1 前备知识
图像直方图比较,就是比较两幅图像的直方图数据,比较两组数据的相似性,从而得到两幅图像之间的相似程度,直方图比较在早期的CBIR(基于内容的图像检索Content-based image retrieval)是较常应用的技术手段,通常结合边缘处理、词袋模型等技术一起使用。
词袋模型(英语:Bag-of-words model)是个在自然语言处理和信息检索(IR)下被简化的表达模型。此模型下,一段文本(比如一个句子或是一个文档)可以用一个装着这些词的袋子来表示,这种表示方式不考虑文法以及词的顺序。最近词袋模型也被应用在计算机视觉领域。
词袋模型被广泛应用在文件分类,词出现的频率可以用来当作训练分类器的特征。
2 所用到的主要OpenCv API
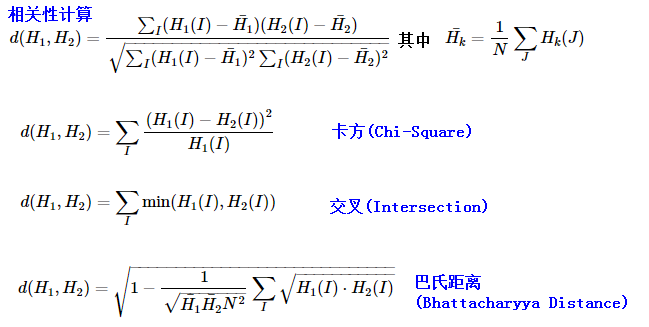
CV_EXPORTS void calcHist( const Mat* images, int nimages, const int* channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist, int dims, const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform = true, bool accumulate = false );
/** @brief Calculates a histogram of a set of arrays.//计算一组数组的直方图
@param images Source arrays. They all should have the same depth, CV_8U, CV_16U or CV_32F , and the same
size. Each of them can have an arbitrary number of channels(任意的通道数).
@param nimages Number of source images. //原图数量
@param channels List of the dims channels used to compute the histogram. The first array channels
are numerated from 0 to images[0].channels()-1 , the second array channels are counted from
images[0].channels() to images[0].channels() + images[1].channels()-1, and so on.
@param mask Optional mask. If the matrix is not empty, it must be an 8-bit array of the same size
as images[i] . The non-zero mask elements mark the array elements counted in the histogram.
@param hist Output histogram, which is a dense or sparse dims -dimensional array.
@param dims Histogram dimensionality that must be positive and not greater than CV_MAX_DIMS
(equal to 32 in the current OpenCV version).
@param histSize Array of histogram sizes in each dimension.
@param ranges Array of the dims arrays of the histogram bin boundaries in each dimension. When the
histogram is uniform ( uniform =true), then for each dimension i it is enough to specify the lower
(inclusive) boundary f$L_0f$ of the 0-th histogram bin and the upper (exclusive) boundary
f$U_{ exttt{histSize}[i]-1}f$ for the last histogram bin histSize[i]-1 . That is, in case of a
uniform histogram each of ranges[i] is an array of 2 elements. When the histogram is not uniform (
uniform=false ), then each of ranges[i] contains histSize[i]+1 elements:
f$L_0, U_0=L_1, U_1=L_2, ..., U_{ exttt{histSize[i]}-2}=L_{ exttt{histSize[i]}-1}, U_{ exttt{histSize[i]}-1}f$
. The array elements, that are not between f$L_0f$ and f$U_{ exttt{histSize[i]}-1}f$ , are not
counted in the histogram.
@param uniform Flag indicating whether the histogram is uniform or not (see above).
@param accumulate Accumulation flag. If it is set, the histogram is not cleared in the beginning
when it is allocated. This feature enables you to compute a single histogram from several sets of
arrays, or to update the histogram in time.
