申明:此教程加工于 caffe 如何训练自己的数据图片
一、准备数据
有条件的同学,可以去imagenet的官网http://www.image-net.org/download-images,下载imagenet图片来训练。但是我没有下载,一个原因是注册账号的时候,验证码始终出不来(听说是google网站的验证码,而我是上不了google的)。第二个原因是数据太大了。。。
我去网上找了一些其它的图片来代替,共有500张图片,分为大巴车、恐龙、大象、鲜花和马五个类,每个类100张。需要的同学,可到我的网盘下载:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nuqlTnN(已保存至个人网盘)
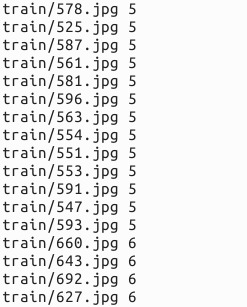
编号分别以3,4,5,6,7开头,各为一类。我从其中每类选出20张作为测试,其余80张作为训练。因此最终训练图片400张,测试图片100张,共5类。我将图片放在caffe根目录下的data文件夹下面。即训练图片目录:data/re/train/ ,测试图片目录: data/re/test/
二、转换为lmdb格式
具体的转换过程,可参见我的前一篇博文:Caffe学习系列(11):图像数据转换成db(leveldb/lmdb)文件
首先,在examples下面创建一个myfile的文件夹,来用存放配置文件和脚本文件。然后编写一个脚本create_filelist.sh,用来生成train.txt和test.txt清单文件
# sudo mkdir examples/myfile
# sudo vi examples/myfile/create_filelist.sh
编辑此文件,写入如下代码,并保存
#!/usr/bin/env sh
DATA=data/re/
MY=examples/myfile
echo "Create train.txt..."
rm -rf $MY/train.txt #删除原有数据
for i in 3 4 5 6 7
do
find $DATA/train -name $i*.jpg | cut -d '/' -f4-5 | sed "s/$/ $i/">>$MY/train.txt
done
echo "Create test.txt..."
rm -rf $MY/test.txt
for i in 3 4 5 6 7
do
find $DATA/test -name $i*.jpg | cut -d '/' -f4-5 | sed "s/$/ $i/">>$MY/test.txt
done
echo "All done"
然后,运行此脚本
# sudo sh examples/myfile/create_filelist.sh
成功的话,就会在examples/myfile/ 文件夹下生成train.txt和test.txt两个文本文件,里面就是图片的列表清单。
接着再编写一个脚本文件,调用convert_imageset命令来转换数据格式。
# sudo vi examples/myfile/create_lmdb.sh
插入:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
MY=examples/myfile
# 这里说明下:一共有6处需要修改
# 原数据为256×256 现在为了优化训练速度改成32×32,精确度降低可忽略(4个)
# /home/xxx/caffe/data/re/,修改xxx为自己用户的目录,这里为undo (2个)
echo "Create train lmdb.."
rm -rf $MY/img_train_lmdb
build/tools/convert_imageset
--shuffle
--resize_height=32
--resize_width=32
/home/undo/caffe/data/re/
$MY/train.txt
$MY/img_train_lmdb #转换成lmdb格式的训练数据
echo "Create test lmdb.."
rm -rf $MY/img_test_lmdb
build/tools/convert_imageset
--shuffle
--resize_width=32
--resize_height=32
/home/undo/caffe/data/re/
$MY/test.txt
$MY/img_test_lmdb
echo "All Done.."
因为图片大小不一,因此我统一转换成256*256(32×32速度更快,精度影响不大)大小。运行成功后,会在 examples/myfile下面生成两个文件夹img_train_lmdb和img_test_lmdb,分别用于保存图片转换后的lmdb文件。
三、计算均值并保存
图片减去均值再训练,会提高训练速度和精度。因此,一般都会有这个操作。
caffe程序提供了一个计算均值的文件compute_image_mean.cpp,我们直接使用就可以了
# sudo build/tools/compute_image_mean examples/myfile/img_train_lmdb examples/myfile/mean.binaryproto
compute_image_mean带两个参数,第一个参数是lmdb训练数据位置,第二个参数设定均值文件的名字及保存路径。
运行成功后,会在 examples/myfile/ 下面生成一个mean.binaryproto的均值文件。
四、创建模型并编写配置文件(使用原作者的配置文件,训练不成功,后参考其他教程该用cifar-10的配置文件成功训练)
由于在32*32位框架中,cifar-10有现成的学习框架,我们只需要进行一些关键数据的改写就可以快速的训练进行我们的训练了,以下时详细的说明。
首先拷贝文件。
sudo cp examples/cifar10/cifar10_quick_solver.prototxt examples/myfile/ sudo cp examples/cifar10/cifar10_quick_train_test.prototxt examples/myfile/ sudo mv examples/myfile/cifar10_quick_solver.prototxt examples/myfile/quick_solver.prototxt sudo mv examples/myfile/cifar10_quick_train_test.prototxt examples/myfile/quick_train_test.prototxt
sudo vi examples/myfile/quick_train_test.prototxt
修改的地方:(name之类自己随便修改)
1.
