字符流:顾名思义操作(读、写)字符的流对象
字符流的体系:
1、Reader
|--BufferedReader:从字符输入流中读取文本到缓冲区,便于有效读取字符,数组,和行
|--LineNumberReader:有行号(setLineNumber(int) 、getLineNumber())
|--InputStreamReader:字节流到字符流
|--FileReader:将字符文件数据读取到缓冲区中
2、Writer
|--BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流到缓冲区,便于有效写入单个字符,数组和字符串。
|--OutputStreamWriter:字符流到字节流
|--FileWriter:将缓冲区数据写入字符文件
一、FileReader和FileWriter
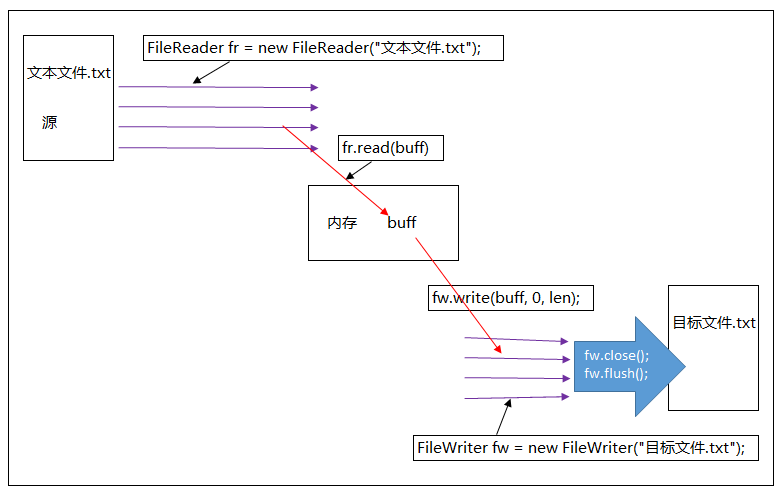
FileReader原理:将指定的文本文件读到内存中
FileWriter原理:把内存中字符数据写入到实体设备上(落地)。
以文本文件Copy为例:
1 private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 fileCopy(); 5 } 6 7 private static void fileCopy() { 8 FileReader fr=null; 9 FileWriter fw=null; 10 try { 11 /* 12 * 1、必须要明确被读取的文件,一定要确认文件时存在的。 13 */ 14 fr=new FileReader("demo.txt"); 15 /* 16 * 2、明确copy目的地 17 * 如果文件不存在,自动创建 如果文件存在,会覆盖(删除再创建) 18 */ 19 fw=new FileWriter("CopyDemo2.txt"); 20 21 //方式一:一个字符读取 22 // int ch=0; 23 // while((ch=fr.read())!=-1) { 24 // fw.write(ch); 25 // } 26 27 //方式二:先把读取数据放入固定缓存中,然后把固定缓存写到硬盘 28 //创建一个临时容器,用于缓存读取到的字符 29 char[] buff=new char[BUFFER_SIZE]; 30 //记录读取到的字符数(其实就时向数组中装的字符个数) 31 int len=0; 32 while((len=fr.read(buff))!=-1) { 33 /* 34 * 把内容存储器读到内容全部写入到输出流中 35 * 此时没有写入实体设备中(这里指硬盘) 36 */ 37 fw.write(buff,0,len); 38 } 39 40 } catch (IOException e) { 41 throw new RuntimeException(); 42 }finally { 43 if(fr!=null) 44 try { 45 fr.close(); 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 48 throw new RuntimeException(); 49 } 50 if(fw!=null) 51 try { 52 fw.close();//先刷新,将输出流中数据写到实体设备中,关闭系统资源, 53 } catch (IOException e) { 54 throw new RuntimeException(); 55 } 56 } 57 }
分析:
二、BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
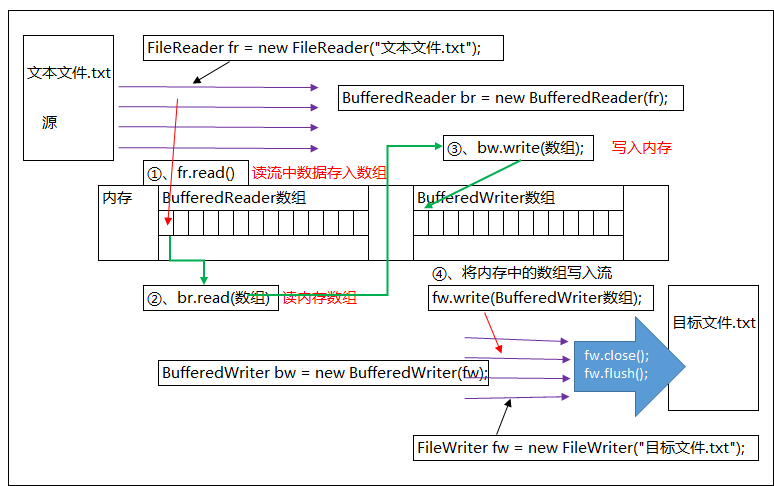
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter其实就是Reader和Writer的装饰类,主要目的是为了提高读写效率。
Copy文本文件实例:
