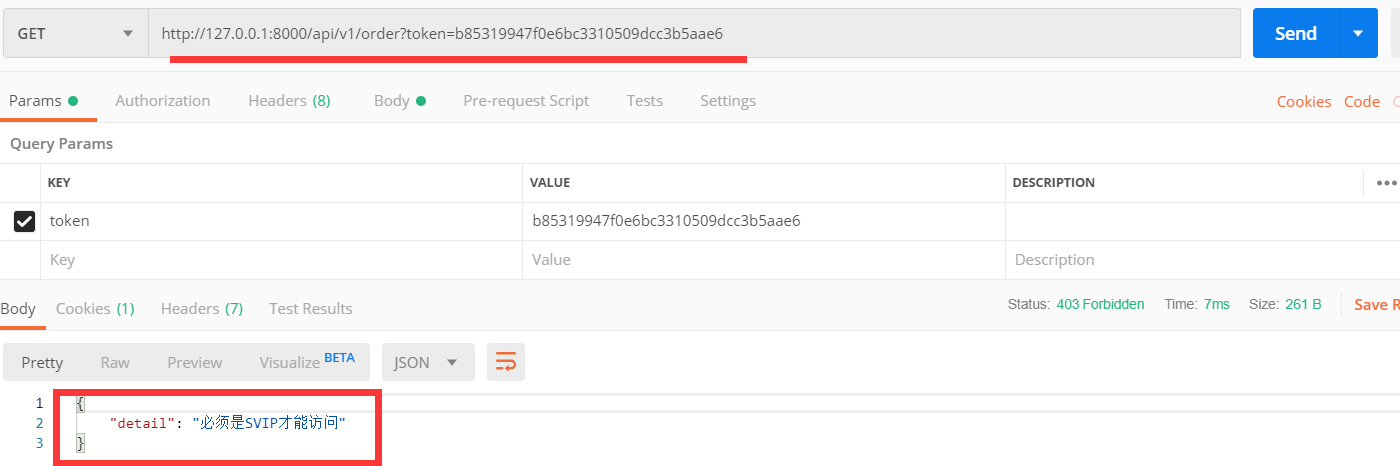
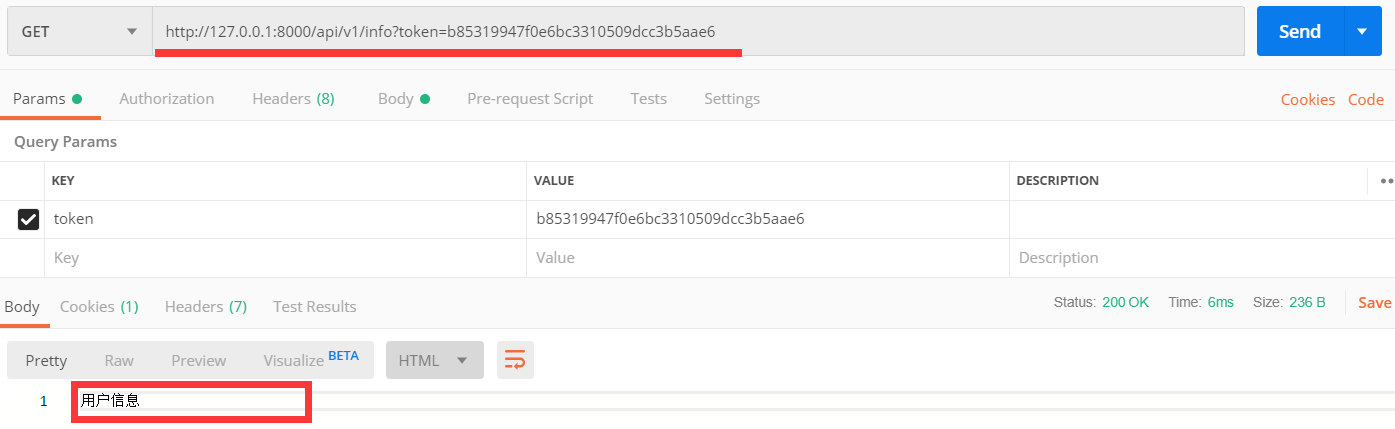
普通用户访问UserInfoView,可以返回信息
权限源码流程
(1)dispatch
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
#对原始request进行加工,丰富了一些功能
#Request(
# request,
# parsers=self.get_parsers(),
# authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
# negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
# parser_context=parser_context
# )
#request(原始request,[BasicAuthentications对象,])
#获取原生request,request._request
#获取认证类的对象,request.authticators
#1.封装request
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate?
try:
#2.认证
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
# Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc)
self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response
(2)initial
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
# Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
# Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
#4.实现认证
self.perform_authentication(request)
#5.权限判断
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request)
(3)check_permissions
里面有个has_permission这个就是我们自己写的权限判断
def check_permissions(self, request):
"""
Check if the request should be permitted.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is not permitted.
"""
#[权限类的对象列表]
for permission in self.get_permissions():
if not permission.has_permission(request, self):
self.permission_denied(
request, message=getattr(permission, 'message', None)
)
(4)get_permissions
def get_permissions(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of permissions that this view requires.
"""
return [permission() for permission in self.permission_classes]
(5)permission_classes

所以settings全局配置就如下
#全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":['API.utils.permission.SVIPPremission'],
}
内置权限
django-rest-framework内置权限BasePermission
默认是没有限制权限
class BasePermission(object):
"""
A base class from which all permission classes should inherit.
"""
def has_permission(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
"""
return True
def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
"""
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
"""
return True
我们自己写的权限类,应该去继承BasePermission,修改之前写的permission.py文件
# utils/permission.py
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
class SVIPPremission(BasePermission):
message = "必须是SVIP才能访问"
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user.user_type != 3:
return False
return True
class MyPremission(BasePermission):
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user.user_type == 3:
return False
return True
总结:
(1)使用
- 自己写的权限类:1.必须继承BasePermission类; 2.必须实现:has_permission方法
(2)返回值
- True 有权访问
- False 无权访问
(3)局部
- permission_classes = [MyPremission,]
(4)全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
#权限
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":['API.utils.permission.SVIPPremission'],
}