transform_param { mean_file: “examples/myfile/mean.binaryproto”#修改 } data_param { source: “examples/myfile/img_train_lmdb”#修改 batch_size: 50#修改 backend: LMDB }
2.
transform_param {
mean_file: “examples/myfile/mean.binaryproto”#修改
}
data_param {
source: “examples/myfile/img_test_lmdb”#修改
batch_size: 50 #修改
backend: LMDB
这里直接贴上我个人的配置文件

name: "selfimg_quick" layer { name: "selfimg" type: "Data" top: "data" top: "label" include { phase: TRAIN } transform_param { mean_file: "examples/myfile/mean.binaryproto" } data_param { source: "examples/myfile/img_train_lmdb" batch_size: 50 backend: LMDB } } layer { name: "selfimg" type: "Data" top: "data" top: "label" include { phase: TEST } transform_param { mean_file: "examples/myfile/mean.binaryproto" } data_param { source: "examples/myfile/img_test_lmdb" batch_size: 50 backend: LMDB } } layer { name: "conv1" type: "Convolution" bottom: "data" top: "conv1" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } convolution_param { num_output: 32 pad: 2 kernel_size: 5 stride: 1 weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.0001 } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "pool1" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv1" top: "pool1" pooling_param { pool: MAX kernel_size: 3 stride: 2 } } layer { name: "relu1" type: "ReLU" bottom: "pool1" top: "pool1" } layer { name: "conv2" type: "Convolution" bottom: "pool1" top: "conv2" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } convolution_param { num_output: 32 pad: 2 kernel_size: 5 stride: 1 weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "relu2" type: "ReLU" bottom: "conv2" top: "conv2" } layer { name: "pool2" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv2" top: "pool2" pooling_param { pool: AVE kernel_size: 3 stride: 2 } } layer { name: "conv3" type: "Convolution" bottom: "pool2" top: "conv3" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } convolution_param { num_output: 64 pad: 2 kernel_size: 5 stride: 1 weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "relu3" type: "ReLU" bottom: "conv3" top: "conv3" } layer { name: "pool3" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv3" top: "pool3" pooling_param { pool: AVE kernel_size: 3 stride: 2 } } layer { name: "ip1" type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "pool3" top: "ip1" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } inner_product_param { num_output: 64 weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.1 } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "ip2" type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "ip1" top: "ip2" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } inner_product_param { num_output: 10 weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.1 } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "accuracy" type: "Accuracy" bottom: "ip2" bottom: "label" top: "accuracy" include { phase: TEST } } layer { name: "loss" type: "SoftmaxWithLoss" bottom: "ip2" bottom: "label" top: "loss" }
$ sudo vi examples/myfile/quick_train_test.prototxt
只需要修改几句,其它参数默认即可。想要调优的话,可以试试其它的参数。
这里直接贴上我的配置
# The train/test net protocol buffer definition
net: "examples/myfile/quick_train_test.prototxt"
# test_iter specifies how many forward passes the test should carry out.
# In the case of MNIST, we have test batch size 100 and 100 test iterations,
# covering the full 100 testing images.
test_iter: 2
# Carry out testing every 50 training iterations.
test_interval: 50
# The base learning rate, momentum and the weight decay of the network.
base_lr: 0.001
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.004
# The learning rate policy
lr_policy: "fixed"
# Display every 2 iterations
display: 2
# The maximum number of iterations
max_iter: 300
# snapshot intermediate results
snapshot: 100
snapshot_prefix: "examples/myfile/selfimg_quick"
# solver mode: CPU or GPU
solver_mode: CPU
step 5 训练
caffe工具箱下,提供了专门训练的函数。
sudo build/tools/caffe train -solver examples/myfile/quick_solver.prototxt
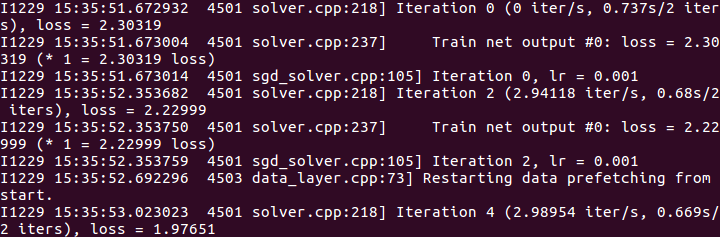
在cpu模式下,大约训练几分钟即可迭代完300次,以下是我的训练结果。
训练时间3分钟(设置32×32)。精确度0.93(还行。。)