1 private static void fileCopy() { 2 BufferedReader br = null; 3 BufferedWriter bw = null; 4 try { 5 /* 6 * 1、必须要明确被读取的文件,一定要确认文件时存在的。 7 */ 8 FileReader fr = new FileReader("demo.txt"); 9 br = new BufferedReader(fr); 10 /* 11 * 2、明确copy目的地 如果文件不存在,自动创建 如果文件存在,会覆盖(删除再创建) 12 */ 13 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("CopyDemo2.txt"); 14 bw = new BufferedWriter(fw); 15 /* 16 String len = null; 17 while ((len = br.readLine()) != null) 18 { 19 bw.write(len); 20 bw.newLine();//会在文本文件最后多一个空行,没想到解决方法 21 bw.flush();//防止程序非正常停止 22 } 23 */ 24 /* 25 int len = 0; 26 while ((len = br.read()) != -1) { 27 bw.write(len); 28 bw.flush();//防止程序非正常停止 29 } 30 */ 31 32 char[] buff=new char[1024]; 33 int len = 0; 34 while ((len = br.read(buff)) != -1) { 35 bw.write(buff,0,len); 36 bw.flush();//防止程序非正常停止 37 } 38 39 40 } catch (IOException e) { 41 throw new RuntimeException(); 42 } finally { 43 if (br != null) 44 try { 45 br.close(); 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 48 throw new RuntimeException(); 49 } 50 if (bw != null) 51 try { 52 bw.close();// 先刷新,将输出流中数据写到实体设备中,关闭系统资源, 53 } catch (IOException e) { 54 throw new RuntimeException(); 55 } 56 } 57 }
其原理:就是一个数组
四、自定义BufferedReader
1 class MyBuferedReader extends Reader { 2 private Reader reader; 3 4 MyBuferedReader(Reader reader) { 5 this.reader = reader; 6 } 7 8 /* 9 * 自定义缓冲区 10 */ 11 private char[] buff = new char[1024]; 12 /* 13 * 缓冲区数组角标 14 */ 15 private int pos = 0; 16 /* 17 * 用于记录缓冲区中的数据个数 为0时,就从源中继续获取数据到缓冲区中 18 */ 19 private int count = 0; 20 21 public int myRead() throws IOException { 22 if (count == 0) { 23 count = reader.read(buff); 24 pos = 0; 25 } 26 /* 27 * 数据读完 28 */ 29 if (count < 0) { 30 return -1; 31 } 32 33 char ch = buff[pos++]; 34 count--; 35 return ch; 36 } 37 38 public String myReadLine() throws IOException { 39 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 40 int ch = 0; 41 while ((ch = myRead()) != -1) { 42 if (ch == ' ') 43 continue; 44 if (ch == ' ') 45 return builder.toString(); 46 builder.append((char) ch); 47 } 48 if (builder.length() != 0) 49 return builder.toString(); 50 return null; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException { 55 // 56 return 0; 57 } 58 59 @Override 60 public void close() throws IOException { 61 reader.close(); 62 } 63 }