Map:存储键值对数据,map集合必须保证键的唯一性
一、常用方法:
1、添加
value put(K key,V value); 返回前一个和Key关联的值,如果没有就返回null
2、删除
void clear();
value remove(K key);根据指定的key删除这个键值对
3、判断
boolean containsKey(key);
boolean containsValue(value);
boolean isEmpty();
4、获取
value get(key);通过键获取值,如果没有该键返回null
当然可以通过返回null,判断是否包含指定键
int size();获取键值对的个数
Set<K> keySet();
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet();
Collection<V> values();
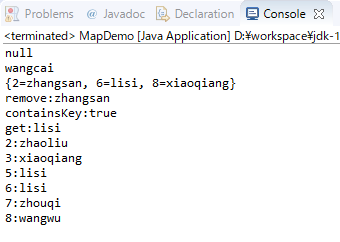
1 import java.util.Collection; 2 import java.util.HashMap; 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 public class MapDemo { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); 11 method(map); 12 getData(map); 13 } 14 15 public static void getData(Map<Integer, String> map) { 16 map.put(8, "wangwu"); 17 map.put(2, "zhaoliu"); 18 map.put(5, "lisi"); 19 map.put(3, "xiaoqiang"); 20 map.put(7, "zhouqi"); 21 22 Collection<String> values = map.values(); 23 Iterator<String> it = values.iterator(); 24 while (it.hasNext()) { 25 String value = it.next(); 26 } 27 28 /* 29 * 取出map中所有元素 30 * 原理:通过keySet方法获取map中所有键的Set集合 31 * 通过Set集合的迭代器获取到每一个键 32 * 通过map的get方法获取键对应的值 33 * 34 */ 35 //第一种方式: 36 Set<Integer> keySet = map.keySet(); 37 Iterator<Integer> itInteger = keySet.iterator(); 38 while (itInteger.hasNext()) { 39 Integer key = itInteger.next(); 40 String value = map.get(key); 41 } 42 43 //第二种方式: 44 Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entryMaps = map.entrySet(); 45 46 Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> itEntry = entryMaps.iterator(); 47 48 while (itEntry.hasNext()) { 49 Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = itEntry.next(); 50 51 Integer key = entry.getKey(); 52 String value = entry.getValue(); 53 System.out.println(key + ":" + value); 54 } 55 } 56 57 public static void method(Map<Integer, String> map) { 58 // 添加元素 59 System.out.println(map.put(8, "wangcai")); 60 System.out.println(map.put(8, "xiaoqiang"));//新值替换旧值,并返回旧值没有旧值返回null 61 map.put(2, "zhangsan"); 62 map.put(6, "lisi"); 63 System.out.println(map); 64 65 // 删除 66 System.out.println("remove:" + map.remove(2)); 67 68 // 判断 69 System.out.println("containsKey:" + map.containsKey(6)); 70 71 // 获取数据 72 System.out.println("get:" + map.get(6)); 73 74 } 75 }
结果:
二、Map常用子类
|--HashTable:内部结构是哈希表数据结构,是同步的。不允许null键,null值
|--Properties:用于存储键值对型的配置文件的信息,可以和IO技术相结合
|--HashMap:内部结构是哈希表,不同步。允许null键,null值
|--LinkedHashMap:有序
|--TreeMap:内部结构是二叉树,不同步。可以对Map集合中的键进行排序
共享类型
1 public class Person implements Comparable { 2 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 6 public Person() { 7 super(); 8 } 9 10 public Person(String name, int age) { 11 super(); 12 this.name = name; 13 this.age = age; 14 } 15 16 public String getName() { 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 24 public int getAge() { 25 return age; 26 } 27 28 public void setAge(int age) { 29 this.age = age; 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public int hashCode() { 34 System.out.println(this + ":-------hashCode"); 35 return this.name.hashCode() + this.age; 36 } 37 38 @Override 39 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 40 System.out.println(this + ":-------equals-------" + obj); 41 if (!(obj instanceof Person)) 42 throw new ClassCastException("类型不对"); 43 Person person = (Person) obj; 44 return this.name.equals(person.name) && person.age == this.age; 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 public String toString() { 49 50 return this.name + ":" + this.age; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public int compareTo(Object o) { 55 //定义Person类型的自然顺序为:根据年龄排序,年龄相同在根据名称排序 56 if(!(o instanceof Person)){ 57 throw new ClassCastException("类型错误"); 58 } 59 Person p=(Person)o; 60 int temp=this.age-p.age; 61 return temp==0?this.name.compareTo(p.name):temp; 62 } 63 }
三、HashMap
1 import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.Iterator; 3 import java.util.Set; 4 5 import cn.marw.common.bean.Person; 6 7 public class HashMapDemo { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 11 HashMap<Person, String> hm = new HashMap<Person, String>(); 12 13 hm.put(new Person("lisi", 38), "北京"); 14 hm.put(new Person("wangwu", 24), "上海"); 15 hm.put(new Person("qianyi", 31), "沈阳"); 16 hm.put(new Person("zhangsan", 28), "大连"); 17 hm.put(new Person("wangwu", 24), "安徽"); 18 19 Iterator<Person> it = hm.keySet().iterator(); 20 while (it.hasNext()) { 21 Person p = it.next(); 22 String value = hm.get(p); 23 System.out.println(p.getName() + ":" + p.getAge() + "------" + value); 24 } 25 26 } 27 }
结果:
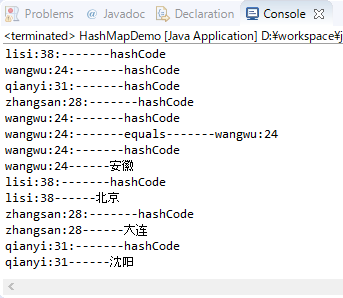
很眼熟和HashSet很像,可以通过hashCode和equals方法,实际上HashSet底层实现就是HashMap。
四、TreeMap
1 import java.util.Iterator; 2 import java.util.Map; 3 import java.util.TreeMap; 4 5 import cn.marw.collections.treeset.demo.PersonComparatorByName; 6 import cn.marw.common.bean.Person; 7 8 public class TreeMapDemo { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 TreeMap<Person, String> tm = new TreeMap<Person, String>(new PersonComparatorByName()); 12 13 tm.put(new Person("lisi", 38), "北京"); 14 tm.put(new Person("wangwu", 24), "上海"); 15 tm.put(new Person("qianyi", 31), "沈阳"); 16 tm.put(new Person("zhangsan", 28), "大连"); 17 tm.put(new Person("wangwu", 24), "安徽"); 18 19 Iterator<Map.Entry<Person,String>> it = tm.entrySet().iterator(); 20 while (it.hasNext()) { 21 Map.Entry<Person,String> entry = it.next(); 22 Person p=entry.getKey(); 23 String value = entry.getValue(); 24 System.out.println(p.getName() + ":" + p.getAge() + "------" + value); 25 } 26 } 27 }
PersonComparatorByName比较器代码:
1 public class PersonComparatorByName implements Comparator { 2 3 @Override 4 public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { 5 //只比较name 6 if(!(o1 instanceof Person)||!(o2 instanceof Person)) 7 throw new ClassCastException("类型错误"); 8 9 return ((Person)o1).getName().compareTo(((Person)o2).getName()); 10 } 11 12 }
结果:
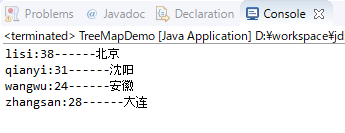
和TreeSet很像,其实TreeSet基于的实现TreeMap,那么TreeMap的键(Key)元素要么具有比较性(自然顺序),要么就要自定义比较器。