一、线程安全问题产生前提:
1、多线程操作共享数据
2、线程任务中有多条代码
1 class Ticket implements Runnable 2 { 3 //2.共享数据 4 private int num = 100; 5 6 public void run() 7 { 8 while(true) 9 { 10 //3.多条代码 11 if(num > 0) 12 { 13 try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e){} 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+num--); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 class TicketDemo 21 { 22 public static void main(String[] args) 23 { 24 Ticket t = new Ticket(); 25 //1.多线程操作同一个对象 26 Thread t1 =new Thread(t); 27 Thread t2 =new Thread(t); 28 Thread t3 =new Thread(t); 29 Thread t4 =new Thread(t); 30 31 t1.start(); 32 t2.start(); 33 t3.start(); 34 t4.start(); 35 } 36 }
运行结果:

出现线程安全问题了
二、解决线程安全问题
解决线程安全问题的两种方式:
①、同步代码块
格式:
1 synchronized(对象) 2 { 3 //需要被同步的代码; 4 ... ... 5 }
解决上面线程安全问题的代码:
1 class Ticket implements Runnable 2 { 3 //2.共享数据 4 private int num = 100; 5 //同步锁:对象 6 private Object o=new Object(); 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(true) 10 { 11 synchronized(o) 12 { 13 //3.多条代码 14 if(num > 0) 15 { 16 try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e){} 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+num--); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 }
结果:
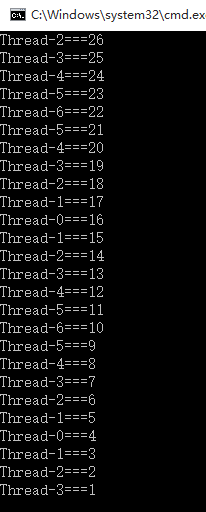
解决原理:多线程在使用同步代码块时,使用了同一个同步锁(Object的对象)
②、同步函数
格式:
1 public synchronized 方法返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) 2 { 3 ... ... 4 }
2.1、非静态同步函数
代码:
1 class Ticket implements Runnable 2 { 3 //2.共享数据 4 private int num = 100; 5 //同步锁:对象 6 //private Object o=new Object(); 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(true) 10 { 11 /* 12 synchronized(o) 13 { 14 //3.多条代码 15 if(num > 0) 16 { 17 try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e){} 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+num--); 19 } 20 } 21 */ 22 show(); 23 } 24 } 25 public synchronized void show() 26 { 27 //3.多条代码 28 if(num > 0) 29 { 30 try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e){} 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+num--); 32 } 33 } 34 }
结果:
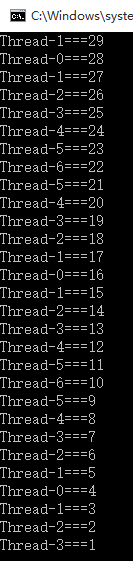
2.2、静态同步函数
代码:
1 class Ticket implements Runnable 2 { 3 //2.共享数据 4 private static int num = 100; 5 //同步锁:对象 6 //private Object o=new Object(); 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(true) 10 { 11 /* 12 synchronized(o) 13 { 14 //3.多条代码 15 if(num > 0) 16 { 17 try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e){} 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+num--); 19 } 20 } 21 */ 22 show(); 23 } 24 } 25 public static synchronized void show() 26 { 27 //3.多条代码 28 if(num > 0) 29 { 30 try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e){} 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+num--); 32 } 33 } 34 }
结果:
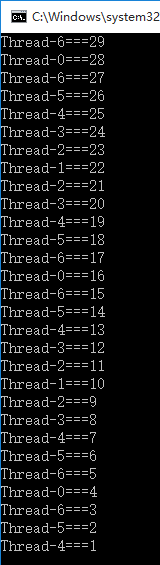
总结:
同步的好处:解决线程的安全问题
同步的弊端:效率低,因为同步外的线程都会判断同步锁
同步的弊端:效率低,因为同步外的线程都会判断同步锁
同步的前提:必须有多个线程使用同一个同步锁(synchronized(同步锁:对象))
同步代码块:可以指定任意对象作为同步锁
同步函数:非静态同步函数的同步锁为当前类对象(this),静态同步函数为当前类的字节码对象(类名.class或this.getClass())