*/
3 程序代码
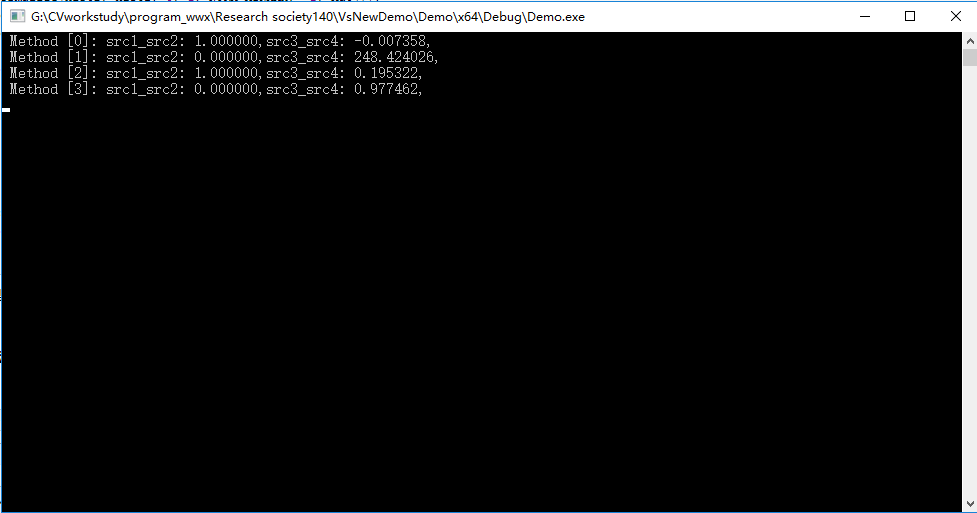
#include<opencv2opencv.hpp> #include <iostream> using namespace std; using namespace cv; int main(int argc, char** argv) { //load the image Mat src1 = imread("G:\CVworkstudy\program_wwx\Research society140\ZhaiZhigang140\m1.png"); Mat src2 = imread("G:\CVworkstudy\program_wwx\Research society140\ZhaiZhigang140\m2.png"); Mat src3 = imread("G:\CVworkstudy\program_wwx\Research society140\ZhaiZhigang140\flower.png"); Mat src4 = imread("G:\CVworkstudy\program_wwx\Research society140\ZhaiZhigang140\wm.jpg"); //show the image imshow("input1", src1); imshow("input2", src2); imshow("input3", src3); imshow("input4", src4); //convert hte HSV to BGR Mat hsv1, hsv2, hsv3, hsv4; cvtColor(src1, hsv1, COLOR_BGR2HSV); cvtColor(src2, hsv2, COLOR_BGR2HSV); cvtColor(src3, hsv3, COLOR_BGR2HSV); cvtColor(src4, hsv4, COLOR_BGR2HSV); //calculate the hist int h_bins = 60; int s_bins = 64; int histSize[] = { h_bins,s_bins }; float h_ranges[] = { 0,180 }; float s_ranges[] = { 0,255 }; const float* ranges[] = { h_ranges,s_ranges }; int channels[] = { 0,1 }; Mat hist1, hist2, hist3, hist4; calcHist(&hsv1, 1, channels, Mat(), hist1, 2, histSize, ranges, true, false); calcHist(&hsv2, 1, channels, Mat(), hist2, 2, histSize, ranges, true, false); calcHist(&hsv3, 1, channels, Mat(), hist3, 2, histSize, ranges, true, false); calcHist(&hsv4, 1, channels, Mat(), hist4, 2, histSize, ranges, true, false); normalize(hist1, hist1, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat()); normalize(hist2, hist2, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat()); normalize(hist3, hist3, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat()); normalize(hist4, hist4, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat()); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int compare_method = i; double src1_src2 = compareHist(hist1, hist2, compare_method); double src3_src4 = compareHist(hist3, hist4, compare_method); printf(" Method [%d]: src1_src2: %f,src3_src4: %f, ", i, src1_src2, src3_src4); } waitKey(0); return 0; }
4 运行结果




5 扩展及注意事项
null