【微语】立志要如山,行道要如水。不如山,不能坚定,不如水,不能曲达

1 import cv2 as cv 2 import numpy as np 3 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 4 5 img = cv.imread(r'picturesgradient.png') 6 h , w ,ch = img.shape 7 8 ret , thresh1 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY) 9 ret , thresh2 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV) 10 ret , thresh3 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_TRUNC) 11 ret , thresh4 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_TOZERO) 12 ret , thresh5 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_TOZERO_INV) 13 14 titles = ['orignal image','binary','binary_inv','trunc','tozero','tozero_inv'] 15 images = [img,thresh1,thresh2,thresh3,thresh4,thresh5] 16 17 for i in range(len(images)): 18 plt.subplot(2,3,i+1),plt.imshow(images[i]) 19 plt.title(titles[i]) 20 plt.xticks(()) 21 plt.yticks(()) #隐藏y轴 22 23 plt.show()



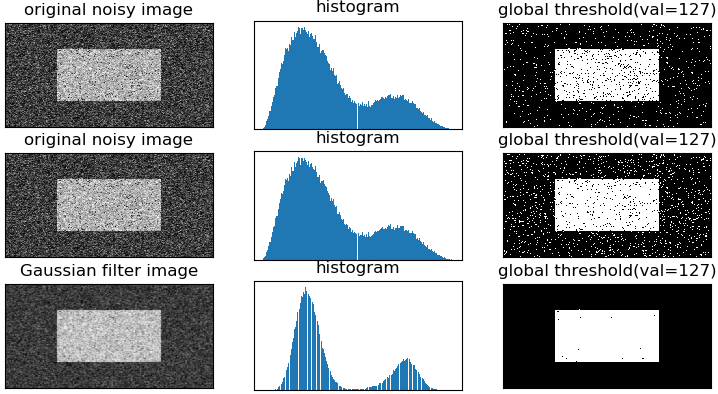
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt img = cv.imread(r'pictures oisy2.png') gray = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #global thresholding ret1,binary1 = cv.threshold(gray,127,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY) #Otsu's thresholding ret2,binary2 = cv.threshold(gray,0,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY+cv.THRESH_OTSU) #Otsu's thresholding after Gaussian filtering blur = cv.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0) ret3,binary3 = cv.threshold(blur,0,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY+cv.THRESH_OTSU) # cv.imshow('binary1',binary1) # cv.imshow('binary2',binary2) # cv.imshow('blur',blur) # cv.imshow('binary3',binary3) #Plot all the images and their histograms images = [img,0,binary1, img,0,binary2, blur,0,binary3] titles = ['original noisy image','histogram','global threshold(val=127)', 'original noisy image','histogram',"Otsu's threshold", 'Gaussian filter image','histogram',"Otsu's threshold(Gaussian)"] """ 使用pyplot中画直方图的方法plt.hist(),注意它的参数是一维数组 故使用numpy的ravel()方法或者flatten()方法, 将多维数组转为一维数组 #for循环每次打印出一行3幅图 """ for i in range(3): plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+1),plt.imshow(images[i*3],'gray') #plt,imshow(img,'gray') 灰度图 plt.title(titles[i*3]),plt.xticks(()),plt.yticks(()) plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+2),plt.hist(images[i*3].flatten(),256) plt.title(titles[1]),plt.xticks(()),plt.yticks(()) plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+3),plt.imshow(images[i*3+2],'gray') plt.title(titles[2]),plt.xticks(()),plt.yticks(()) plt.show()