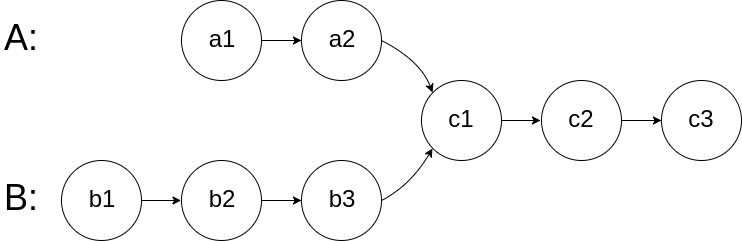
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
begin to intersect at node c1.
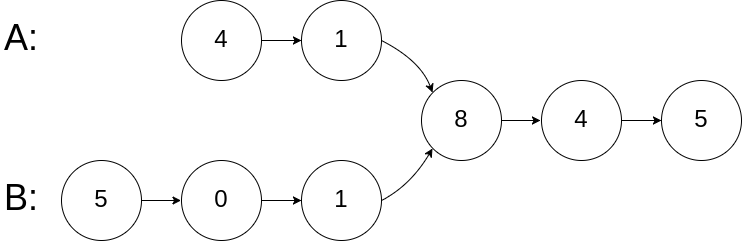
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
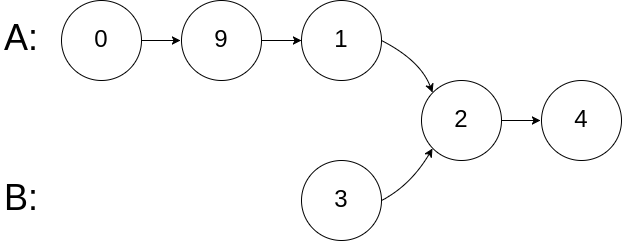
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
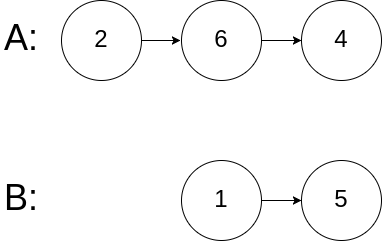
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
中文大意就是返回两个链表的交点
可以用双指针,不过不是慢指针和快指针,而是用两个结点分别指向两个链表中。然后开始迭代,如果最后两个结点相等,说明不是相遇就是都指向了NULL了,另外,如果其中一个结点到了NULL,就指向另一个链表。(emmmm,用语可能有错,不过意思应该一样吧,笑哭)
C++代码:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL) return NULL; ListNode *a = headA; ListNode *b = headB; while(a != b){ a = a?a->next:headB; b = b?b->next:headA; } return a; } };